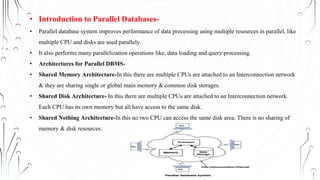
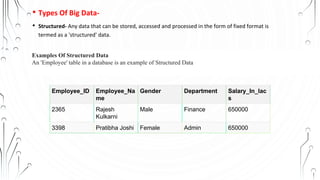
This document summarizes different types of databases including parallel, distributed, object-based, XML, NoSQL, multimedia, and big data databases. Parallel databases improve performance using multiple resources like CPUs and disks. Distributed databases store data across networked computers. Object-based databases store data as objects with properties like inheritance and encapsulation. XML databases store data in XML format. NoSQL databases are non-relational and support large, unstructured data. Multimedia databases contain various media types. Big data databases handle extremely large and complex datasets.