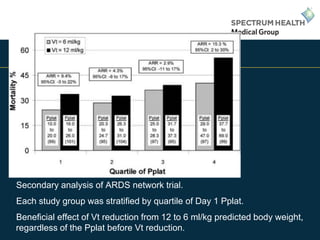
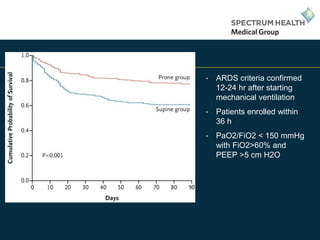
This document discusses updates in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It begins by outlining the speaker's conflicts of interest and objectives to understand the definition, physiology, and treatment options for ARDS. It then reviews the limitations of the original ARDS definition from 1994 and improvements made in the 2012 Berlin definition. Various treatment trials are summarized, including low tidal volume ventilation, use of neuromuscular blocking agents, higher vs. lower positive end-expiratory pressure, prone positioning, and early rescue therapy with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The speaker's contact information is provided at the end.