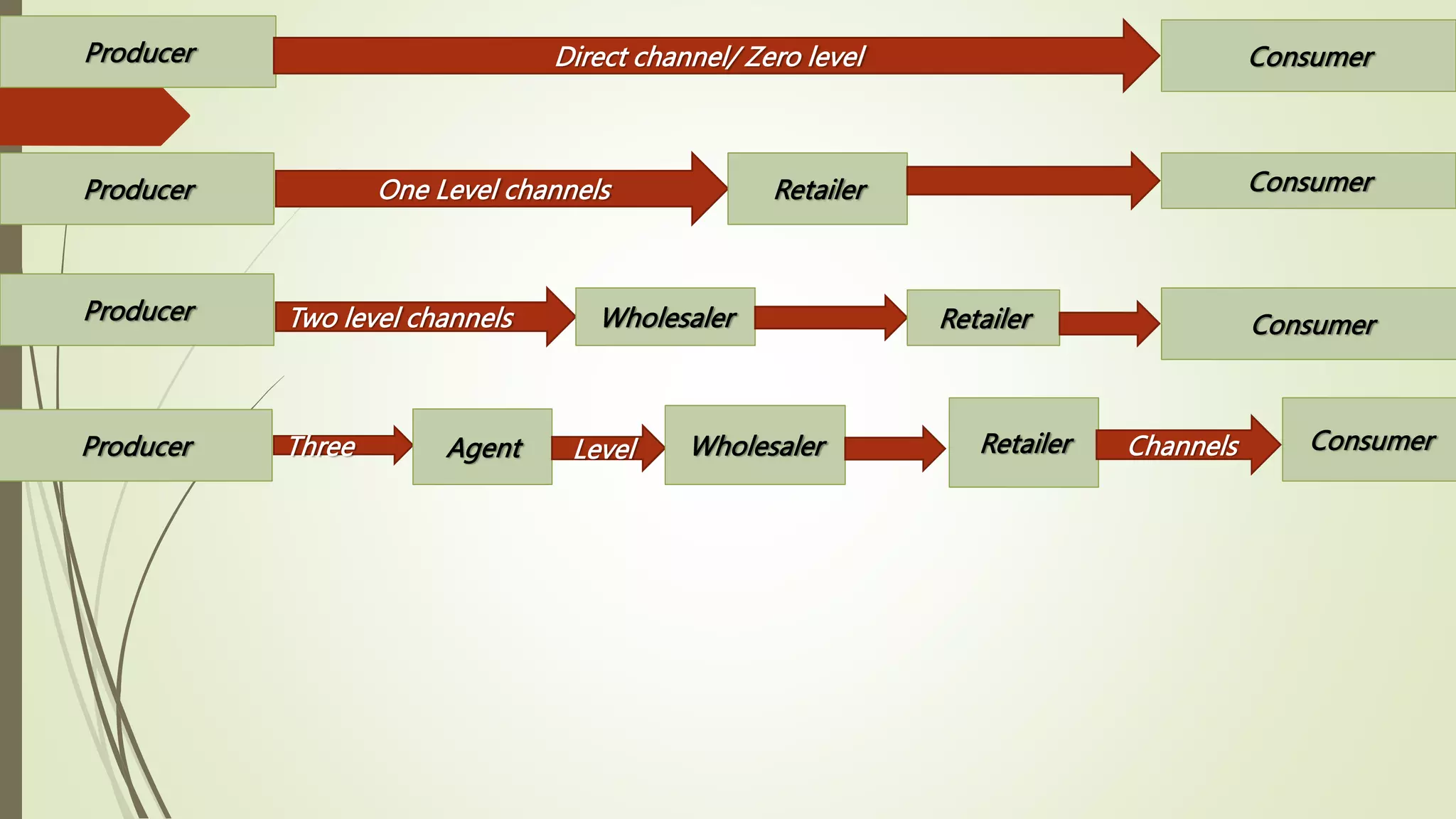
This document discusses marketing channels and intermediaries. It defines marketing channels and intermediaries like retailers and wholesalers. It also explains different types of marketing channels like direct, one level, two level, and three level channels. It describes various types of retailers like department stores, warehouse retailers, and convenience retailers. It also discusses types of wholesalers such as merchant, general, and specialty wholesalers.