w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables in relational database
w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables in relational database
w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables in relational database
w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables in relational database
w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables in relational database




![Querying Multiple TablesRSL 6
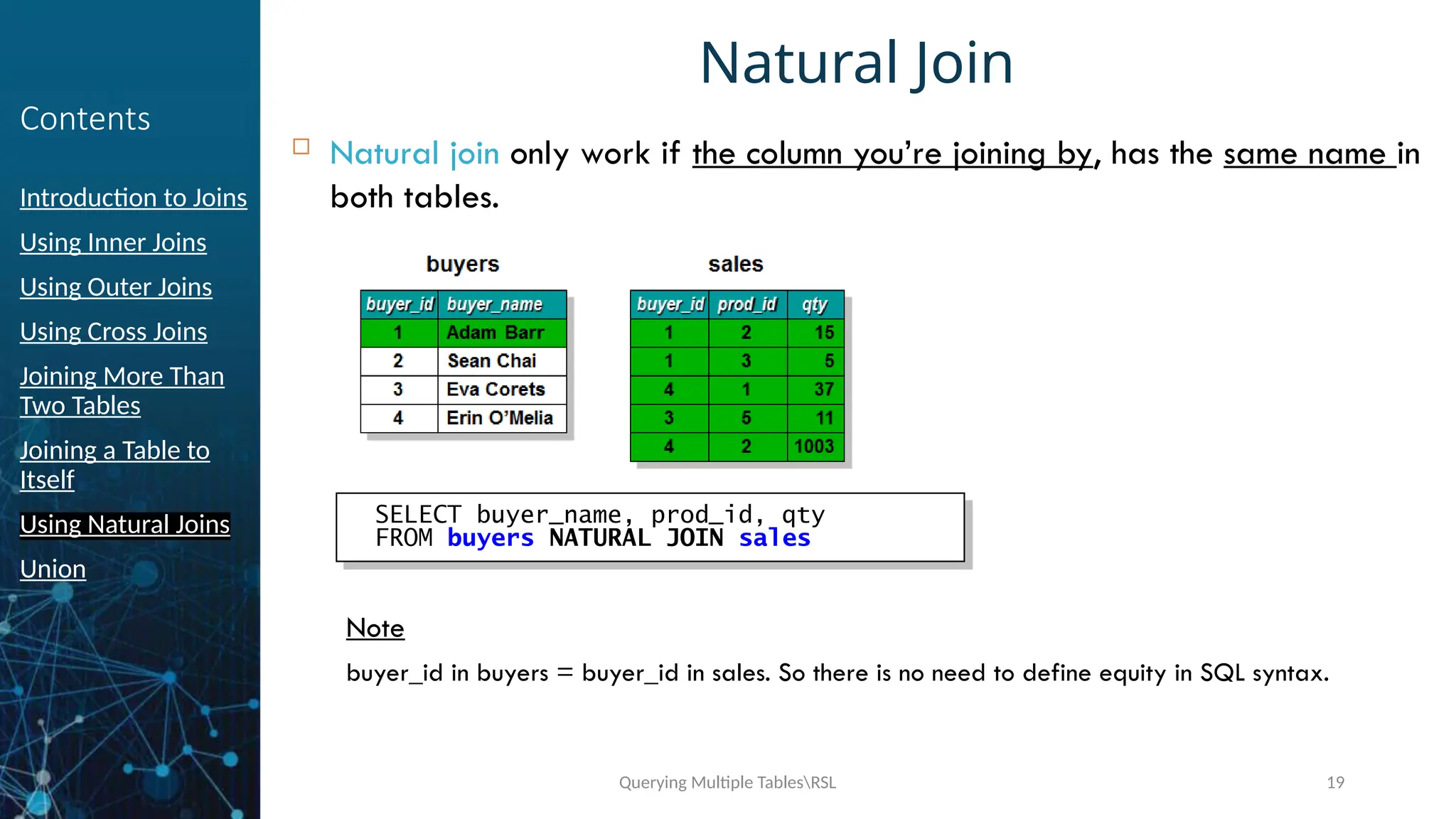
Contents
Introduction to Joins
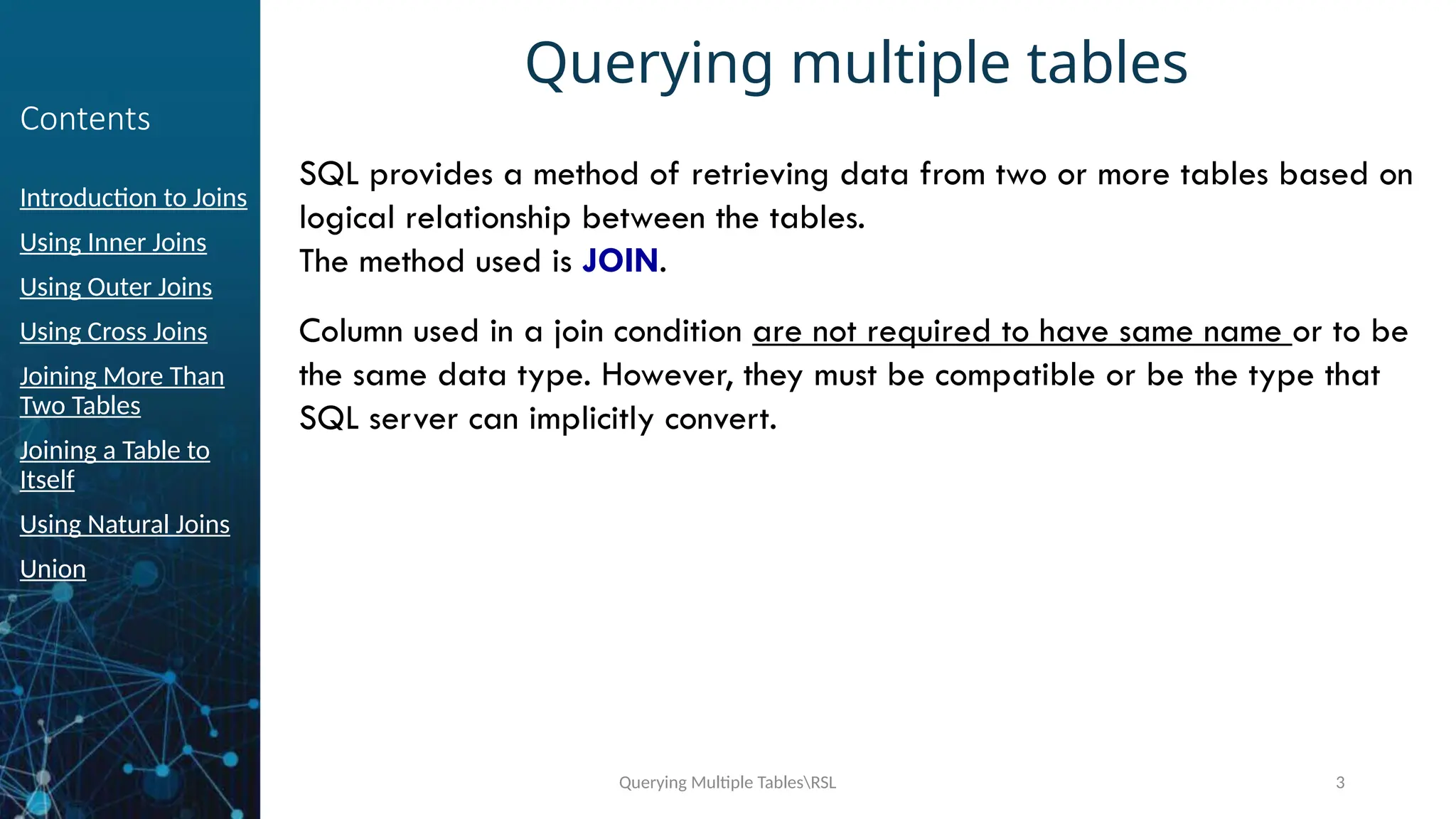
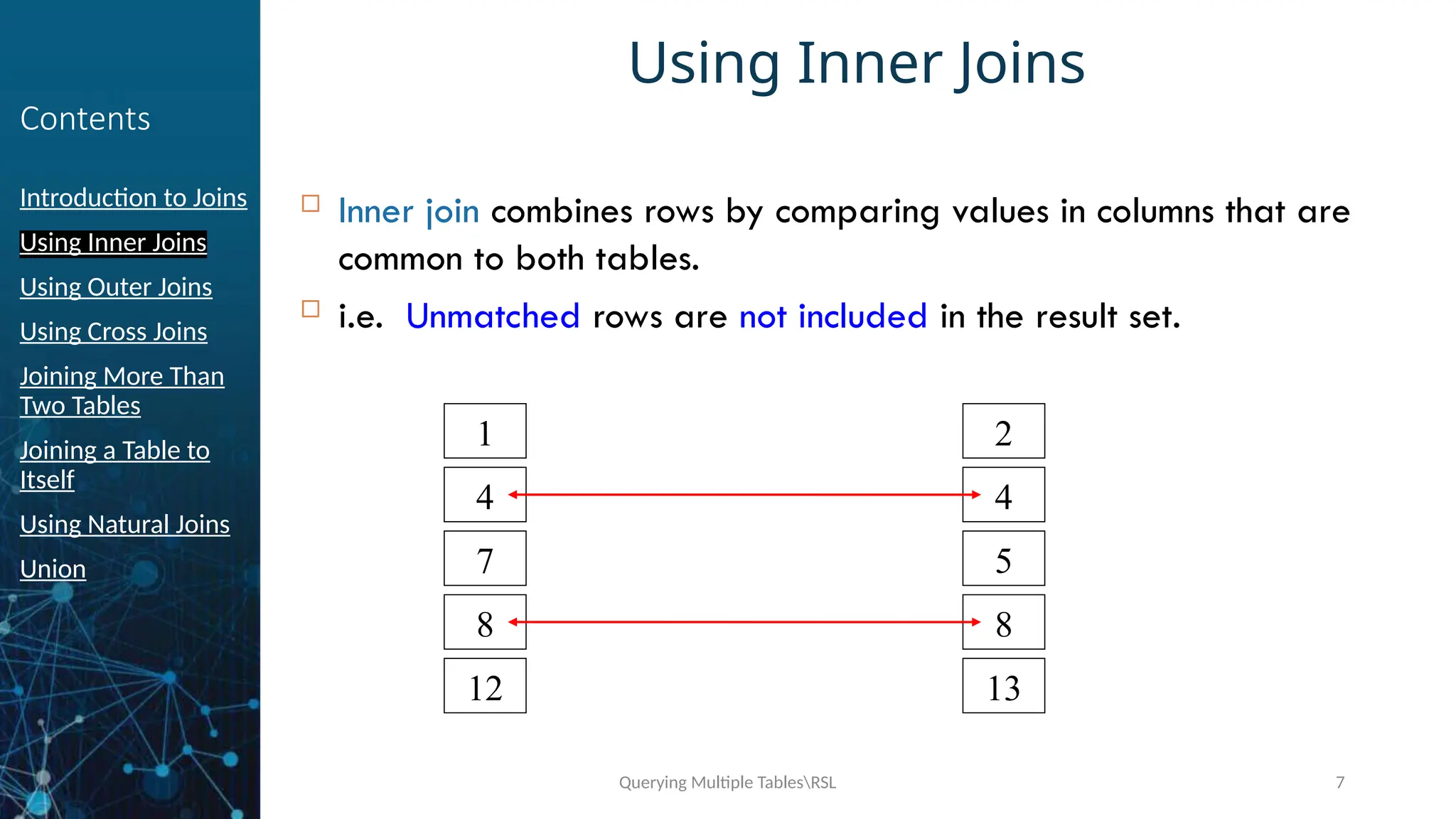
Using Inner Joins
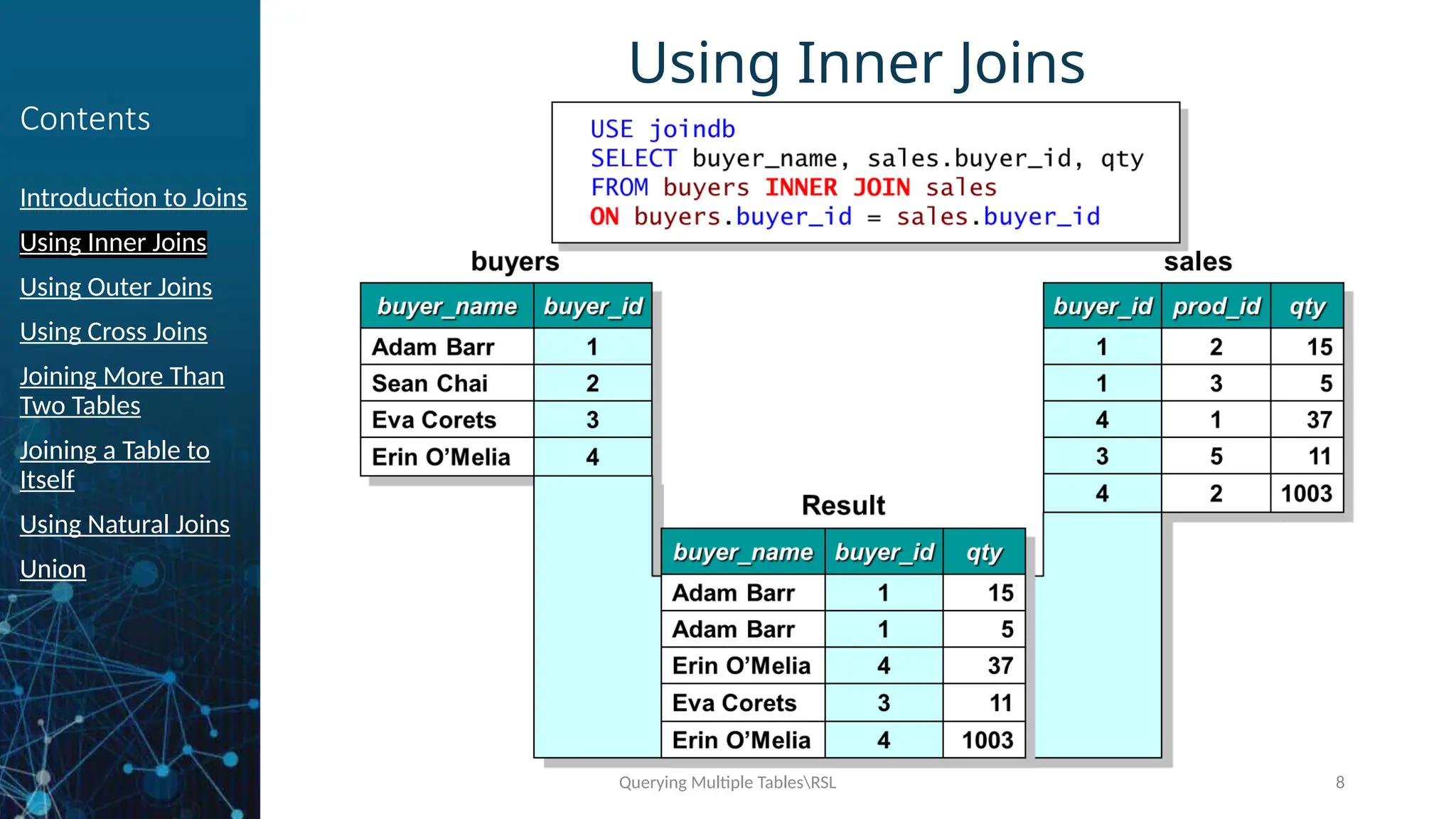
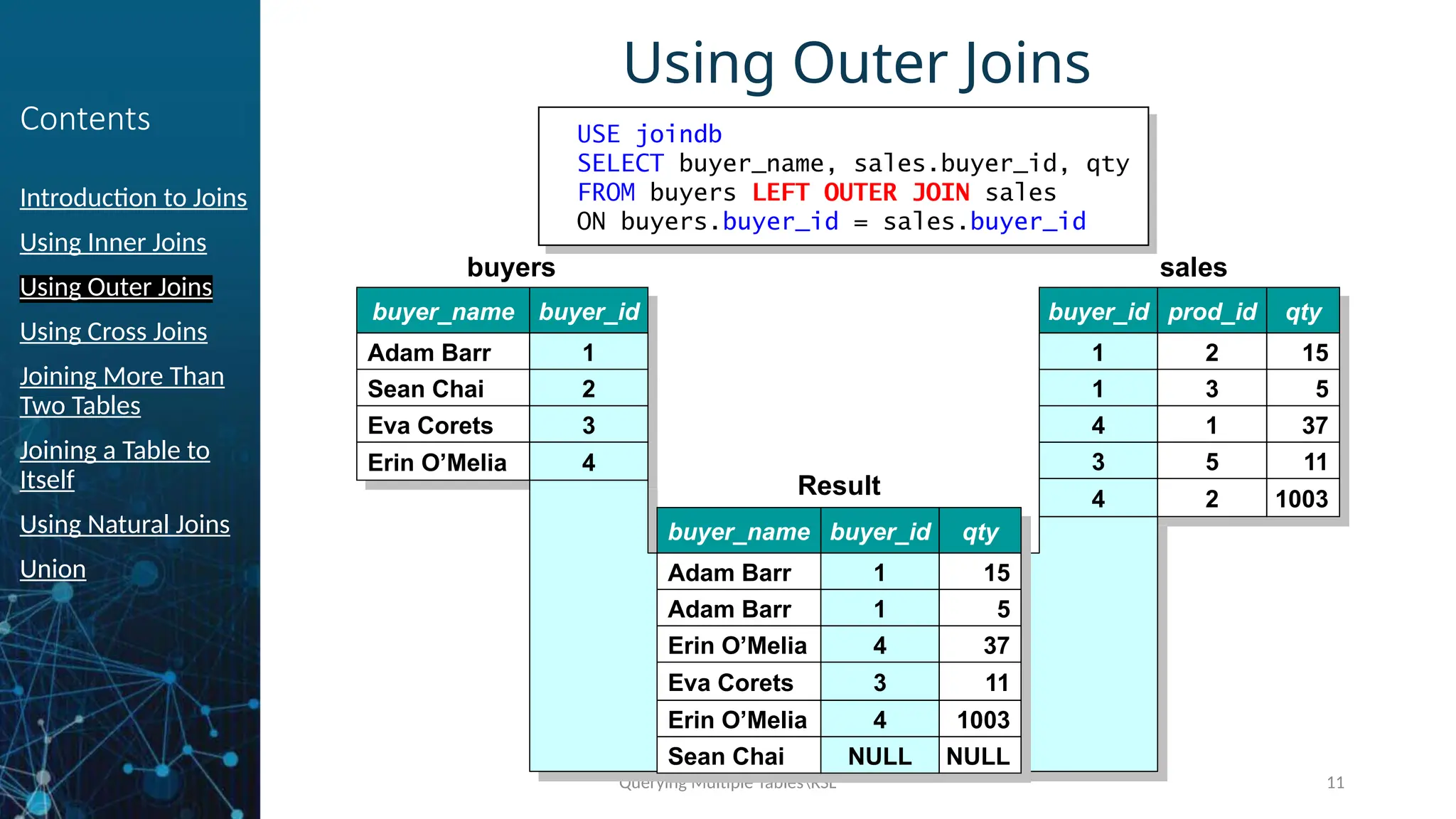
Using Outer Joins
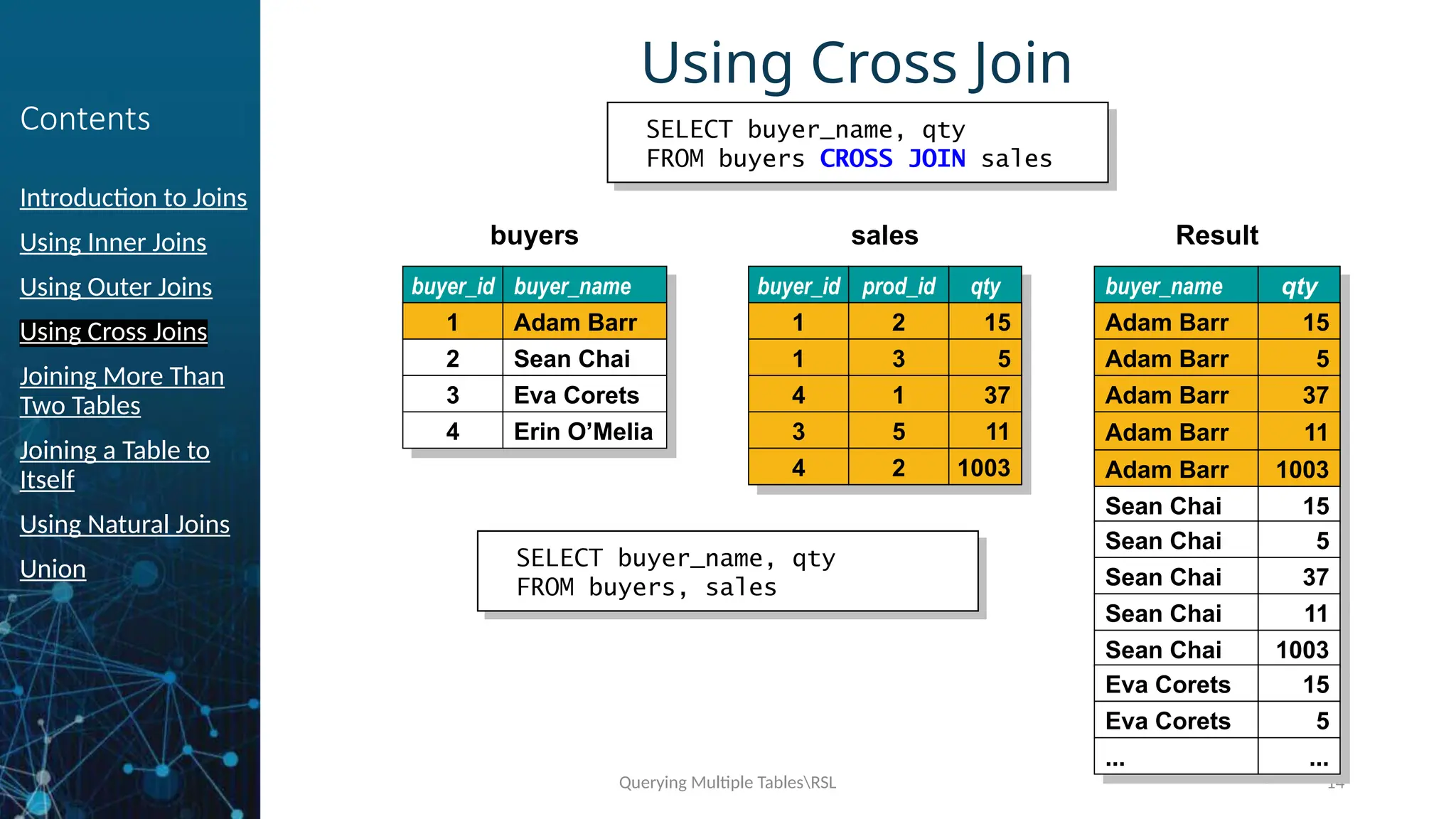
Using Cross Joins
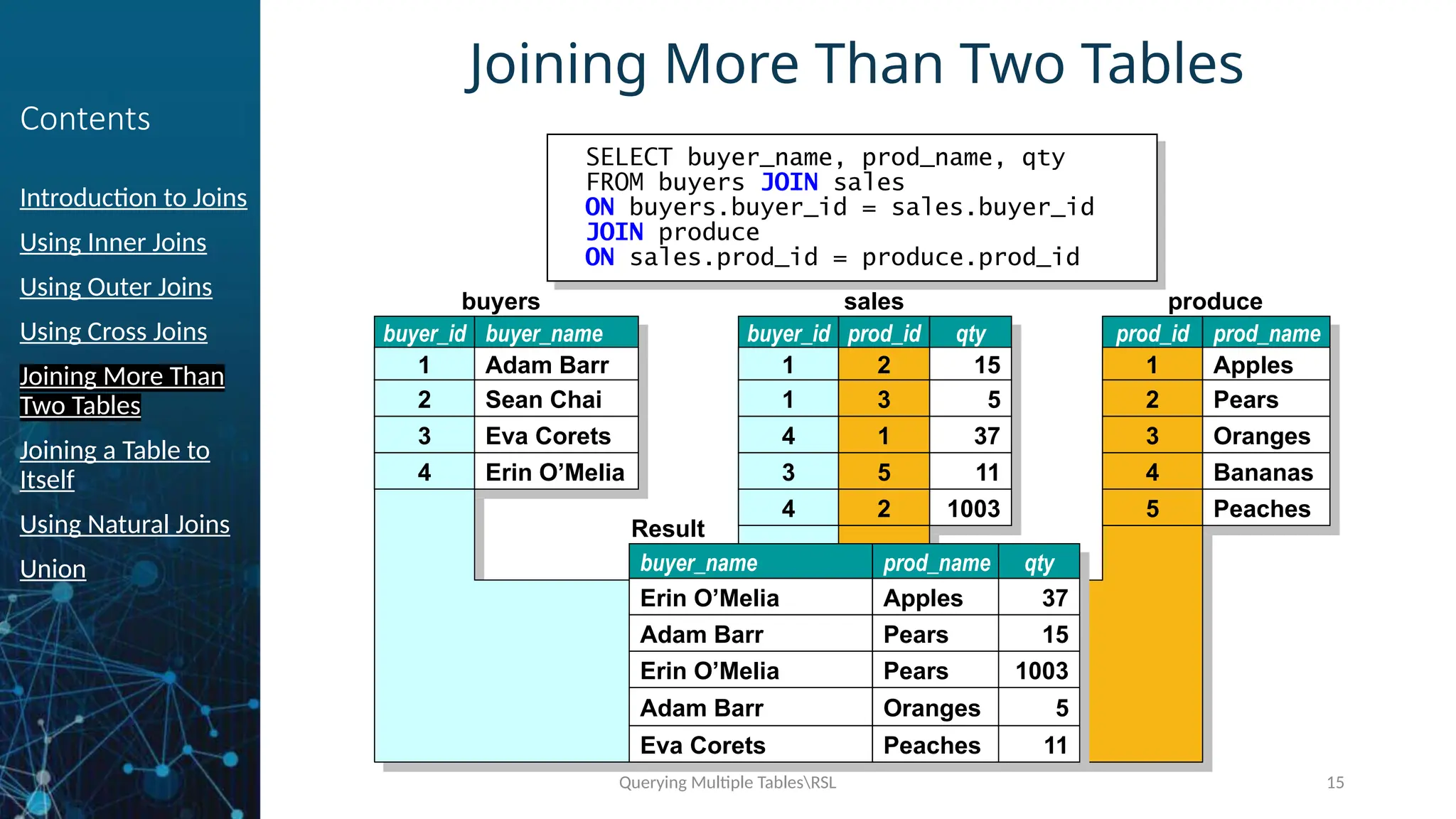
Joining More Than
Two Tables
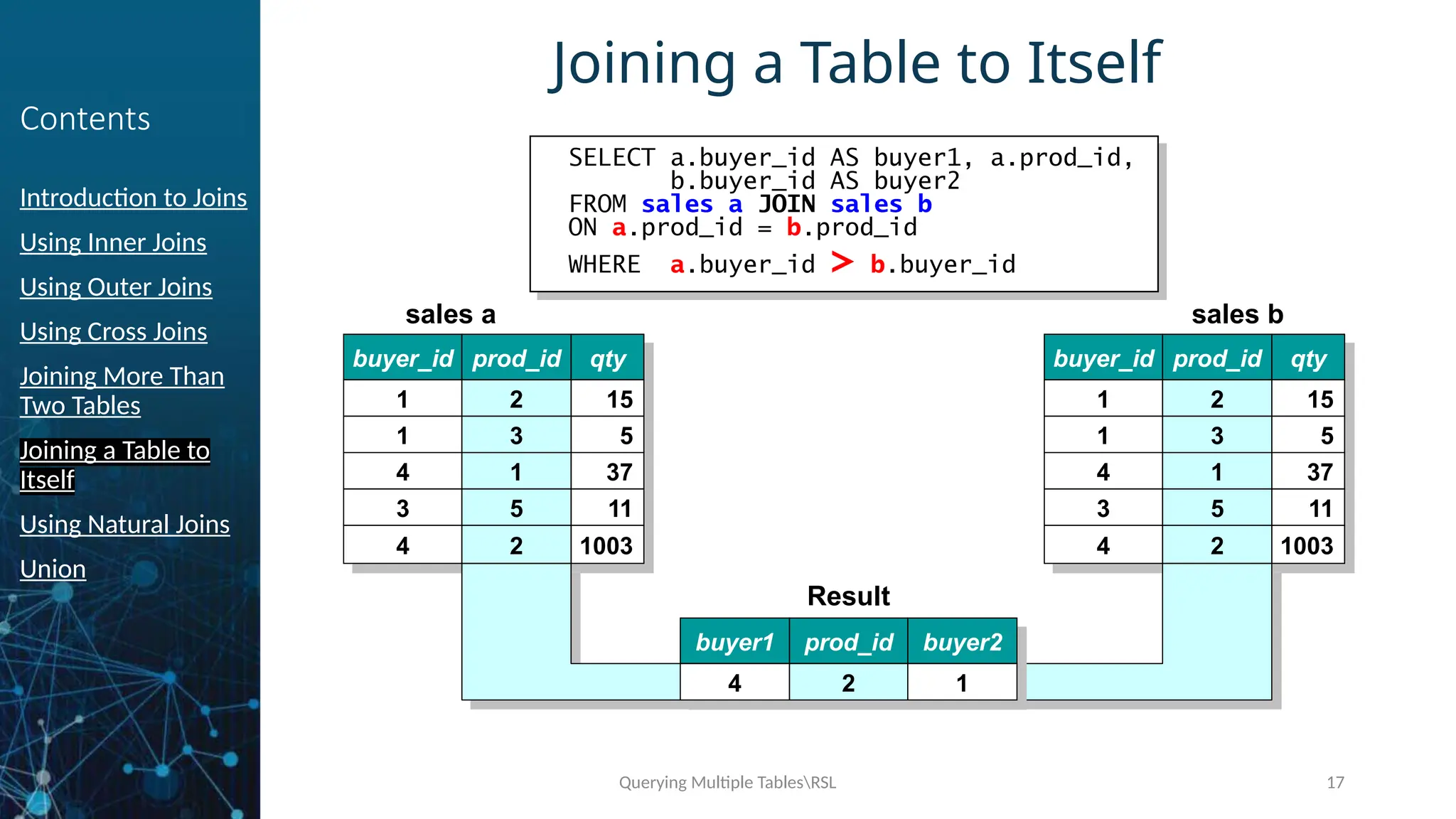
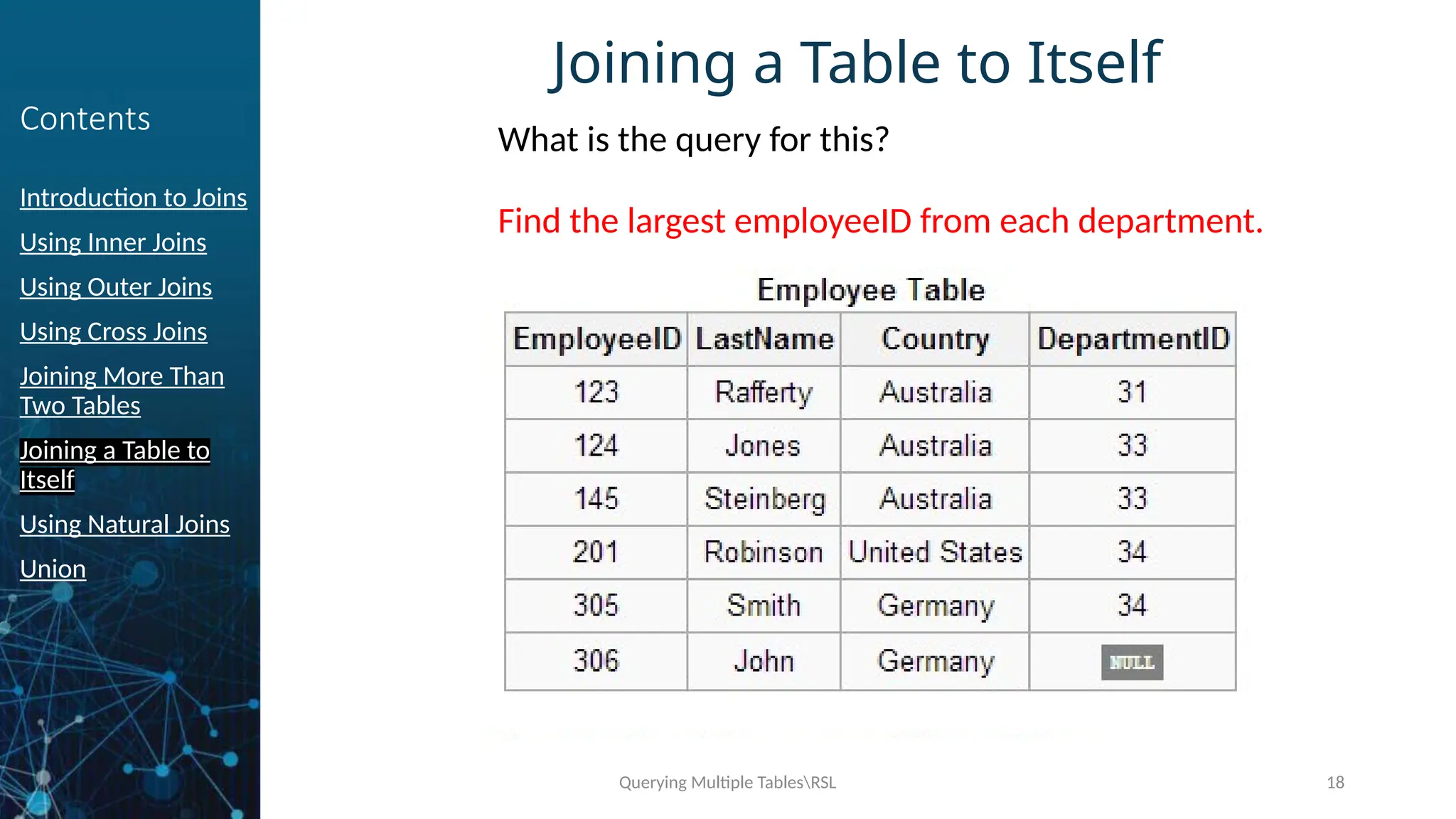
Joining a Table to
Itself
Using Natural Joins
Union
Syntax & Type of Joins
SELECT column_name,column-name[,column_name]
FROM table_name1 [CROSS |INNER| [LEFT | RIGHT] OUTER] JOIN
table_name2
ON table_name1.ref_colum_name JOIN_OPERATOR
table_name2.ref_column_name
Inner Join
Outer Join
LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN
RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN
FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN
Cross Join (Cartesian Product)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/w5s1queryingmultipletables-250908235327-6149a73e/75/w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables-in-relational-database-6-2048.jpg)





![Querying Multiple TablesRSL 20
Contents
Introduction to Joins
Using Inner Joins
Using Outer Joins
Using Cross Joins
Joining More Than
Two Tables
Joining a Table to
Itself
Union
Union
The UNION operator allows you to combine the results of two or more set
of rows into a single result set.
Whereas a join combines two sets of columns into a single result set.
Example
SELECT * FROM Table1
UNION [ALL]
SELECT * FROM Table2
Example :
select pub_name, city, state from
publishers
union
select au_lname, city, state from
authors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/w5s1queryingmultipletables-250908235327-6149a73e/75/w5s1_QueryingMultipleTables-in-relational-database-20-2048.jpg)

