This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 2 of the book "Data Structures and Algorithms in C++". It covers object-oriented design principles like inheritance, polymorphism, and templates. It also discusses exceptions, recursion, and design patterns. Specific topics covered include inheritance hierarchies, abstract base classes, class templates, throwing and catching exceptions, and recursive functions.




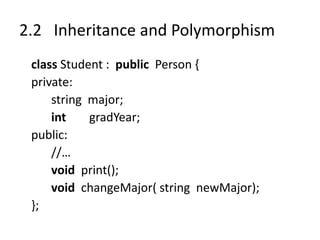
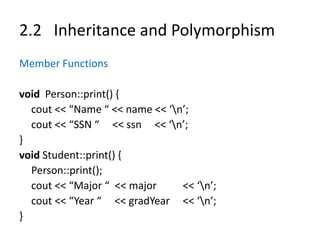


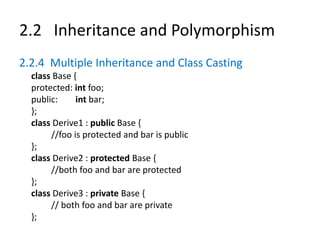
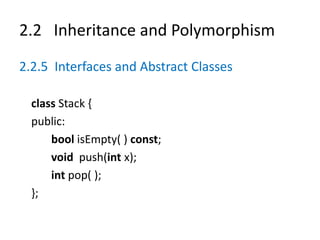
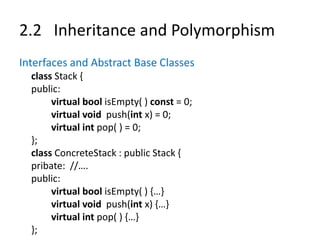
![2.2 Inheritance and Polymorphism
Static Binding
Person* pp[100];
pp[0] = new Person(…);
pp[1] = new Student(…);
cout << pp[1] ->getName() <<‘n’; //okay
pp[0] ->print();
pp[1] ->print();
pp[1] ->changeMajor(“English”); //ERROR!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vdocument-230217093534-636804a7/85/vdocument-in_data-structures-and-algorithms-in-c-michael-t-goodrich-roberto-tamassia-5689cfa959a68-ppt-9-320.jpg)
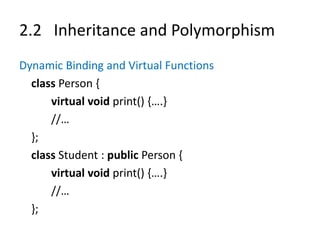

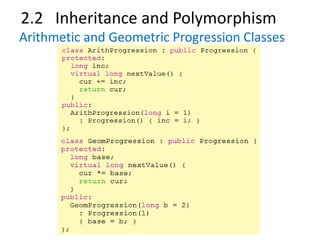


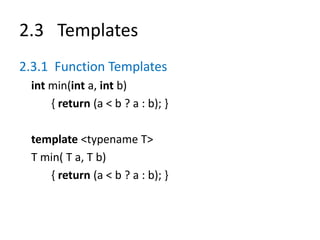
![2.3 Templates
2.3.2 Class Templates
template <typename Object>
class BasicVector {
Object* a;
int capacity;
public:
BasicVector(int capac = 10) {
capacity = capac;
a = new Object[ capacity ];
}
Object& elemAtRank(int r)
{ return a[r]; }
//…
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vdocument-230217093534-636804a7/85/vdocument-in_data-structures-and-algorithms-in-c-michael-t-goodrich-roberto-tamassia-5689cfa959a68-ppt-19-320.jpg)

![2.3 Templates
Templated Arguments
BasicVector<BasicVector<int> > xv(5);
//…
xv. elemAtRank(2). elemAtRank(8) = 15;
Templated Members
template <typename Object>
Object& BasicVector<Object>::elemAtRank(int r) {
return a[r];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vdocument-230217093534-636804a7/85/vdocument-in_data-structures-and-algorithms-in-c-michael-t-goodrich-roberto-tamassia-5689cfa959a68-ppt-21-320.jpg)






