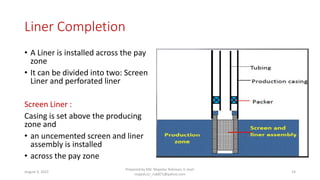
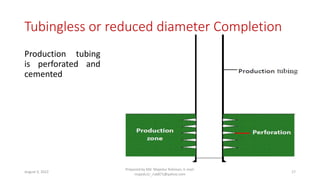
The document provides an overview of well completion and testing methods relevant to the petroleum industry, presented by Md. Majedur Rahman. Key topics include various well completion methods, wellhead equipment, definitions and operations of well testing, and specifics of drill stem tests. It also discusses high pressure and high temperature testing, along with the benefits and limitations of well stimulation.





























![10.6 Describe high pressure and high temperature
testing.
High pressure/high temperature (HP/HT) wells are those where the
undisturbed bottom hole temp at prospective reservoir depth or total depth
is greater than 300°F or 150°C, and either the maximum anticipated pore
pressure of any porous formation to be drilled through exceeds a hydrostatic
gradient of 0.8 psi/ft, or a well requiring pressure control equipment with a
rated working pressure in excess of 10000 psi. Drilling wells with these
characteristics pose special challenges.
A test to measure static filtration behavior of water mud or oil mud at
elevated temperature, up to about 380°F [193°C] maximum (450°F [227°C]
maximum if a special cell is used), usually according to the specifications
of API. Although the test can simulate downhole temperature conditions, it
does not simulate downhole pressure. Total pressure in a cell should not
exceed 700 psi [4900 kPa], and the differential pressure across the filter
medium is specified as 500 psi [3500 kPa]. Because these cells are half the
size of the ambient filtration area, HPHT filtrate volumes after 30 minutes are
doubled.
August 3, 2022
Prepared by Md. Majedur Rahman, E-mail:
majedu1r_ru6871@yahoo.com
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10wellcompletionandtesting-220803145854-888ade89/85/Well-completion-and-testing-pptx-32-320.jpg)






