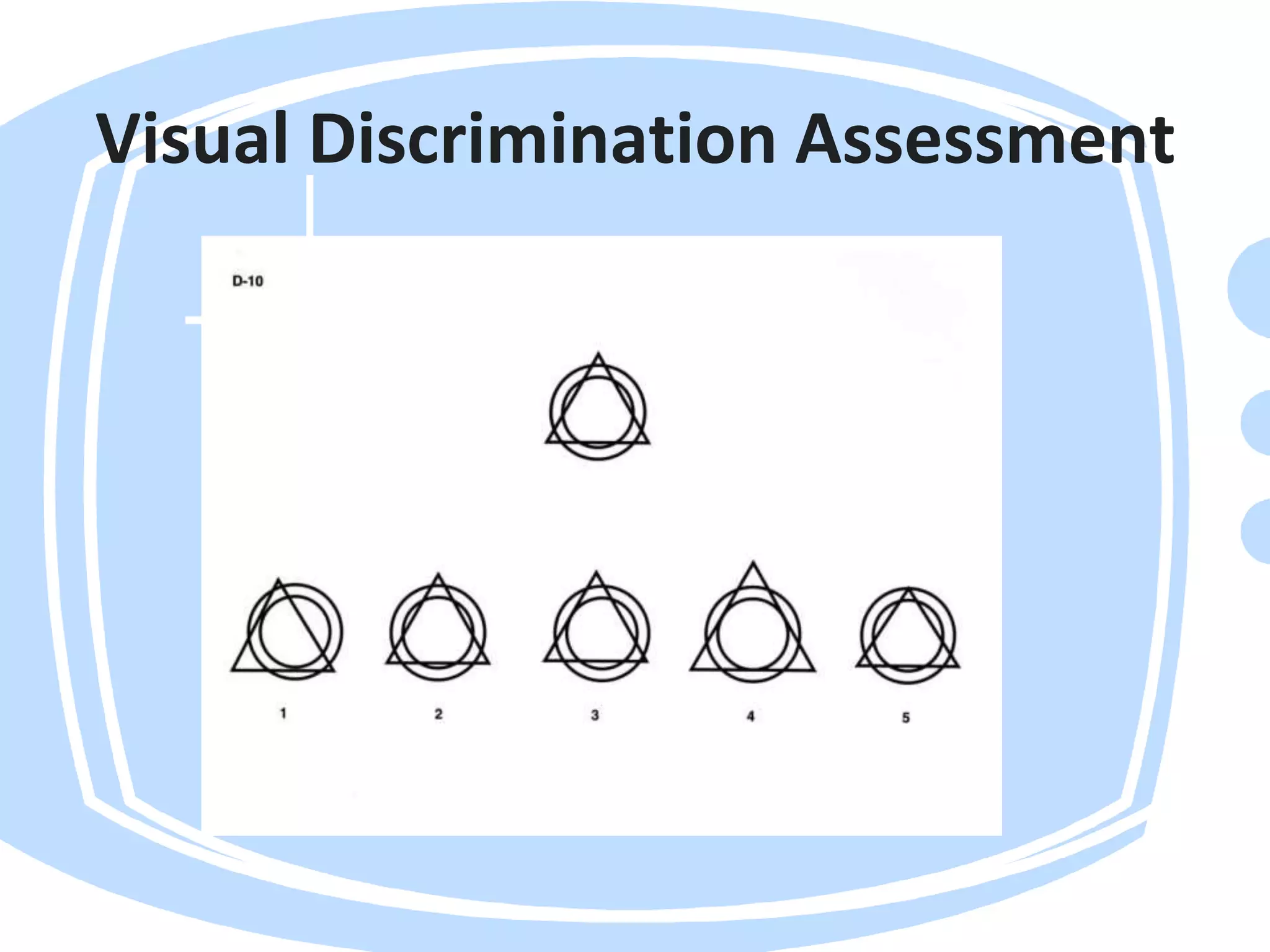
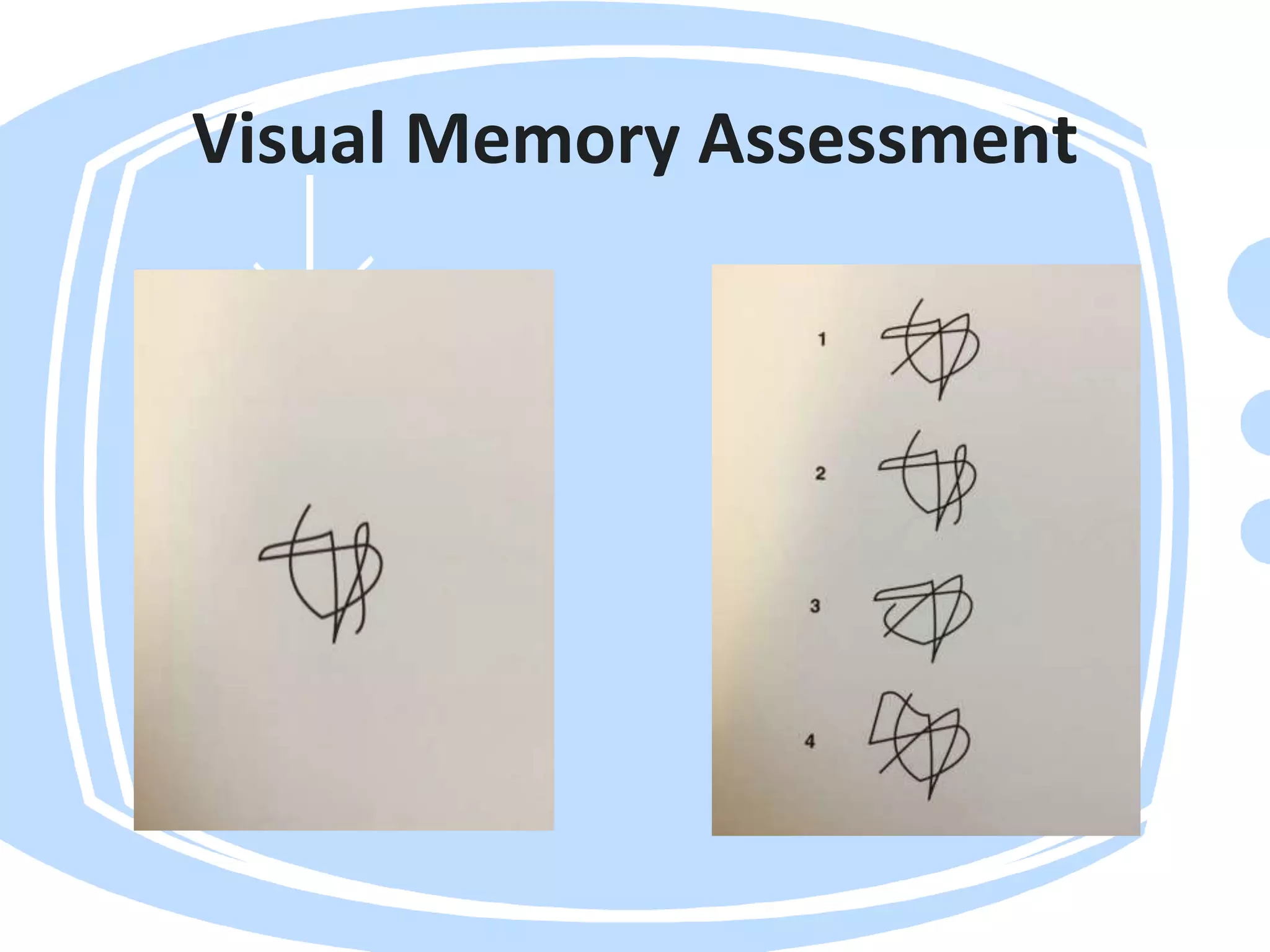
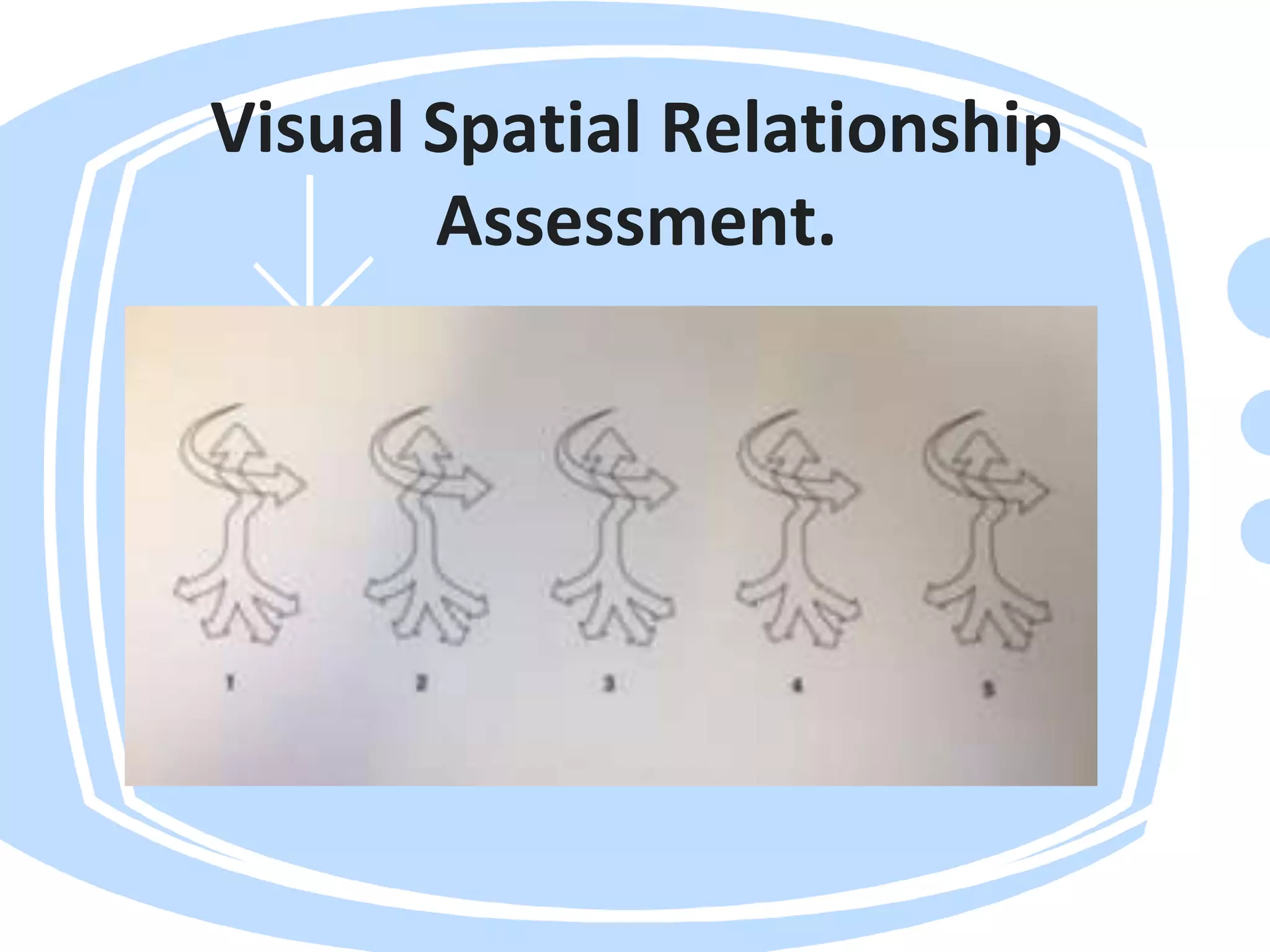
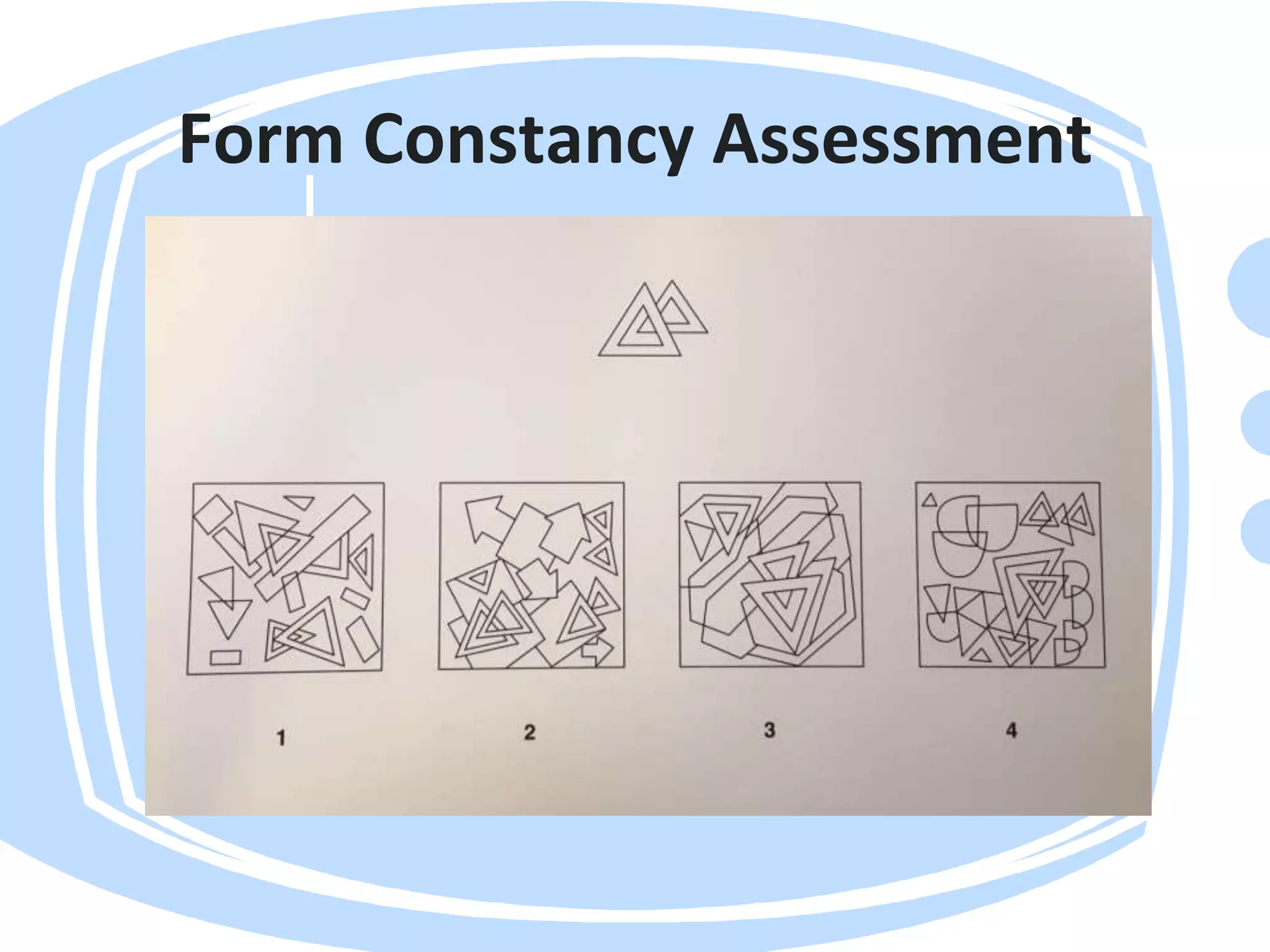
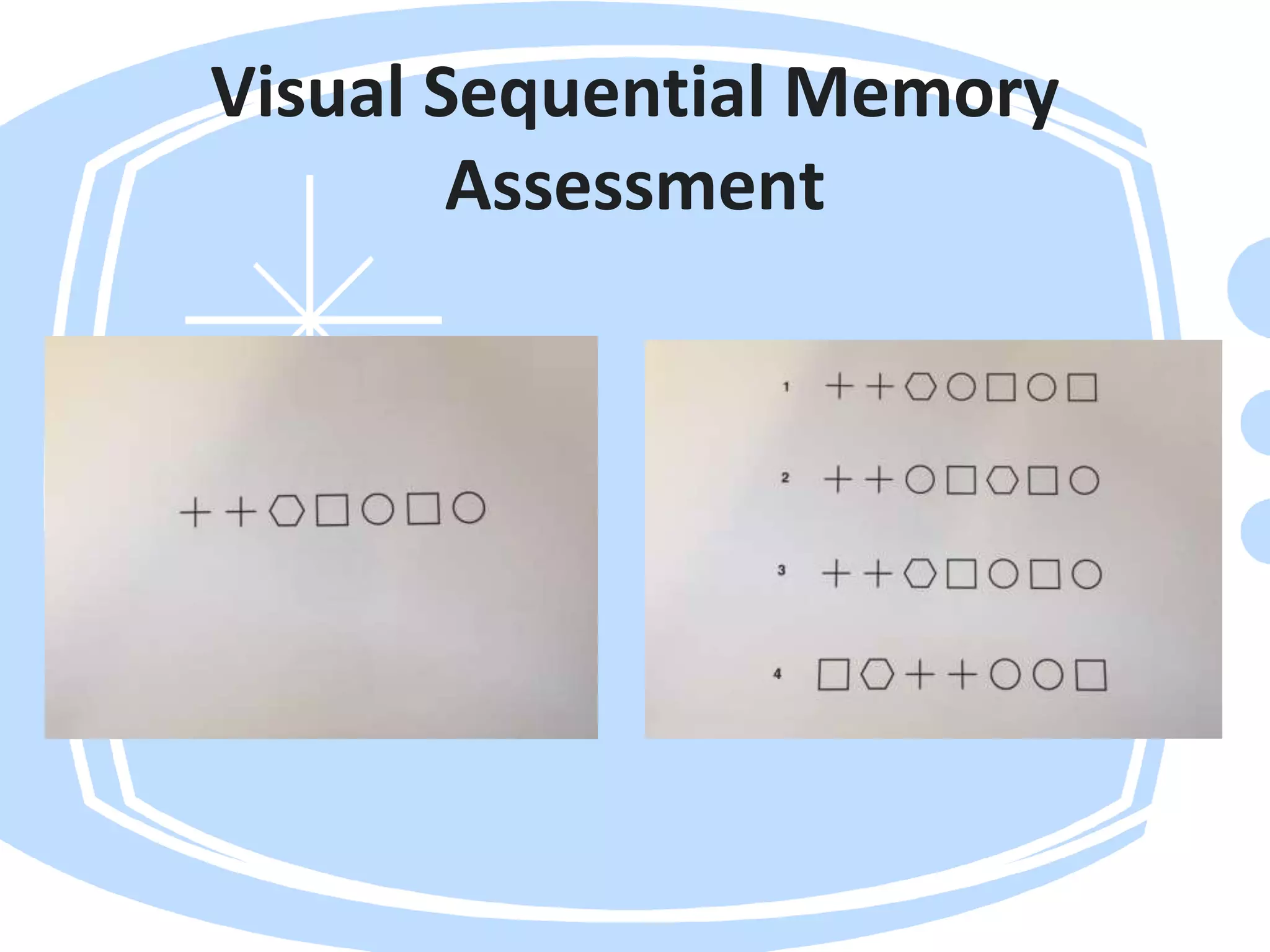
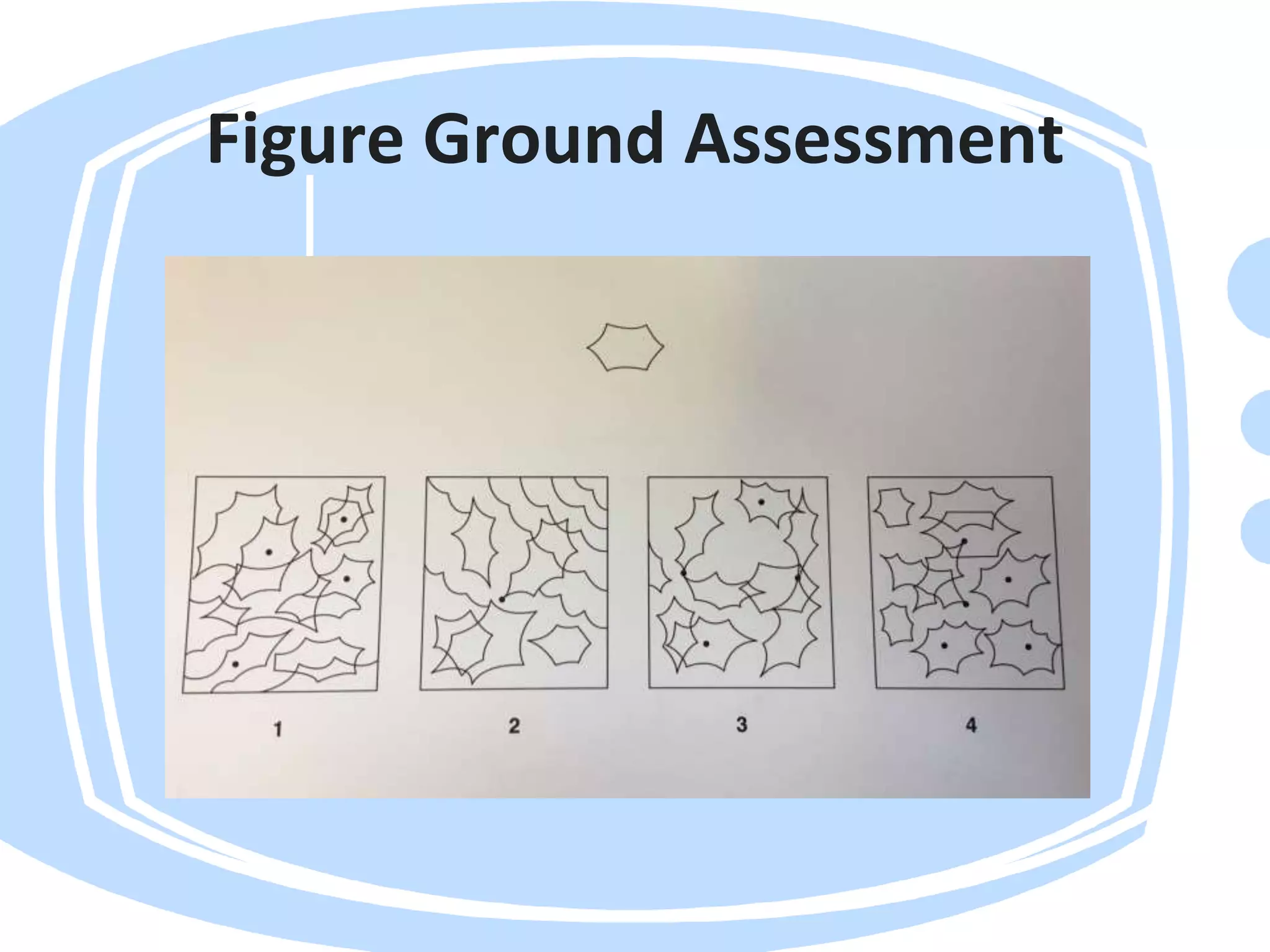
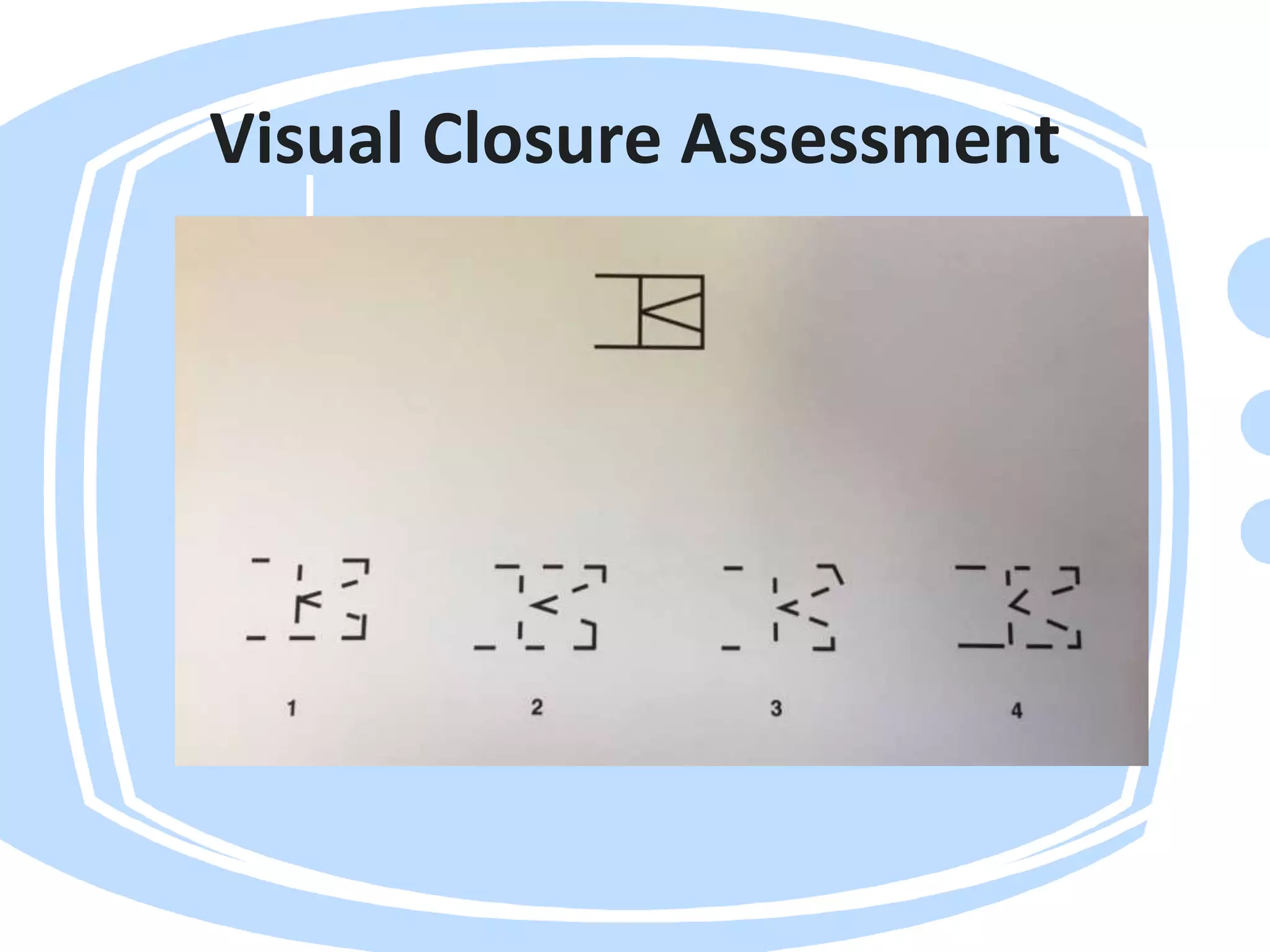
Visual perception refers to how the brain interprets visual information. A visual perception disorder hinders the ability to make sense of visual information. An eye care professional should assess visual perception to fully investigate a child's visual difficulties and answer questions about why a child struggles. The assessment evaluates seven areas: visual discrimination, visual memory, spatial relations, form constancy, sequential memory, figure-ground skills, and visual closure. Difficulties in these areas can cause problems reading, sorting, building, and distractibility. Standardized tests are used to evaluate each area.