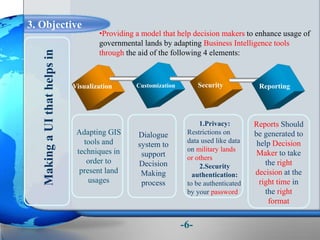
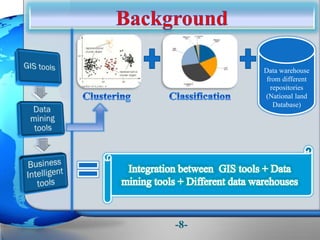
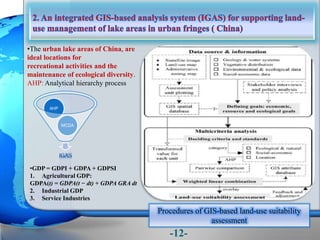
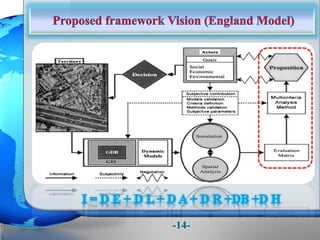
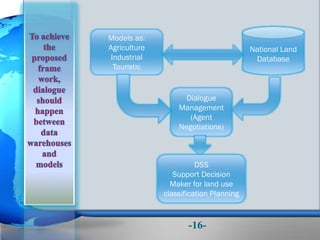
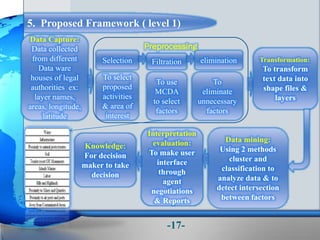
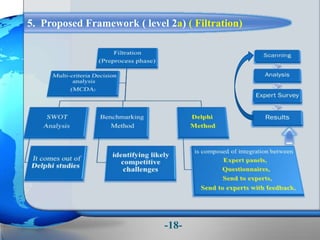
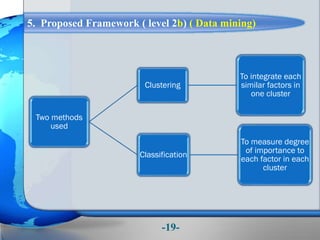
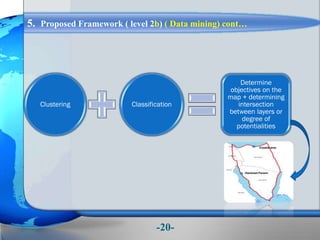
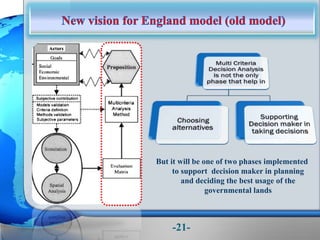
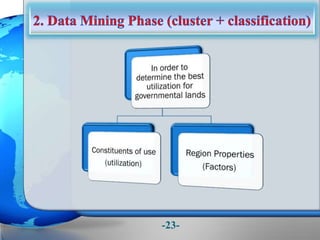
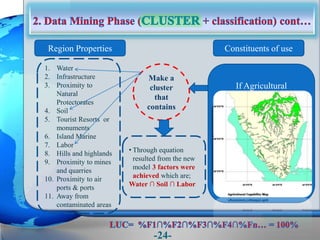
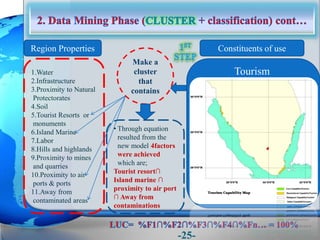
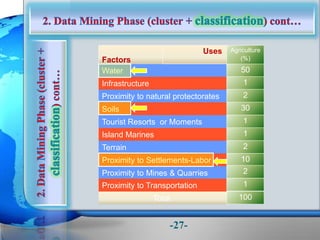
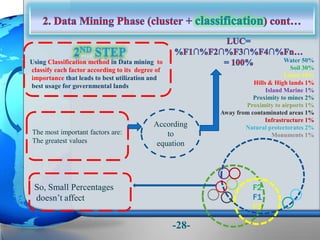
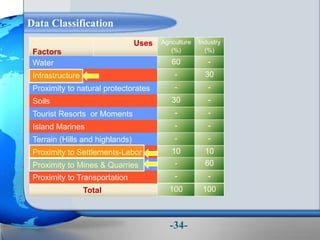
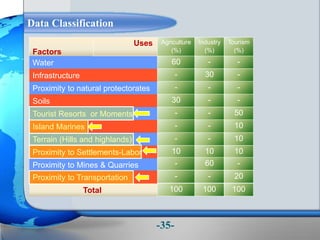
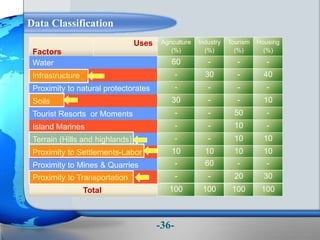
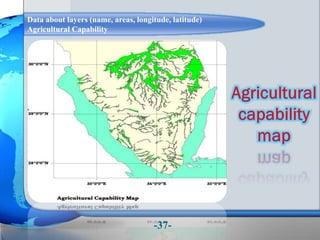
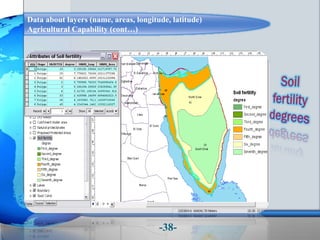
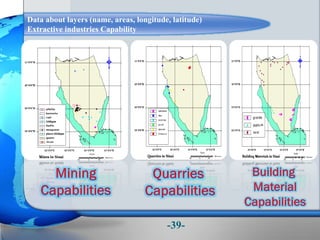
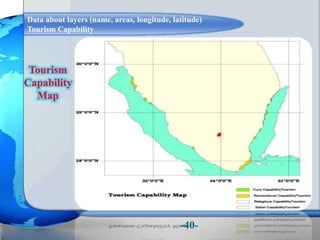
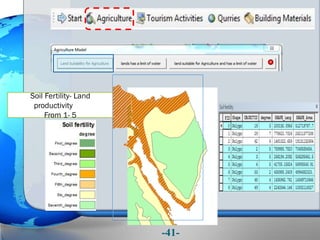
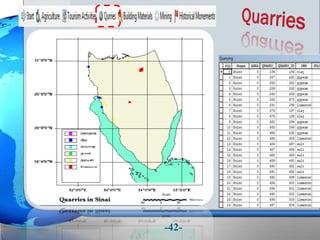
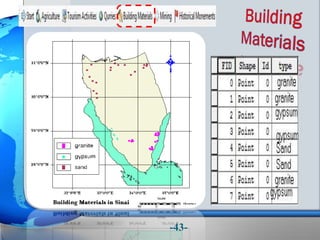
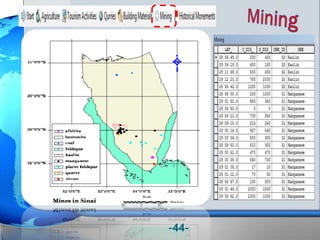
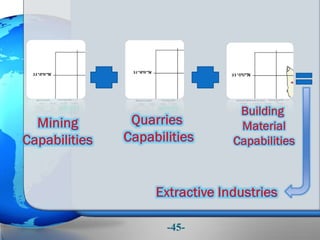
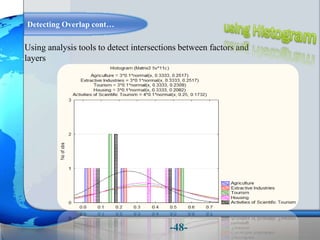
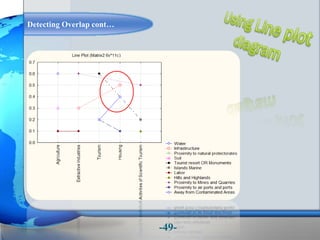
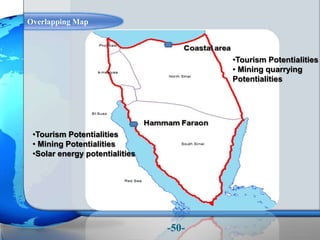
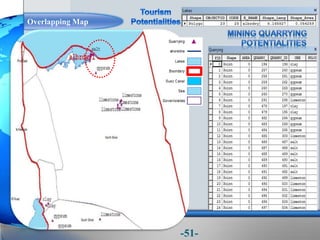
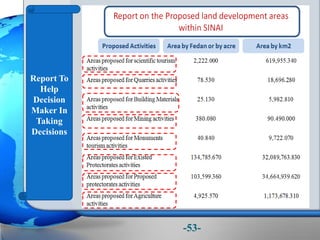
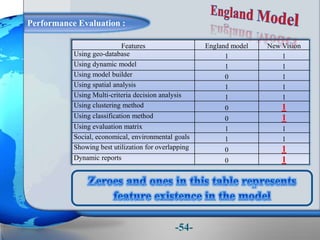
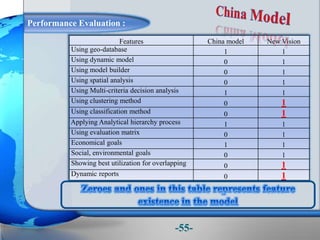
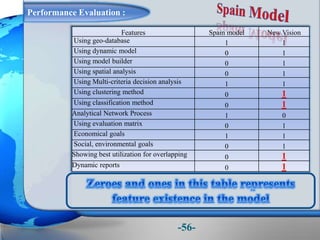
This document presents a framework for optimizing governmental land use through a Business Intelligence Land Use Planning and Classification Model (BILUPC). It highlights the need for a model to assist decision-makers in effectively utilizing governmental lands, addressing motivations, objectives, and related works while proposing a detailed methodology and case studies. The conclusions emphasize enhancing land utilization and reporting mechanisms to support decision-making, alongside future work addressing challenges in land management.