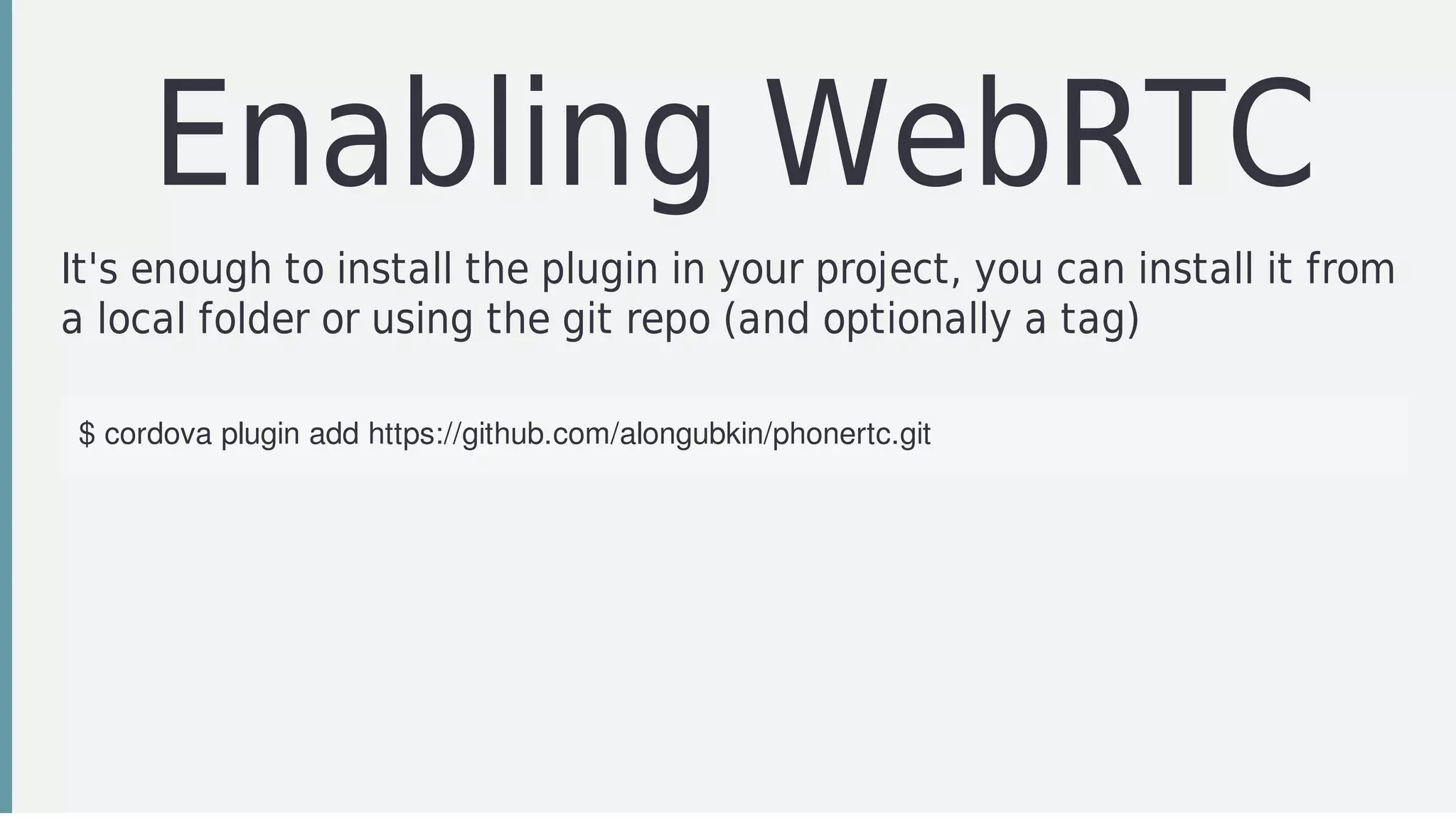
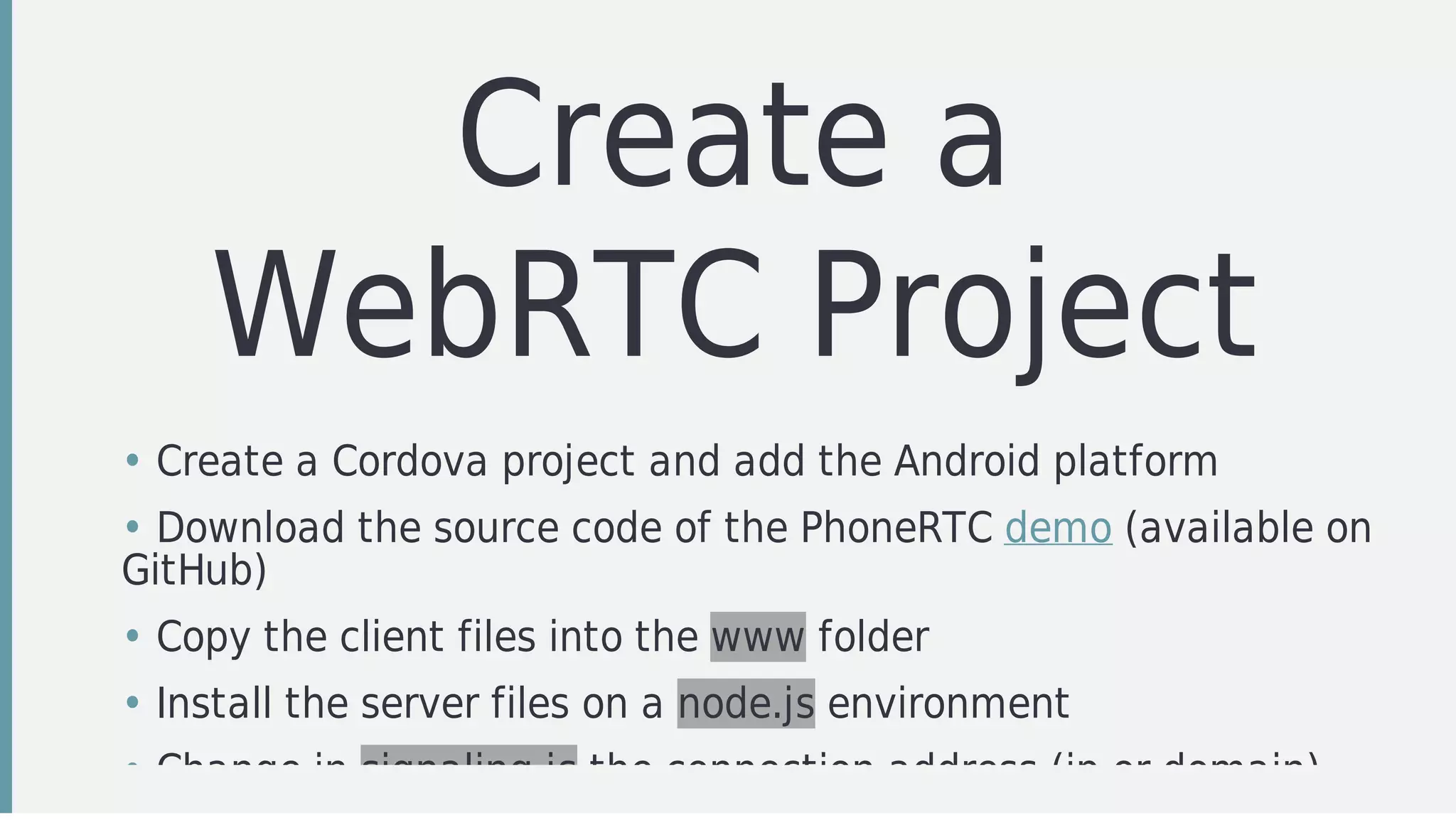
The document discusses technologies for developing hybrid mobile and wearable applications, including Tizen, Android, Cordova, Crosswalk, and PhoneRTC. It provides overviews of each technology and how they can be used together. It also summarizes steps for setting up a development environment for a Tizen wearable application using Cordova and WebRTC, including installing SDKs, configuring a SAP server, importing projects, and building. The presentation concludes with a recap of the setup steps and links to additional resources.


















![Smart Development
Bridge
It’s a tool to manage to devices/emulators that for instance allow you
to copy files, install apps, etc., between the supported commands the
more noticeable are
$ sdb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
$ sdb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
$ sdb pull <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device
$ sdb push <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webrtccommunicationandwearabledevices-150620213745-lva1-app6892/75/WebRTC-communication-and-wearable-devices-19-2048.jpg)





![Command Line (cli)
It's an npm module that acts as a wrapper around the different
supported platforms, the most important commands are:
$ cordova <PATH> [ID [NAME]] - create a new project
$ cordova platform [add|remove|update][platform] - add/remove/update a platform
$ cordova plugin [add|remove|update][plugin] - add/remove/update a plugin
$ cordova prepare [platform] - move the asssets to a platform projects
$ cordova build [platform] - build a specific platform
$ cordova run [platform] - run the project in a target platform
$ cordova serve - run the project in a local web server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webrtccommunicationandwearabledevices-150620213745-lva1-app6892/75/WebRTC-communication-and-wearable-devices-25-2048.jpg)