Embed presentation
Downloaded 94 times
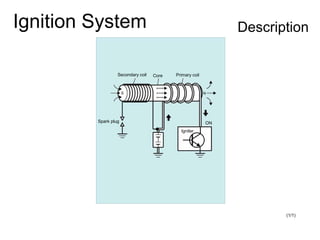
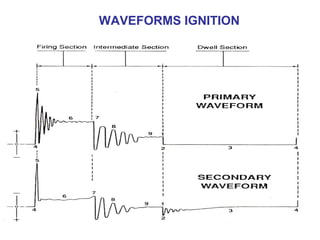

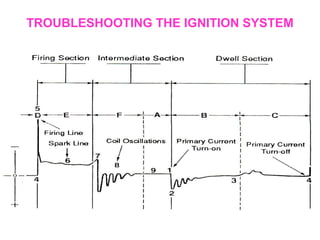
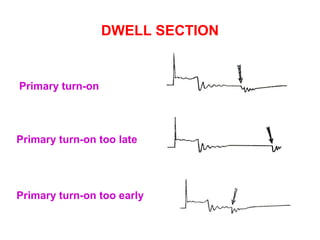
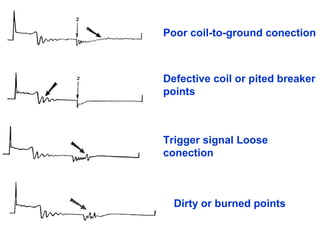

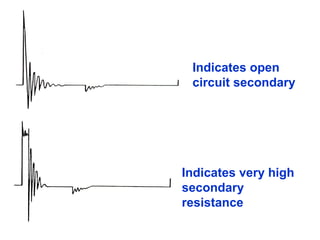
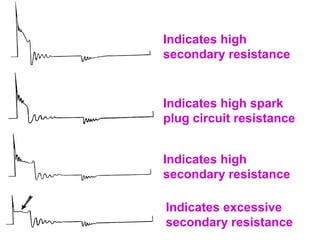
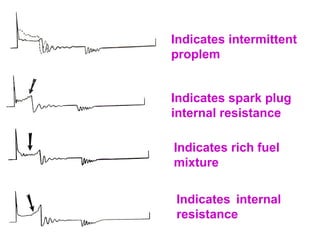
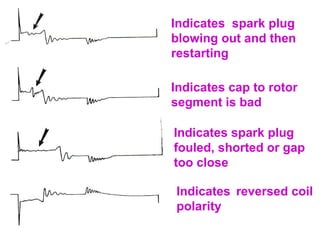

The document discusses the components and operation of an ignition system, including the secondary coil, spark plug, core, igniter, and primary coil. It provides typical waveforms for ignition and troubleshoots potential issues with the ignition system components and signals. Common problems addressed include late or early primary turn-on, loose or dirty connections, defective coils or condensers, and indications of high resistance or fouling in the secondary or spark plug circuits.











