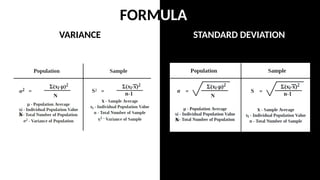
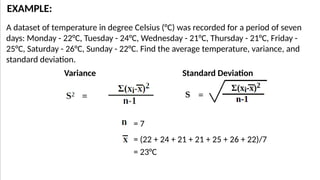
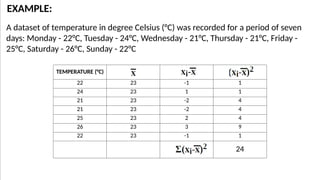
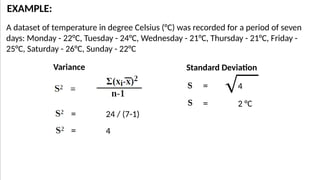
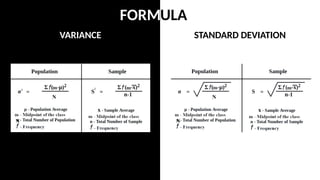
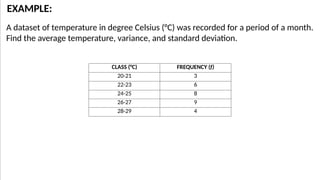
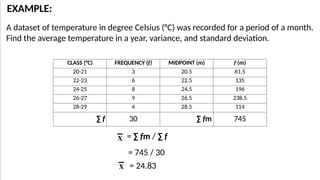
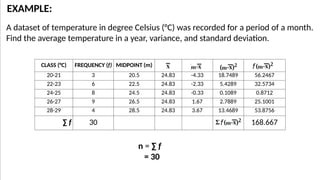
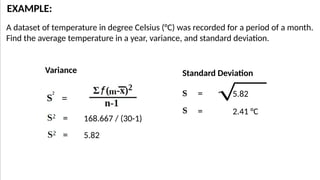
The document discusses measures of variability, specifically variance and standard deviation, explaining how they quantify the spread of data from the mean. It details the calculation methods for both grouped and ungrouped data, including formulas and examples using temperature data recorded over specific periods. The document emphasizes the efficiency of calculating variance and standard deviation for grouped data compared to ungrouped data.