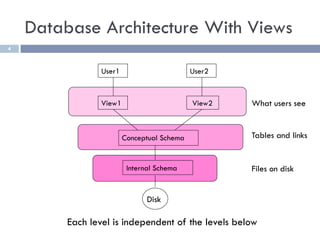
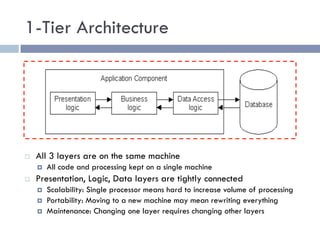
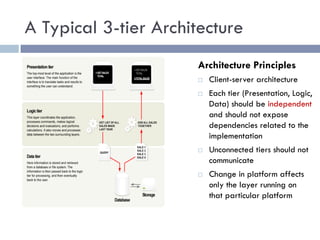
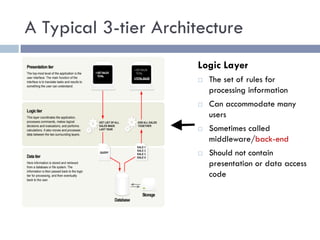
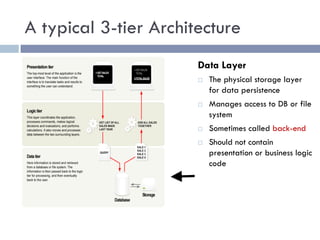
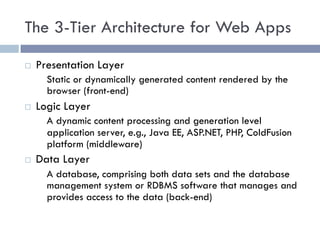
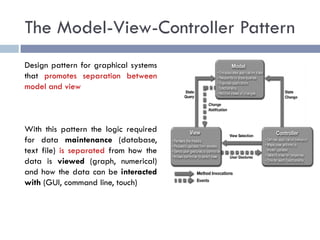
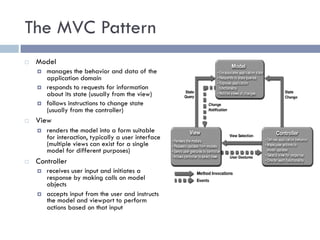
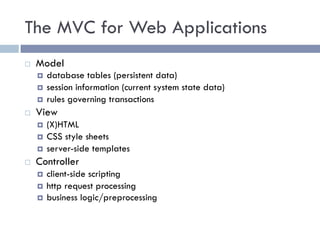
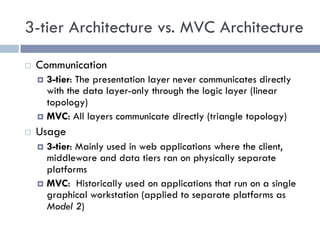
The document discusses several web application architectures: multi-tier architectures which separate an application into presentation, logic, and data tiers; the model-view-controller (MVC) pattern which separates an application into model, view, and controller components; and the REST architectural style. It provides details on each architecture, including their advantages like independence of components, reusability, and ease of maintenance.