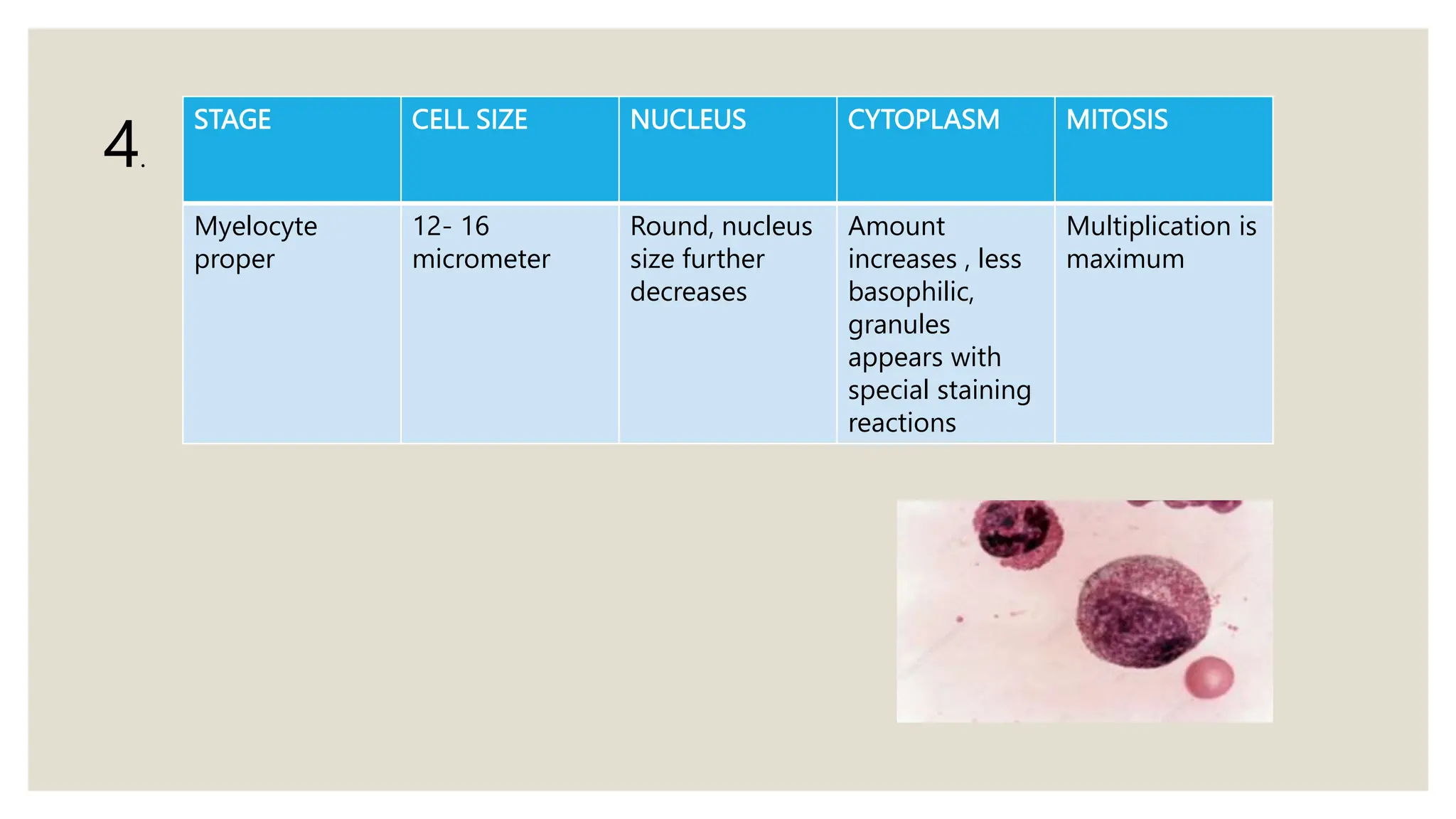
This document summarizes the process of granulopoiesis, the production of granulocytes which are a type of white blood cell. It describes the stages that pluripotent stem cells go through to mature into granulocytes, including the primitive WBC, myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, and metamyelocyte stages where the cell size and nucleus change and cytoplasmic granules develop. The final stage is the mature granulocyte, mainly neutrophils. The production of granulocytes occurs exclusively in the bone marrow through extravascular processes between fat cells. Granulocyte levels are regulated by factors that stimulate or inhibit further release from the bone