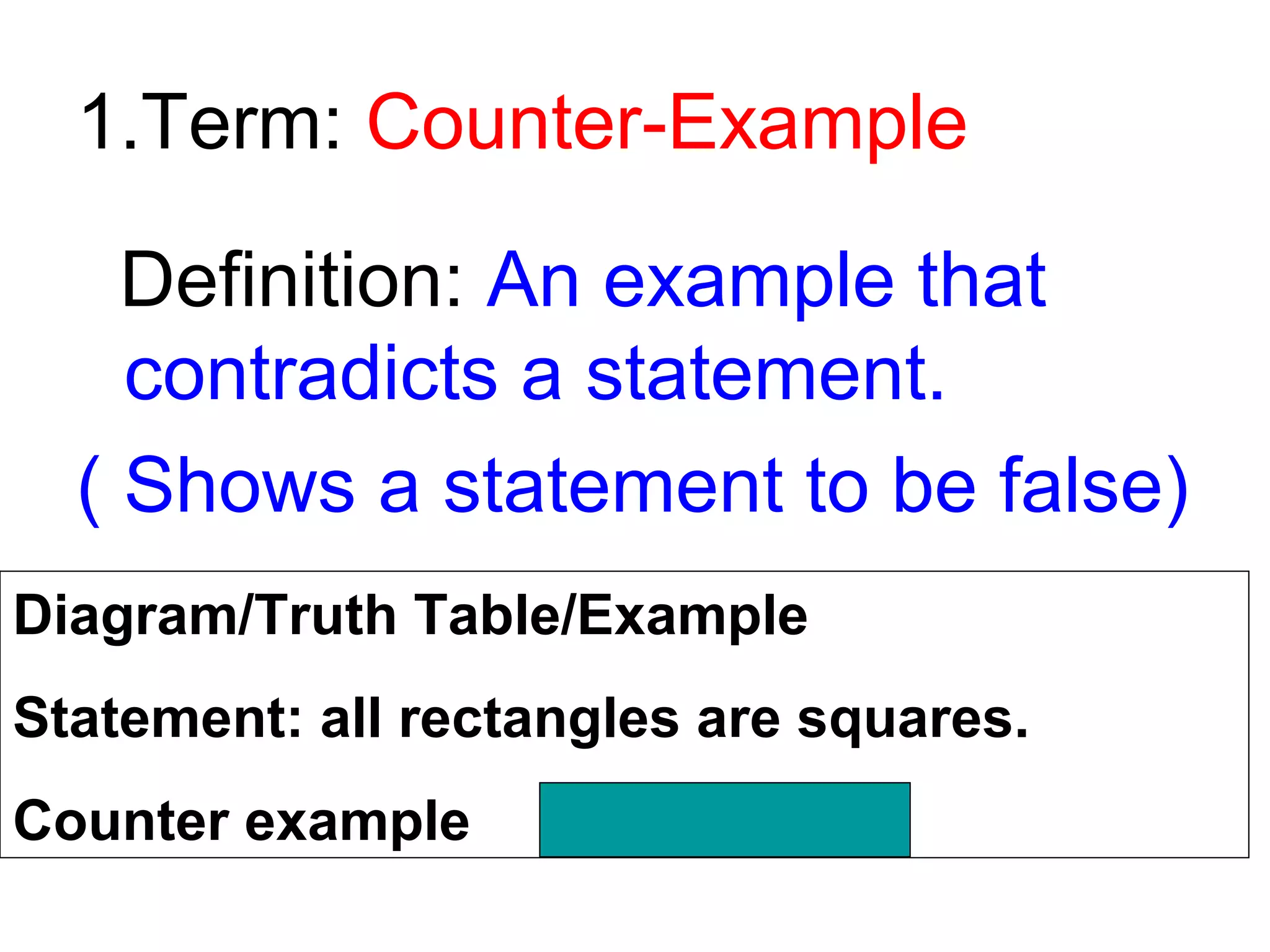
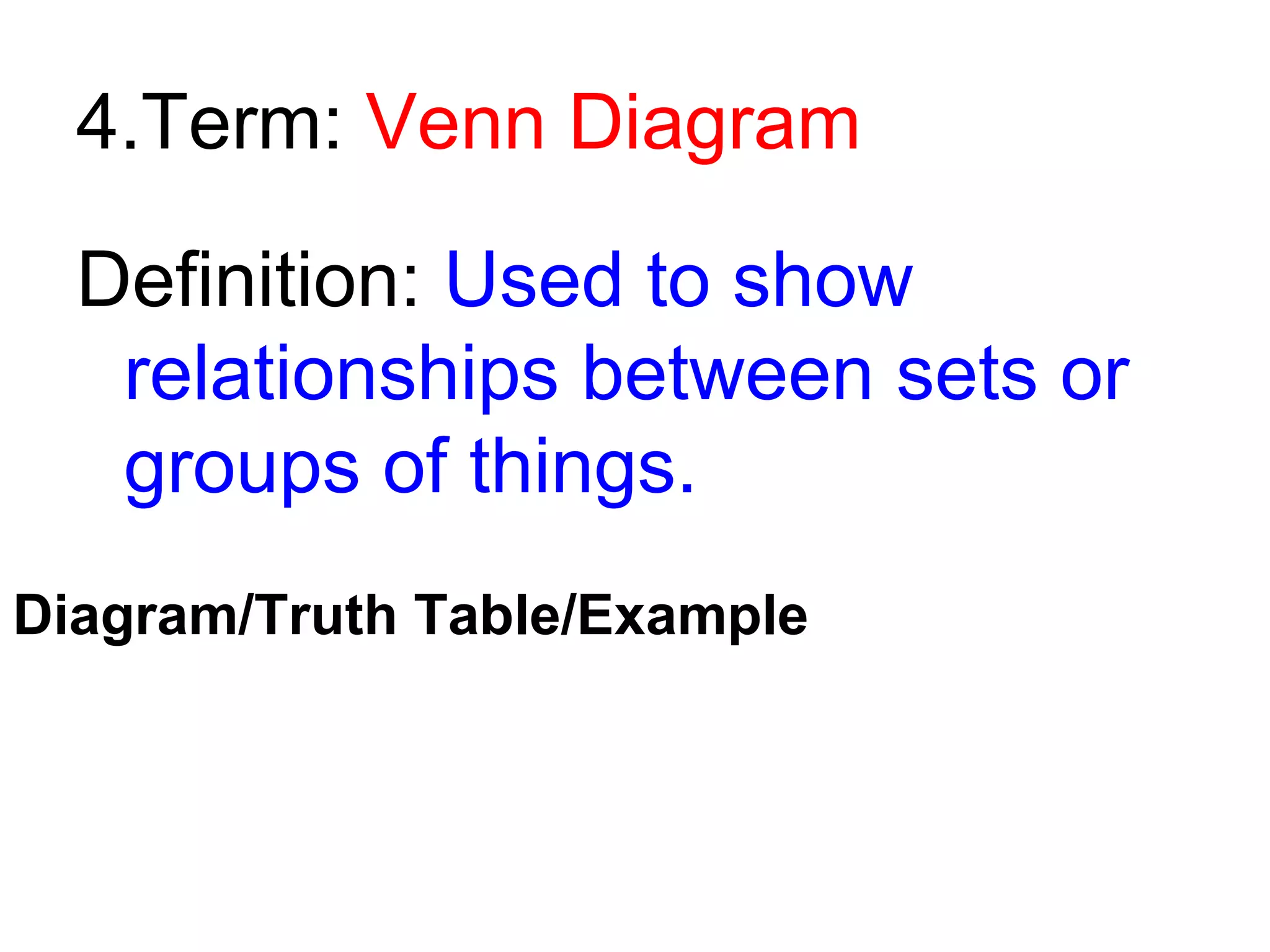
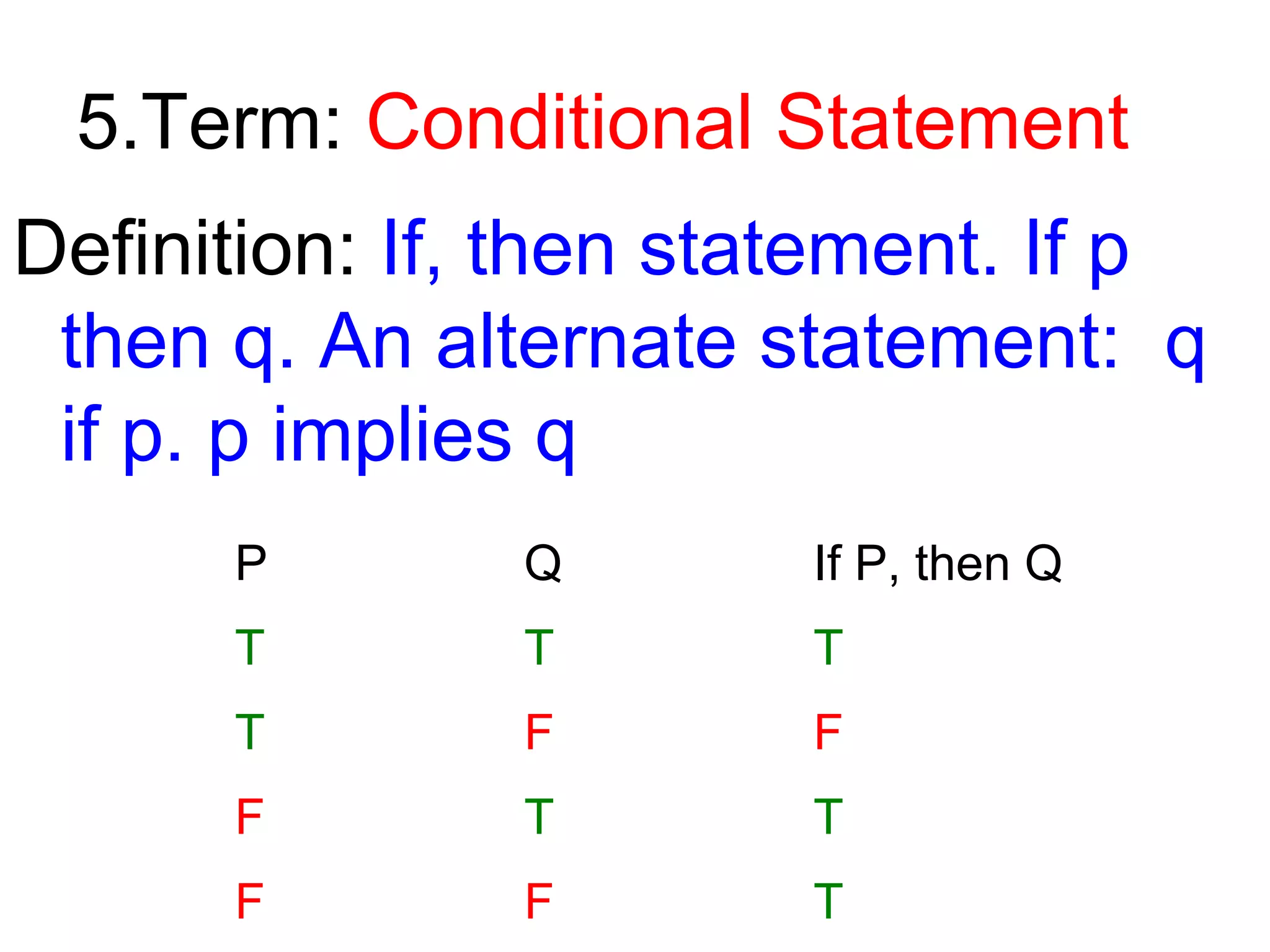
This document defines key logical terms: counter-example, AND/OR statements, Venn diagrams, conditional statements, hypotheses, conclusions, converses, inverses, contrapositives, inductive reasoning, and deductive reasoning. Examples and truth tables are provided to illustrate each term. Inductive reasoning moves from specific to general observations based on past experiences, while deductive reasoning moves from general rules or statements to specific conclusions.