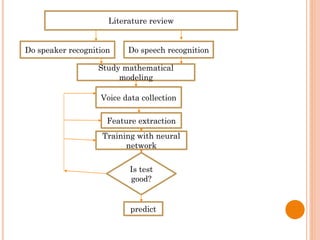
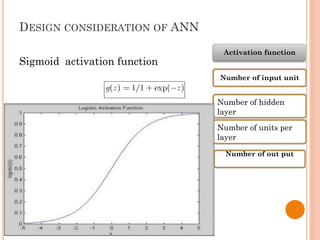
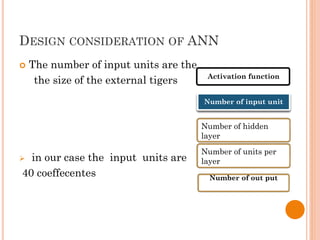
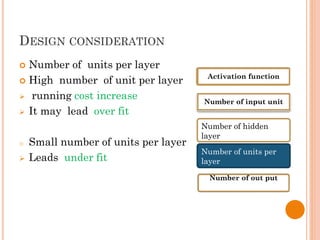
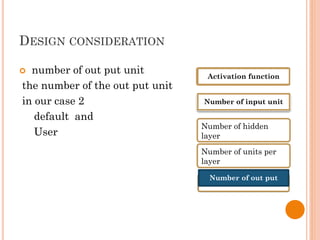
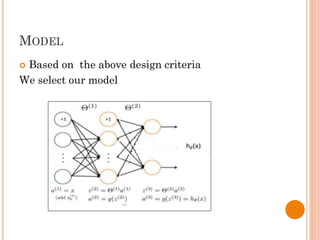
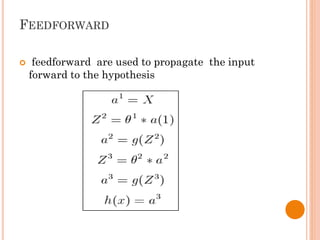
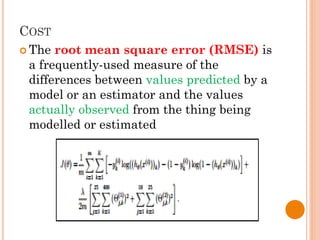
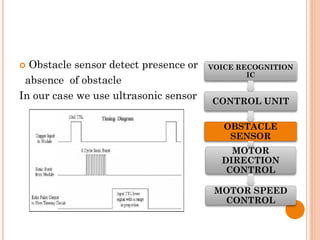
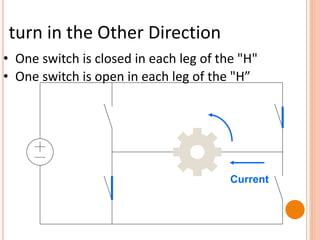
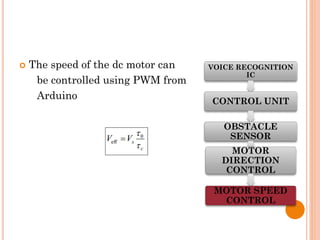
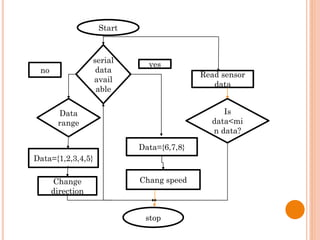
The document presents a final year project on a voice-controlled wheelchair developed by students at Bahir Dar Institute of Technology, detailing components such as voice and speaker recognition systems, control mechanisms through Arduino, and ultrasonic sensors. The project utilizes Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) for feature extraction and artificial neural networks for recognition, achieving high accuracy rates. Challenges faced during the project included limited resources and poor supervision, but the final design is deemed feasible for controlling wheelchair movement.