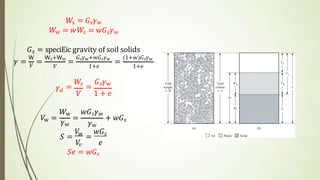
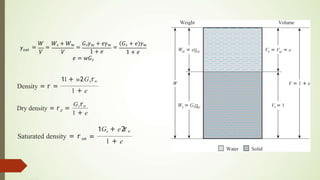
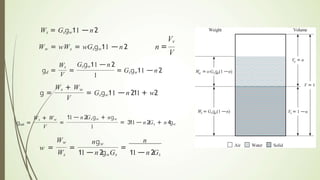
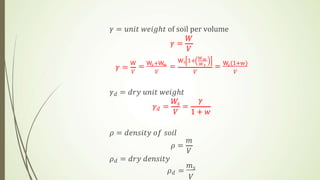The document discusses weight-volume relationships in soil, detailing calculations for various parameters, including unit weight, void ratio, porosity, and moisture content. It provides equations and examples for determining properties of soil samples, including determining density, dry density, and degree of saturation based on moisture content and specific gravity. The information serves as a guide for understanding soil behavior in relation to its physical properties.