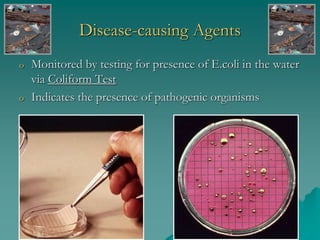
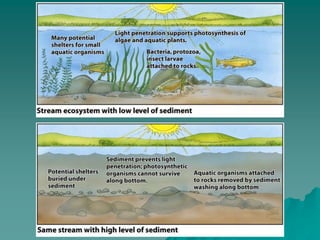
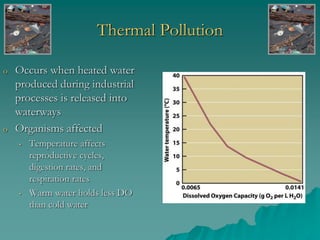
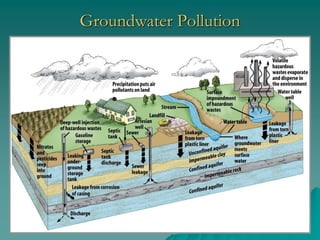
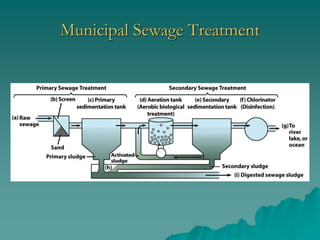
The document provides an overview of water pollution, detailing its types including sewage, disease-causing agents, sediment, and thermal pollution, along with the challenges posed to water quality globally. It discusses sources of pollution, such as agricultural runoff and industrial discharges, and highlights specific cases like pollution in the Ganges and the Po River. The document also outlines treatment methods for sewage and relevant laws aimed at controlling water pollution.