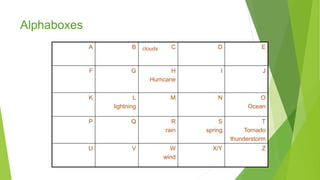
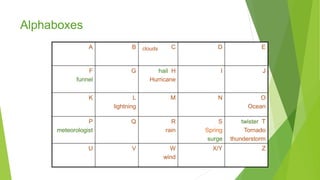
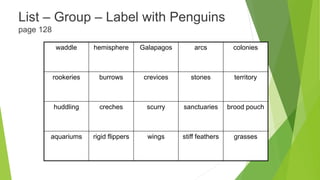
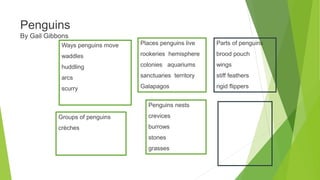
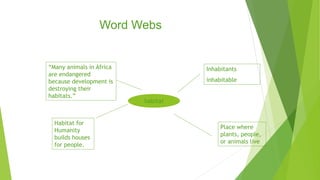
This document provides guidance and strategies for effective vocabulary instruction. It discusses the importance of direct instruction of essential words, using pictures and definitions, repeated exposure through reading and writing, and teaching word-learning strategies like analyzing roots and context clues. Specific strategies described include using alphaboxes to categorize related words, anticipation guides to activate prior knowledge, word webs to connect words to definitions and examples, and word notebooks to track word origins and meanings. The document emphasizes choosing high-utility academic words to focus instruction and engaging students through discussion and interactive activities to deepen understanding of new vocabulary.