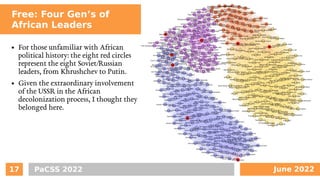
The document discusses the use of complex network analysis (CNA) for the periodization of post-colonial African history. It explores the theoretical background of historical periodization, proposes modeling historical states as complex networks, and presents two case studies: U.S. voting patterns and African leadership dynamics. The findings suggest that CNA is effective in categorizing historical periods based on community detection methods.


![June 2022
PaCSS 2022
3
What Is Historical Periodization?
● Periodization is the process of categorizing the past into discrete, contiguous, quantified,
and named blocks of time and the results of such a process.
● Pertains to history (“the past”).
● Corresponds to classification in machine learning (“categorizing … into discretem quantified
blocks”).
● Mostly subjective and arbitrary (though claimed to be “quantified”).
● Periodization is used for understanding and communicating historical phenomena.
● History as a sequence of social formations (Marx, 1844).
● “[History] can exist as a discipline if it develops a theory of periodization” (Koselleck, 2000).
● Also, confronted by some historians as superficial: History is continuous (Jordheim, 2012).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pacss-2022-220617044442-723d472e/85/Using-Complex-Network-Analysis-for-Periodization-3-320.jpg)
![June 2022
PaCSS 2022
4
Formal Definition
● Given:
● [Historical] state St at a discrete time t that includes essential aspects of the society in a specific
territory (Africa, USA, whole world, etc.).
● A measure of similarity of two states mij = m(Si, Sj), such that mij=mji≥0 and mii=0.
● An ordered sequence of states H=S0, S1, S2, … (the history as such).
● Periodization is:
● A mapping {S P}, where P
→P}, where P ⊆ℕ is a set of at least two periods (non-trivial!).
● Such that if Si P
→P}, where P a and Sj P
→P}, where P a, then Sk P
→P}, where P a ∀*k: i<k<j (non-overlapping!).
*Ideally, for all k; practically, for most k’s.
● That minimizes the goal function: F(H, P)=min.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pacss-2022-220617044442-723d472e/85/Using-Complex-Network-Analysis-for-Periodization-4-320.jpg)