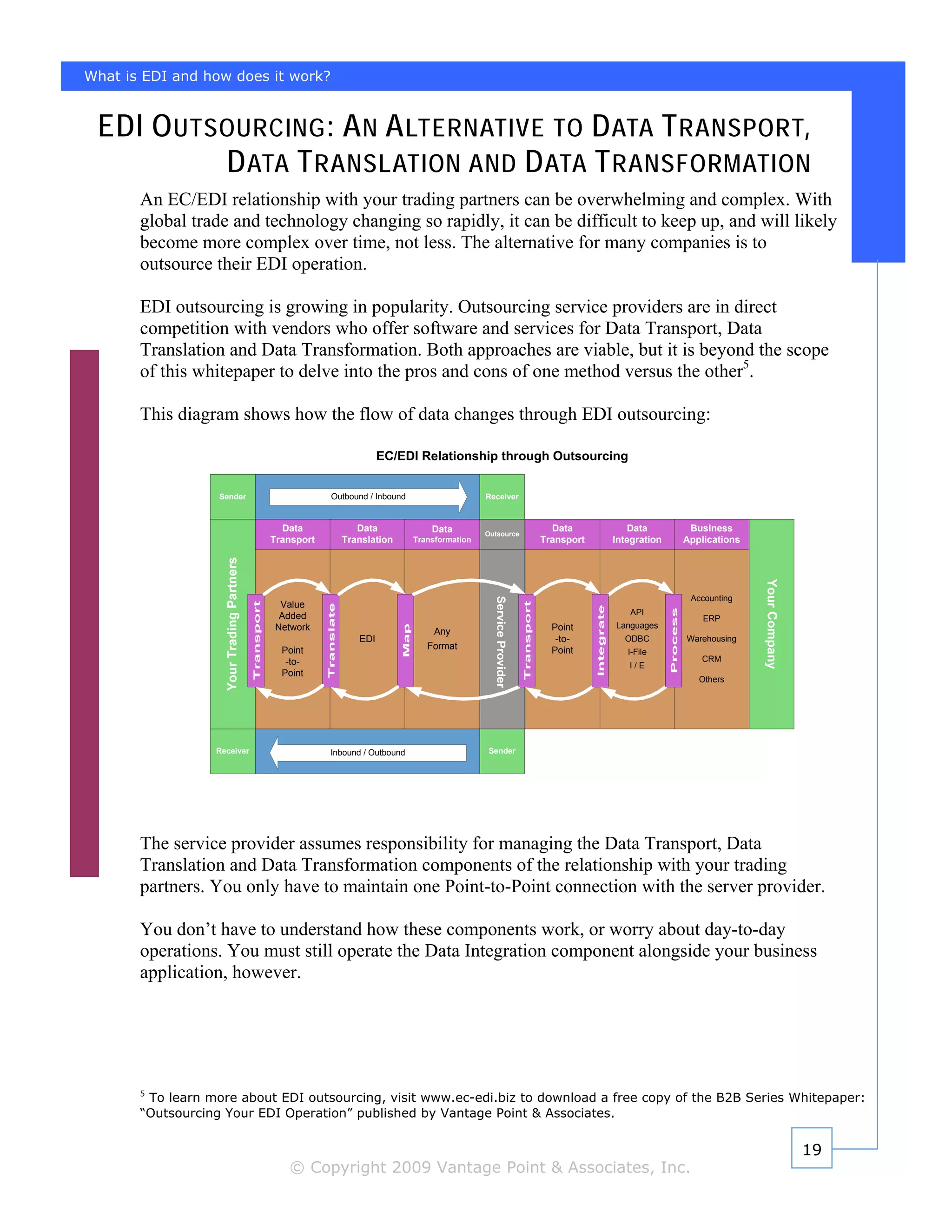
This document provides an overview of electronic data interchange (EDI) and how it works. EDI allows businesses to exchange structured data electronically and has been used since the 1960s, gaining widespread adoption in the 1990s. The document discusses the key components of EDI including data transport, translation, transformation and integration. It also reviews additional technologies that support supply chain management and the option of outsourcing EDI services to a third party provider.