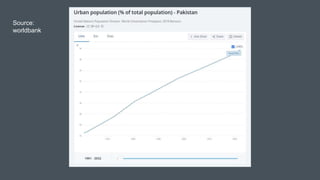
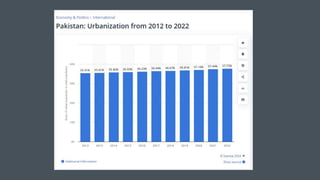
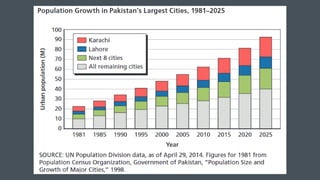
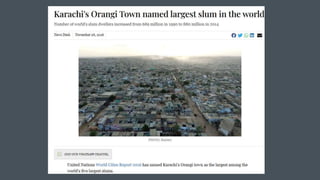
This document discusses urbanization in Pakistan and its negative externalities. It notes that Pakistan has the highest urbanization rate in South Asia, with 36.4% of the population living in urban areas. Unplanned urbanization has resulted in slums, environmental degradation, poverty, and inequality. Cities generate most of Pakistan's GDP but also face challenges like solid waste, water scarcity, and pollution. Effective urban planning, infrastructure investment, affordable housing policies, and investment in public transportation are proposed as solutions to manage the externalities of urbanization.