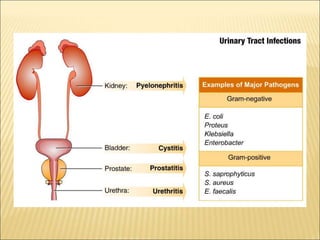
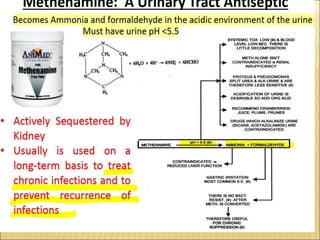
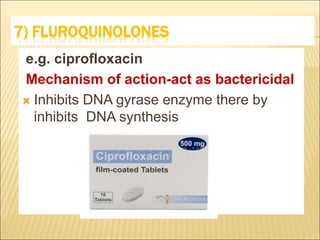
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be classified into upper and lower infections, with kidney infections being more severe. Women are more prone to UTIs due to anatomical differences, and common causes include urinary obstruction, poor hydration, and certain health conditions. Treatment options include various antibiotics and urinary antiseptics, each with unique mechanisms and indications.