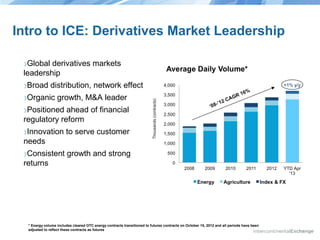
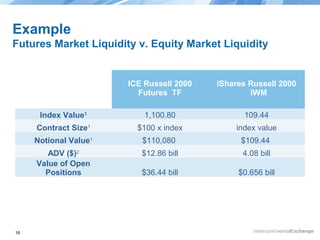
The document discusses the structure and performance of U.S. equities and futures markets, highlighting the challenges of complexity, fragmentation, and lack of transparency in cash equity markets versus the more streamlined futures markets. It emphasizes the need for improvement through regulatory action and market innovation to enhance operational integrity, transparency, and fairness for all stakeholders. The anticipated ICE/NYSE combination aims to address these issues by reducing fragmentation and promoting customer-centric market practices.