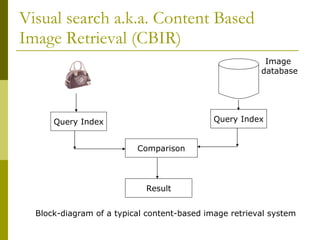
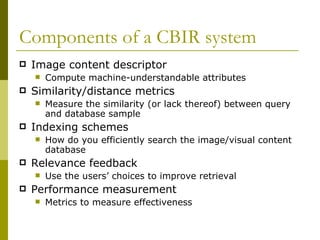
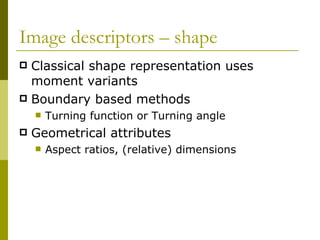
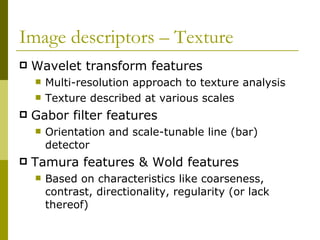
Visual search, also known as content-based image retrieval (CBIR), allows users to search for images using visual queries rather than text. The document outlines the basic components of a CBIR system, including image descriptors that extract features like color, shape, and texture, similarity measures to compare images, and indexing schemes to efficiently search large databases. It also discusses use cases for visual search in applications like product catalogs, engineering design, and law enforcement investigations. Performance is evaluated using precision and recall metrics to balance relevant results returned against total results retrieved.