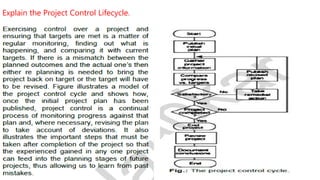
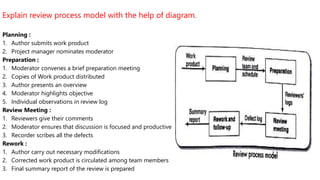
The document discusses various topics related to project management including reasons for project termination, methods of project visualization, priorities for monitoring, change control procedures, software configuration management, stress management techniques, types of contracts, stages in contract placement, and the review process model. Key points include that reasons for project termination can include lack of resources, incomplete requirements, or obsolete technologies, and the termination process involves project surveys, debriefing meetings, and result publication. Project visualization methods include Gantt charts, slip charts, and timeline charts. Priorities for monitoring include critical path activities, activities with no free float, and high risk activities. The review process model involves planning, preparation, a review meeting, and rework stages.