The document provides a comprehensive overview of Linux fundamentals, including its history, architecture, and types of device drivers. It covers essential Linux commands, the vi editor, and the significance of Linux in various applications, emphasizing its open-source nature and flexibility. Additionally, it discusses key features of Linux such as multi-user capabilities, security measures, and common Linux distributions.

![1. Write a short note on : i) LINUX Fundamentals ii) Pieces of Linux (any 4) [8]
2. Write any five commands from Linux with description. [10]
3. What is intertask communication? Describe intertask communication in RTOS. [8]
4. Write a short note on : i) Kernel module ii) Advantages and Disadvantages of Linux
[10]
5. What is linux explain architecture of linux in detail. [8]
6. Write short note on: i) System call ii) Network device driver [9]
7. Explain Linux kernel module in detail. [8]
8. Write short note on: i) Character device driver ii) The Role of Device Driver [9]
9. What is device driver? Explain types of device drivers. [8]
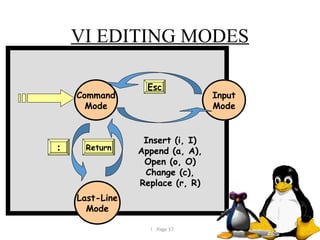
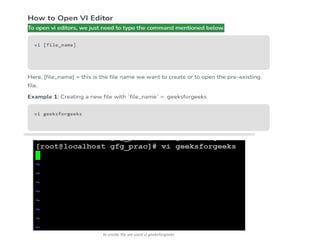
10. Write a short note on i) VI Editors ii) Pieces of Linux (any 4) [8]
11. Explain types of device drivers, with its need. [8]
12. Write a short note on i) Kernel Module ii) Use of Linux in embedded system[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-241013123455-fe7fabc2/85/Unit-6_linux-operating-system_1234-pptx-2-320.jpg)