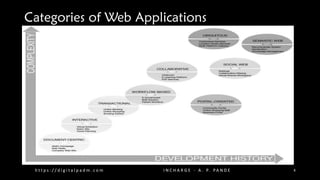
The document provides an overview of web engineering and web applications, defining web applications as software systems that utilize web technology to deliver resources via a browser. It categorizes web applications into six types: document-centric, transactional, workflow-based, collaborative, portal-oriented, and ubiquitous applications, each having distinct functionalities and use cases. Additionally, it outlines key characteristics related to web applications, emphasizing factors like content, user context, development processes, and the importance of integration in creating high-quality web applications.