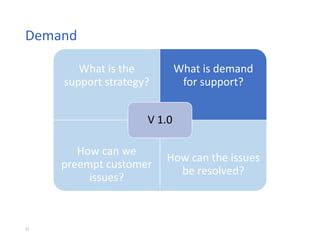
The document outlines best practices for supporting a version 1.0 product, emphasizing the importance of a structured support strategy that addresses customer needs effectively. It poses four critical questions to guide support efforts: defining the support strategy, assessing demand, preempting issues, and resolving problems. Key recommendations include enhancing self-service options, fostering knowledge creation, and establishing a proactive support model to minimize customer contact necessity.