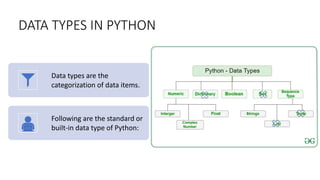
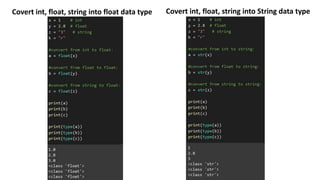
This document discusses Python data types and variables. It covers numeric data types like int and float, as well as Boolean, string, and sequence data types. It also defines what a variable is, how to name variables, and how to print and update variable values. It introduces type casting and the input function for getting user input.