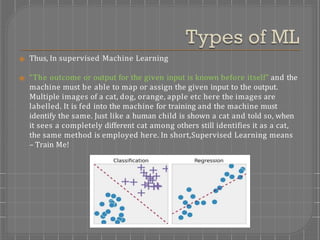
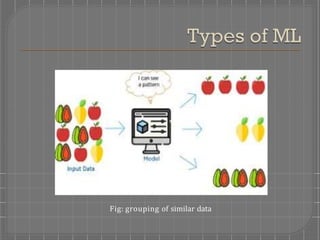
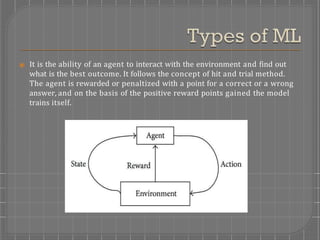
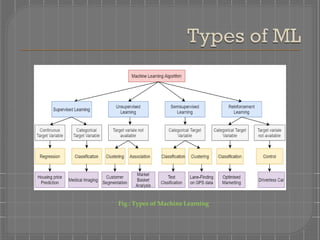
There are four main types of machine learning: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforced learning. Supervised learning uses labeled training data to map inputs to outputs, and includes classification and regression models. Unsupervised learning uses unlabeled data to find patterns and group similar data without labels, including association and clustering models. Semi-supervised learning combines supervised and unsupervised techniques. Reinforced learning trains models through a system of rewards and penalties as it interacts with an environment.