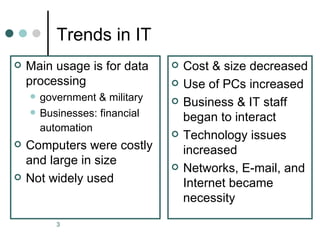
This document outlines trends in information technology and its impact on organizations. It discusses how IT has reshaped organizations by enabling businesses to expand operations globally using telecommunications. It also describes the importance of human resource management for IT and the different skills required for IT personnel, including technical, project management, business, and administration skills. The document further discusses challenges in managing IT human resources, such as attracting and retaining skilled employees, and qualities of effective people management like clear communication and respect for employees.