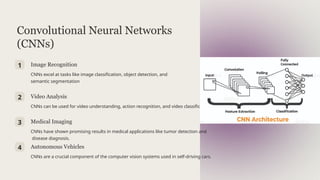
The document discusses the use of deep learning techniques for weed identification in agriculture, emphasizing the role of artificial intelligence in automating and optimizing tasks like herbicide application. It outlines various types of AI, including narrow and general AI, alongside subsets like machine learning and deep learning. Additionally, it details methodologies for data collection, preprocessing, and the YOLO algorithm for object detection, presenting metrics such as precision and recall to evaluate model performance.