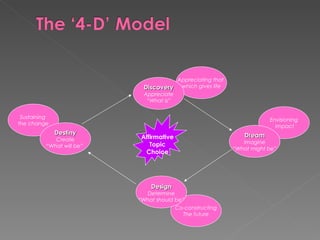
The document discusses Appreciative Inquiry (AI), an approach that focuses on what works well within organizations rather than focusing on problems. It sees organizations as systems that evolve towards positive images and outcomes when using positive language and questioning. Key aspects of AI include discovering an organization's strengths, envisioning positive potential, and inspiring change by focusing on life-giving forces. Research shows organizations using AI exhibit higher ratios of positive to negative dialogue and learning-focused questions, leading to greater employee engagement, performance, and organizational success.