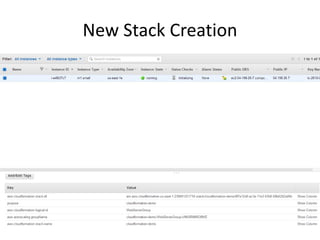
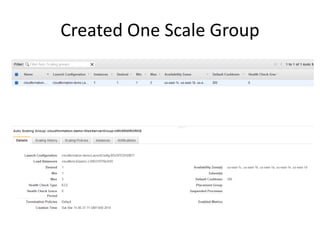
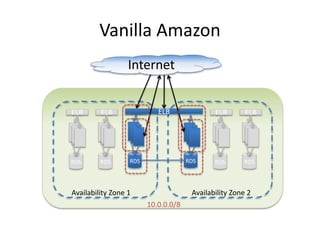
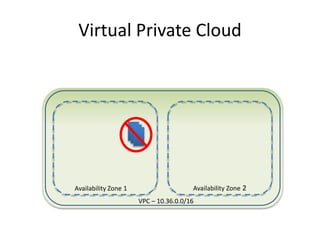
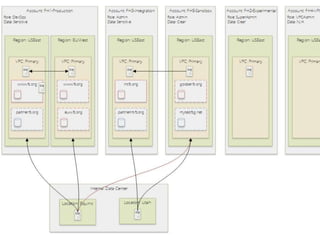
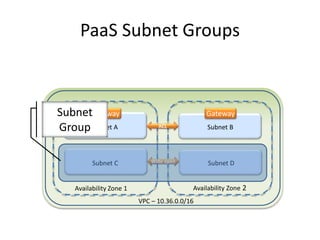
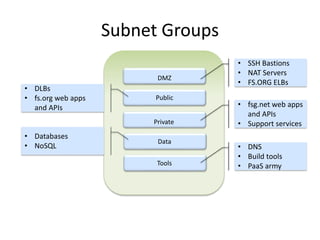
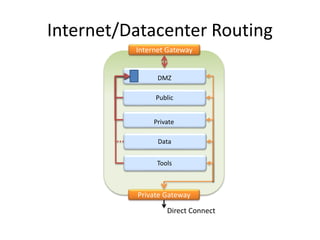
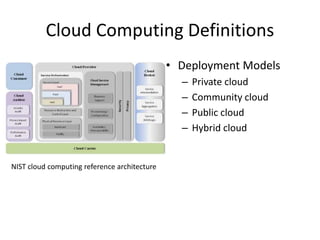
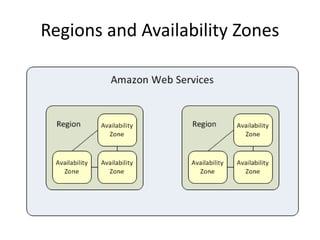
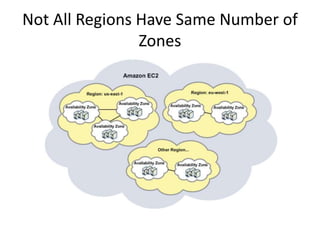
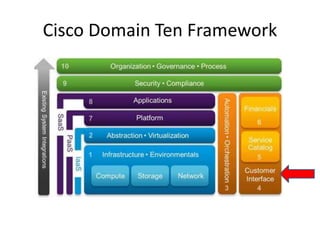
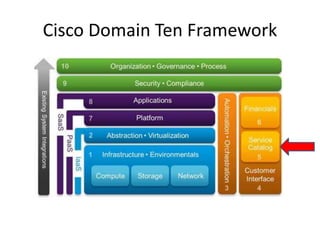
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, outlining its essential characteristics, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and deployment models (private, community, public, hybrid). It discusses the advantages of utilizing cloud services for cost savings and improved data accessibility, as well as challenges related to machine instability and coordination. Finally, it emphasizes the importance of properly leveraging cloud technology for business objectives, highlighting flexibility and governance as key benefits.










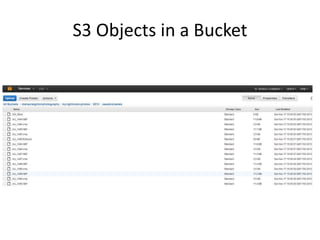







![CloudFormation Template - 1
"Resources" : {
"WebServerGroup" : {
"Type" : "AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup",
"Properties" : {
"AvailabilityZones" : { "Fn::GetAZs" : ""},
"LaunchConfigurationName" : { "Ref" : "LaunchConfig" },
"MinSize" : "1",
"MaxSize" : "3",
"LoadBalancerNames" : [ { "Ref" : "ElasticLoadBalancer" } ]
}
},](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utahcodecamp-cloud-140315211020-phpapp01/85/Utah-Codecamp-Cloud-Computing-31-320.jpg)
![Cloudformation Template - 2
"LaunchConfig" : {
"Type" : "AWS::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration",
"Properties" : {
"KeyName" : { "Ref" : "KeyName" },
"ImageId" : { "Fn::FindInMap" :
[ "AWSRegionArch2AMI",
{ "Ref" : "AWS::Region" }, { "Fn::FindInMap" :
[ "AWSInstanceType2Arch", { "Ref" : "InstanceType" },
"Arch" ]} ] },
"UserData" : { "Fn::Base64" : { "Ref" : "WebServerPort" }},
"SecurityGroups" : [ { "Ref" : "InstanceSecurityGroup" } ],
"InstanceType" : { "Ref" : "InstanceType" } }},](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utahcodecamp-cloud-140315211020-phpapp01/85/Utah-Codecamp-Cloud-Computing-32-320.jpg)


![Cloudformation - 5
"CPUAlarmHigh": {
"Type": "AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm",
"Properties": {
"AlarmDescription": "Scale-up if CPU > 90% for 10 minutes",
"MetricName": "CPUUtilization",
"Namespace": "AWS/EC2",
"Statistic": "Average",
"Period": "300",
"EvaluationPeriods": "2",
"Threshold": "90",
"AlarmActions": [ { "Ref": "WebServerScaleUpPolicy" } ],
"Dimensions": [
{
"Name": "AutoScalingGroupName",
"Value": { "Ref": "WebServerGroup" }
} ],
"ComparisonOperator": "GreaterThanThreshold" } },](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utahcodecamp-cloud-140315211020-phpapp01/85/Utah-Codecamp-Cloud-Computing-35-320.jpg)
![Cloudformation Template - 6
"CPUAlarmLow": {
"Type": "AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm",
"Properties": {
"AlarmDescription": "Scale-down if CPU < 70% for 10 minutes",
“MetricName": "CPUUtilization",
"Namespace": "AWS/EC2",
"Statistic": "Average",
"Period": "300",
"EvaluationPeriods": "2",
"Threshold": "70",
"AlarmActions": [ { "Ref": "WebServerScaleDownPolicy" } ],
"Dimensions": [ {
"Name": "AutoScalingGroupName",
"Value": { "Ref": "WebServerGroup" } } ],
"ComparisonOperator": "LessThanThreshold" } },](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utahcodecamp-cloud-140315211020-phpapp01/85/Utah-Codecamp-Cloud-Computing-36-320.jpg)