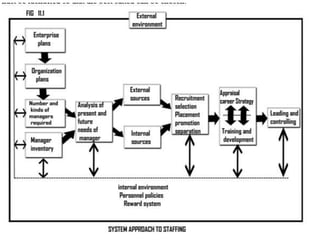
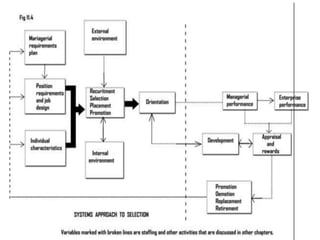
The document discusses staffing as a key managerial function that involves filling positions and developing current employees. It describes staffing as identifying workforce needs, recruiting and selecting candidates, and promoting development. An effective staffing system takes an open approach, considering both internal factors like policies and rewards as well as external factors like the availability of skilled workers. The document outlines the steps in staffing, including determining position requirements, identifying needed skills, matching qualifications to positions, selecting candidates, and orienting new employees.