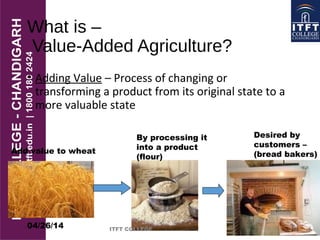
Value-added agriculture involves processing raw agricultural commodities to enhance their value. This can be accomplished by changing the physical form of products, differentiating products, bundling products together, or owning assets along the supply chain. Examples include milling wheat into flour, making jam from strawberries, or branding and marketing beef under a specific label. The global market for value-added agricultural products is growing as consumers have increasing demands around health, nutrition and convenience.