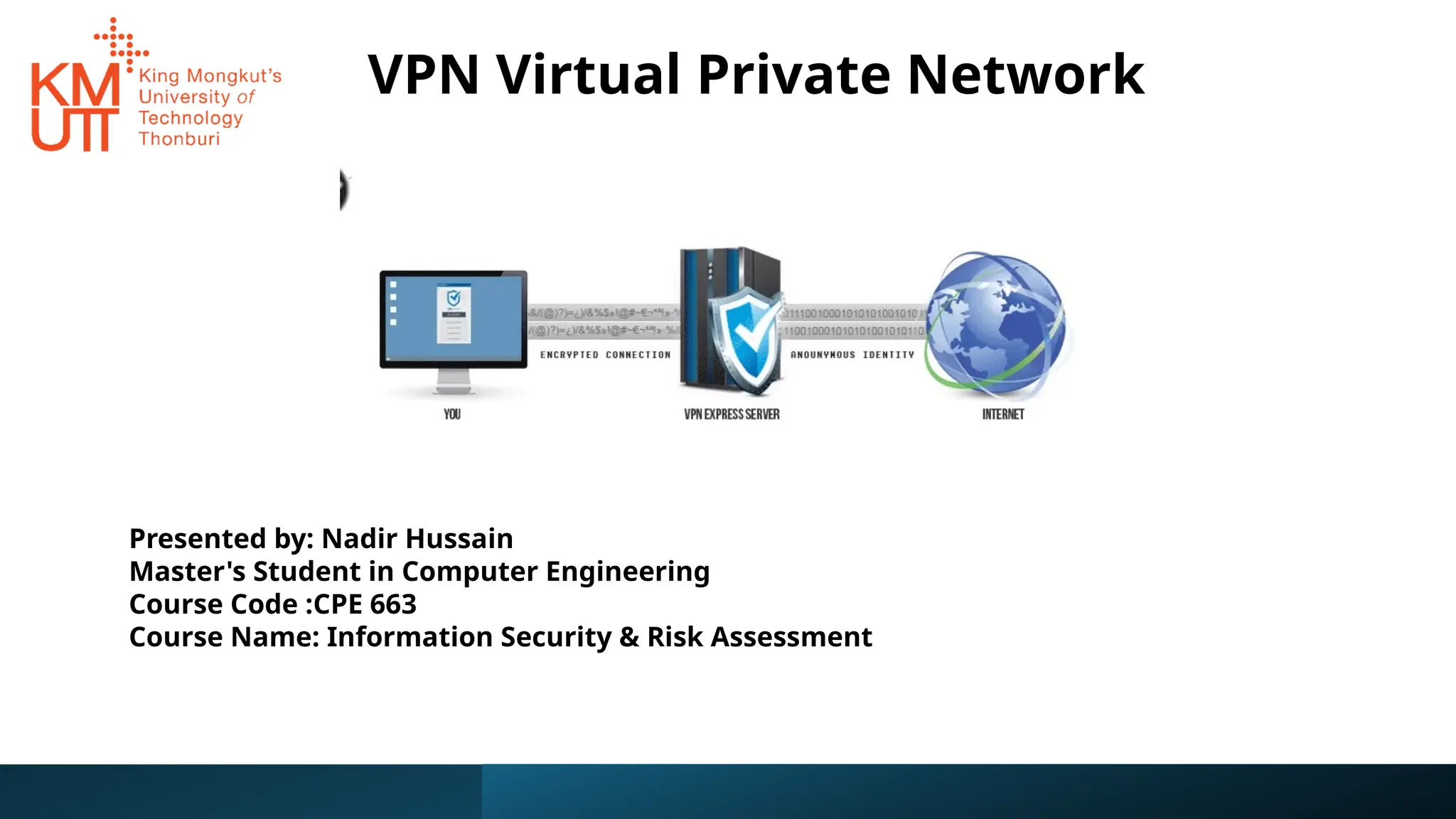
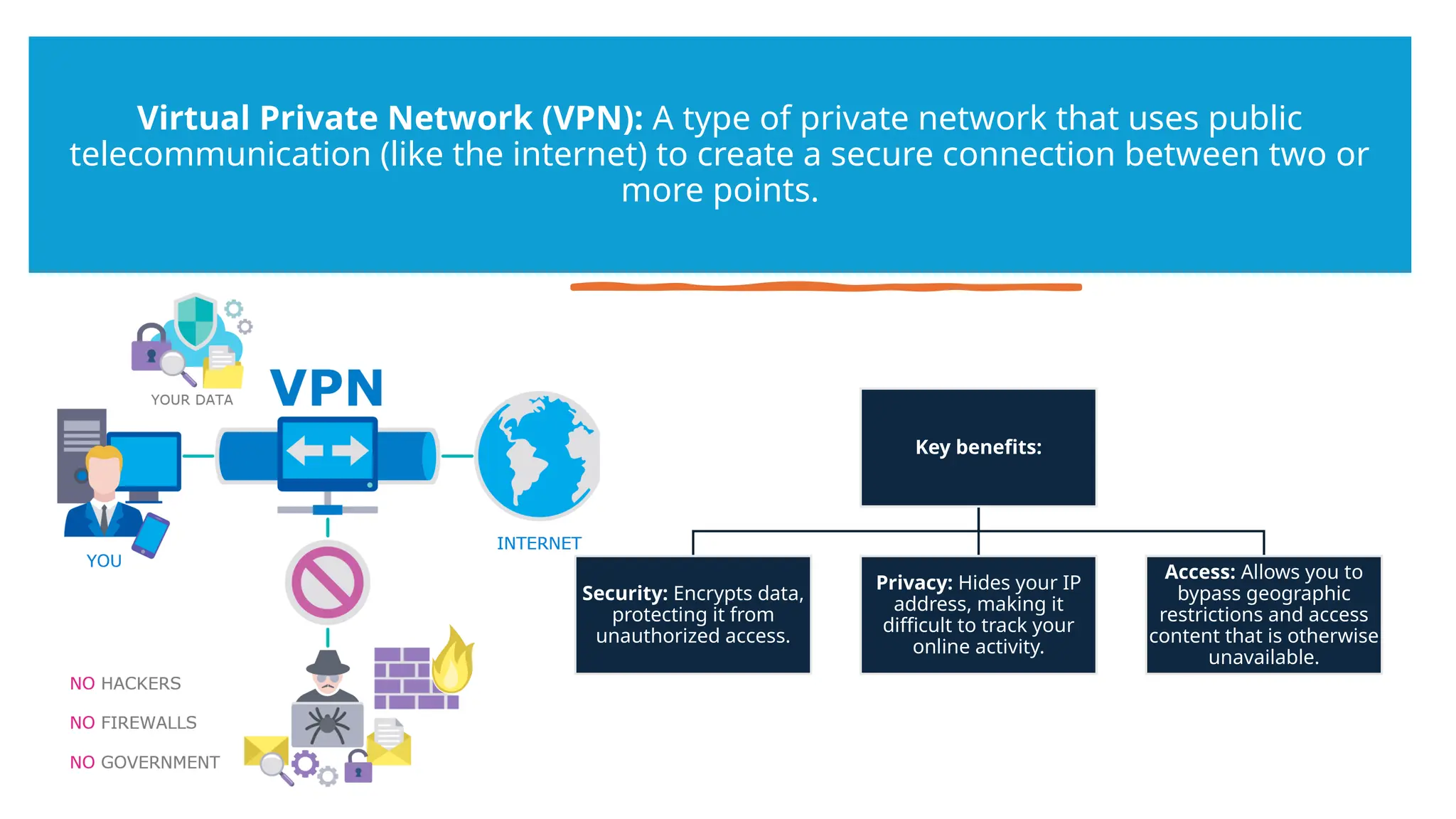
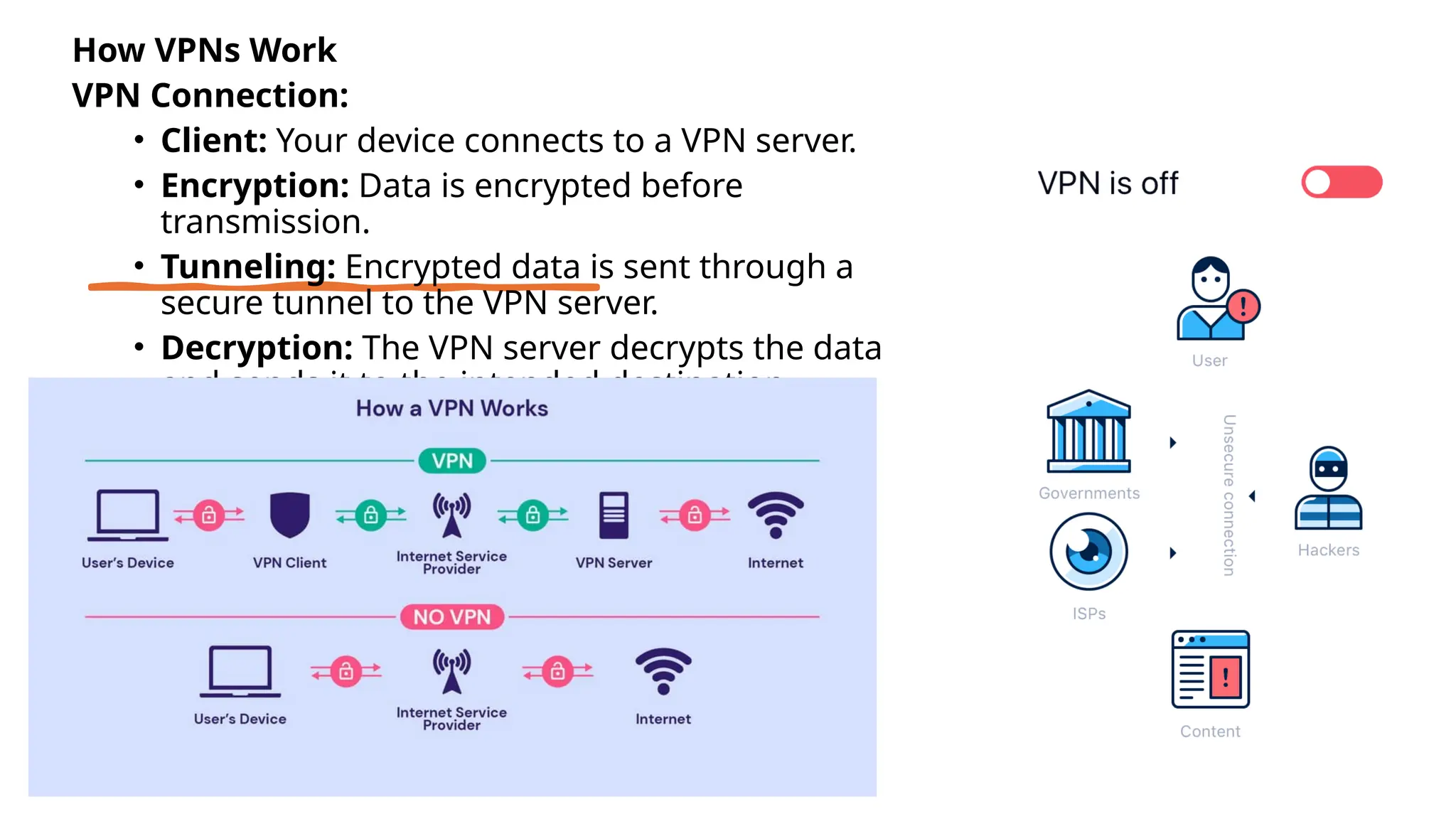
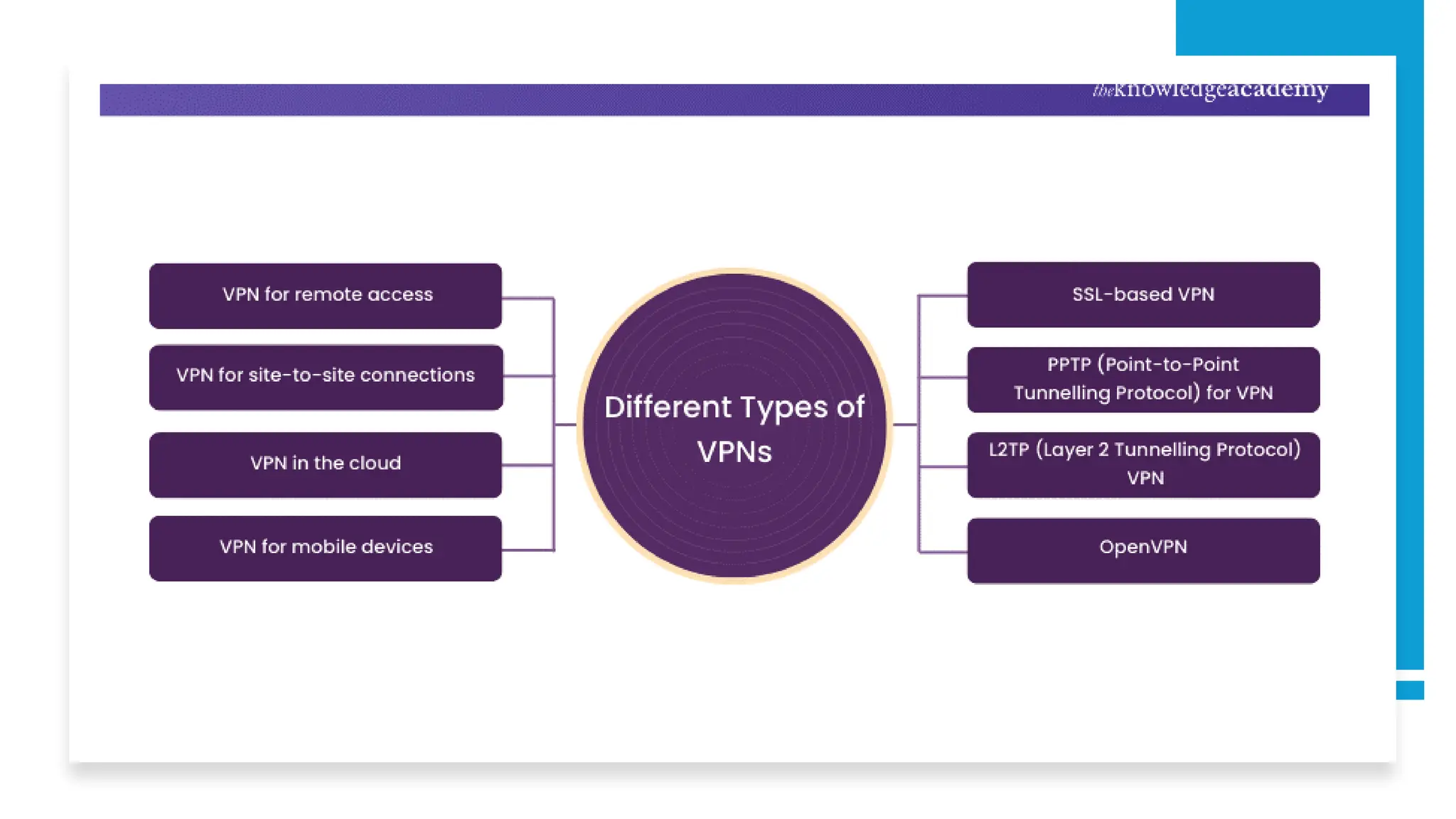
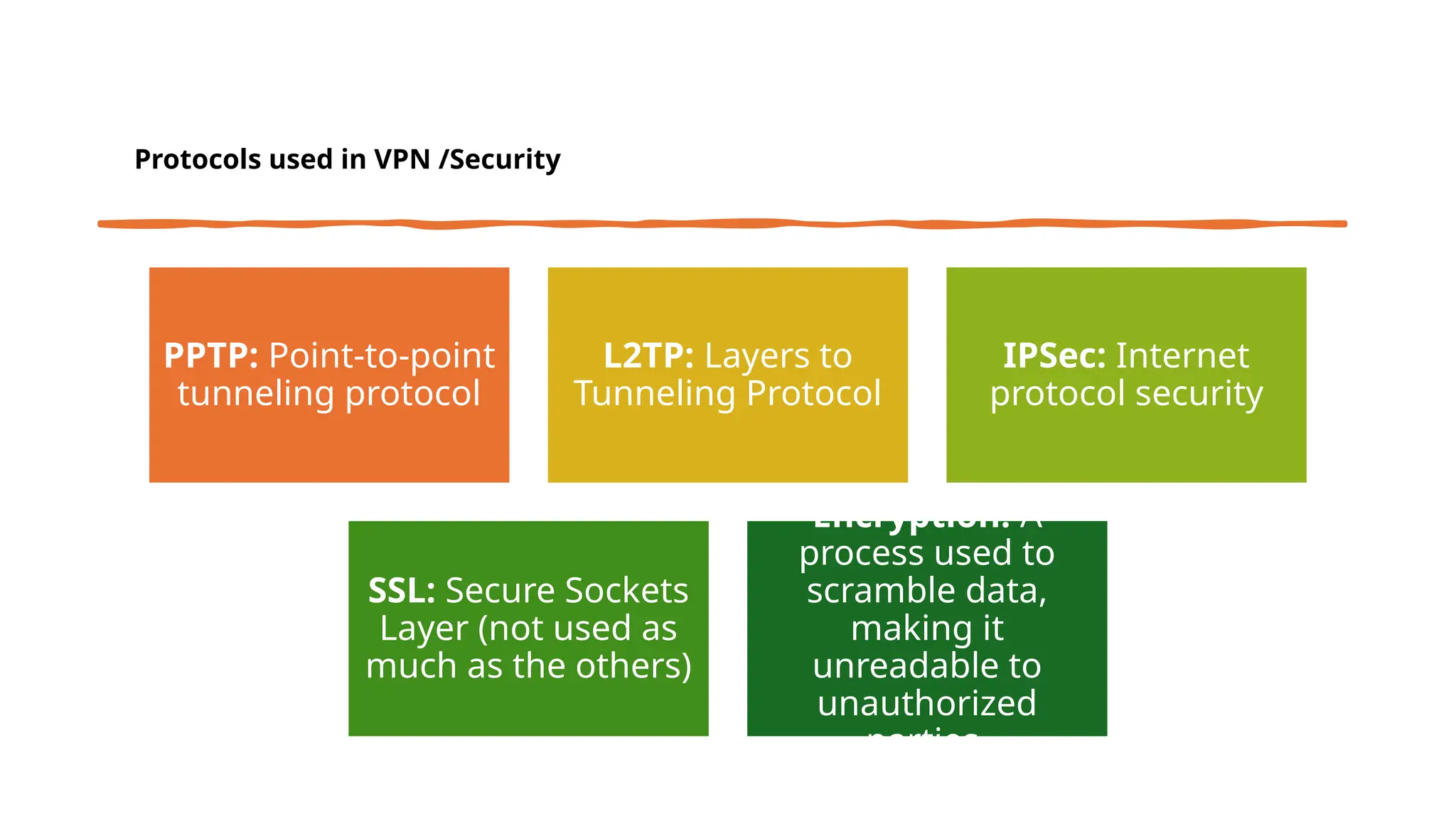
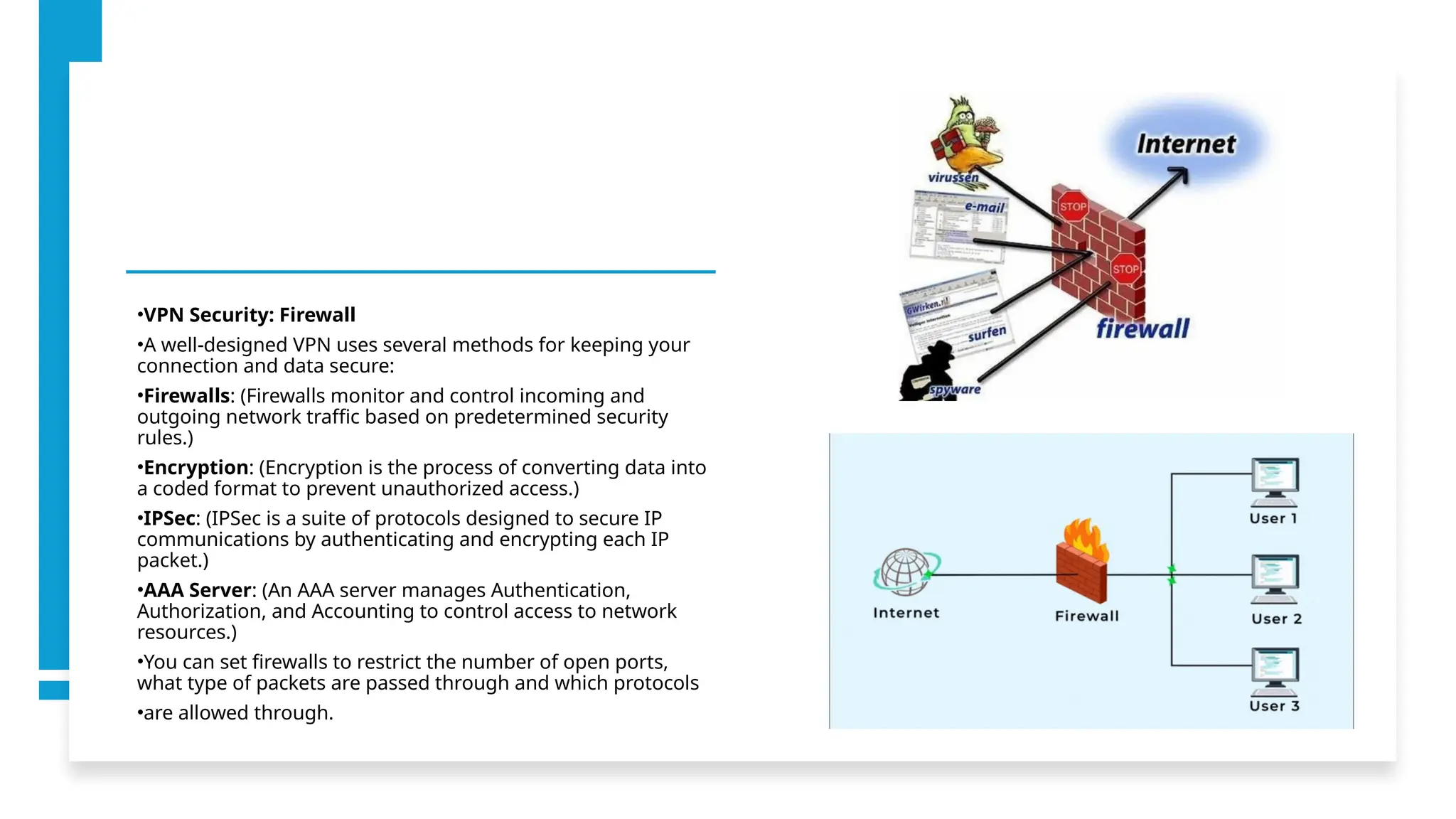
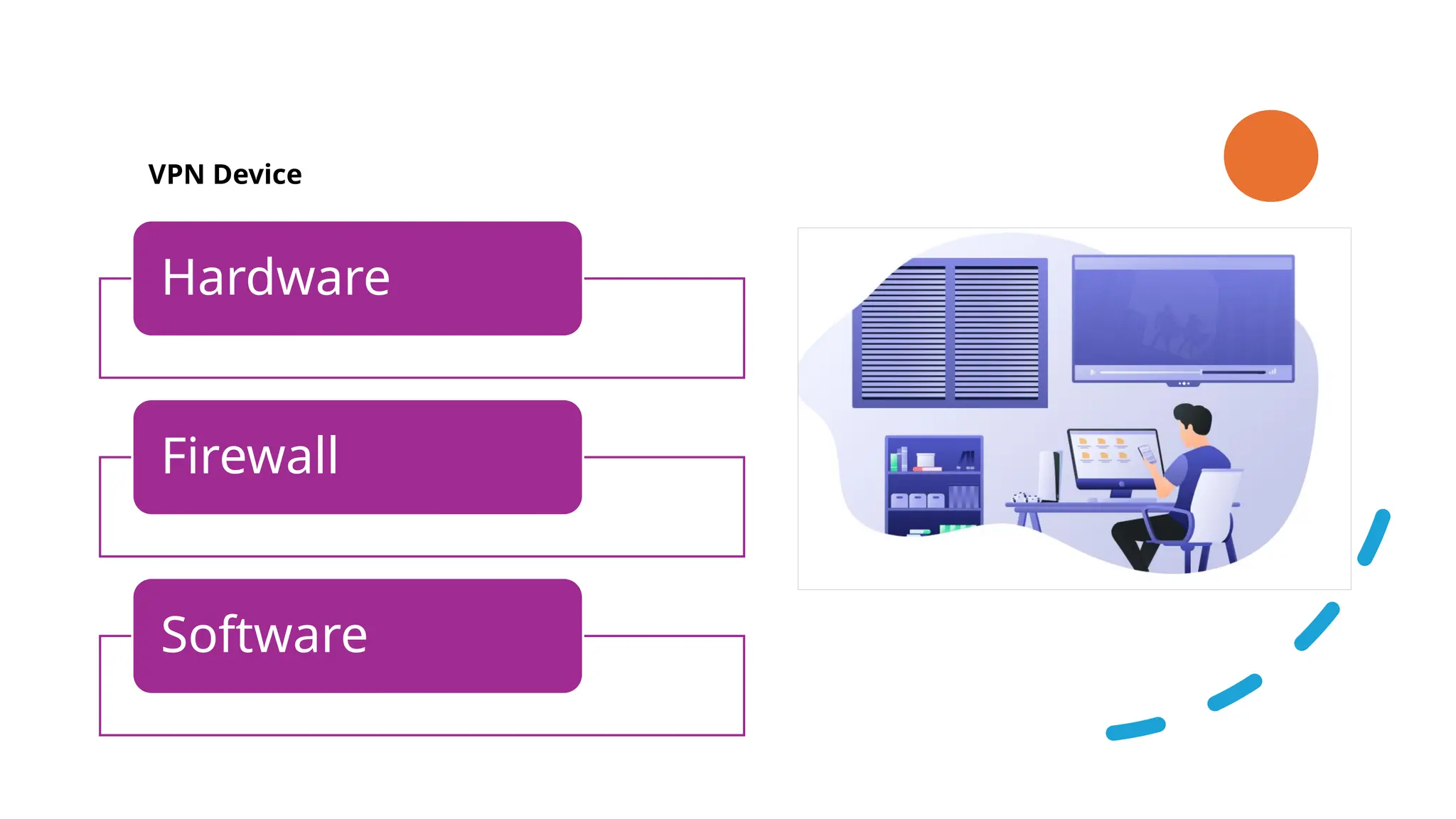
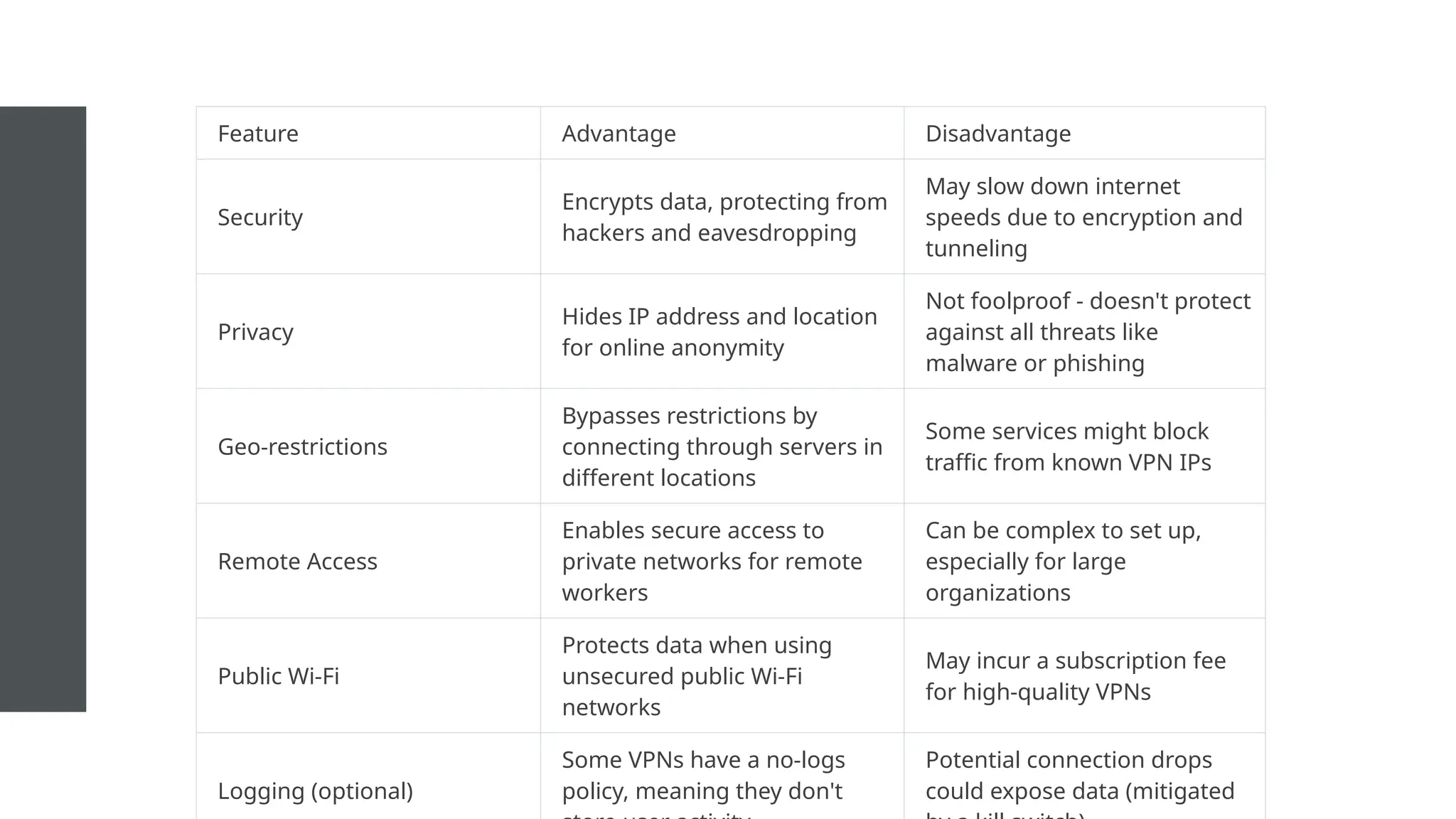
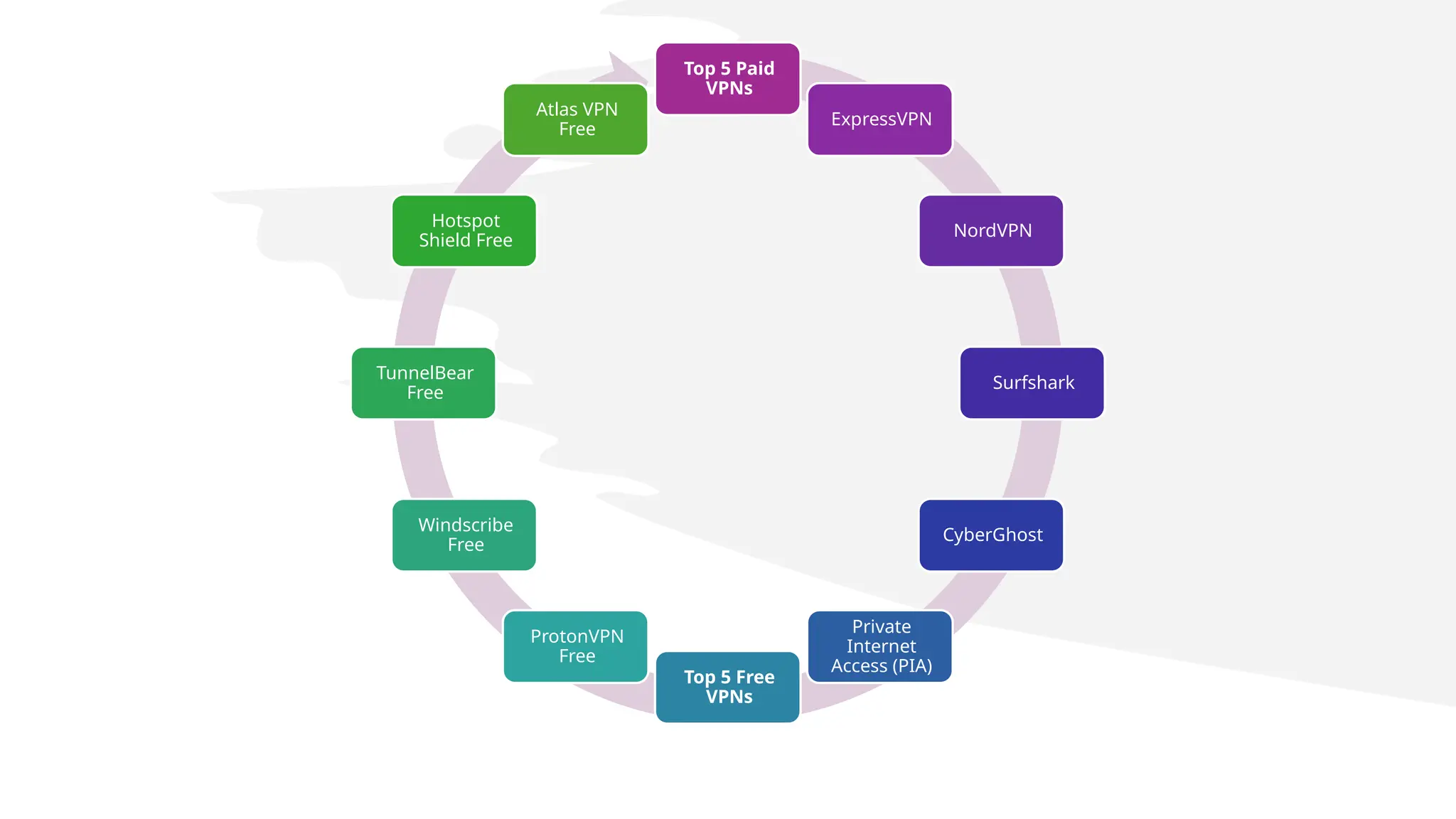
The document provides an overview of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), explaining their purpose, types, protocols, and security features. It highlights the benefits of using VPNs, such as enhanced online privacy, data encryption, and access to restricted content, while also pointing out potential disadvantages like reduced internet speeds and complexity in setup. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of ongoing security measures and suggests that the future of VPN technology may involve advanced security features.