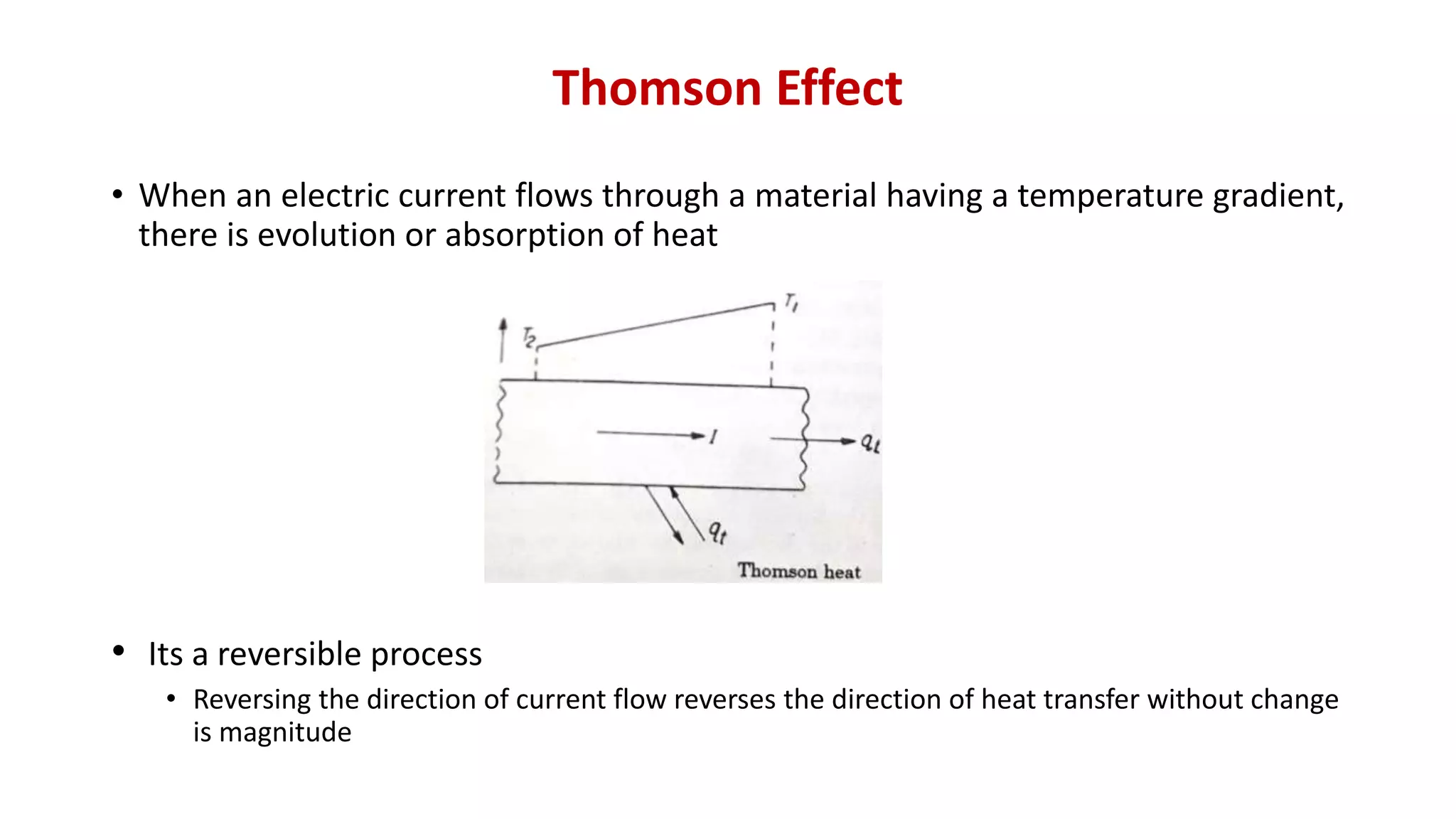
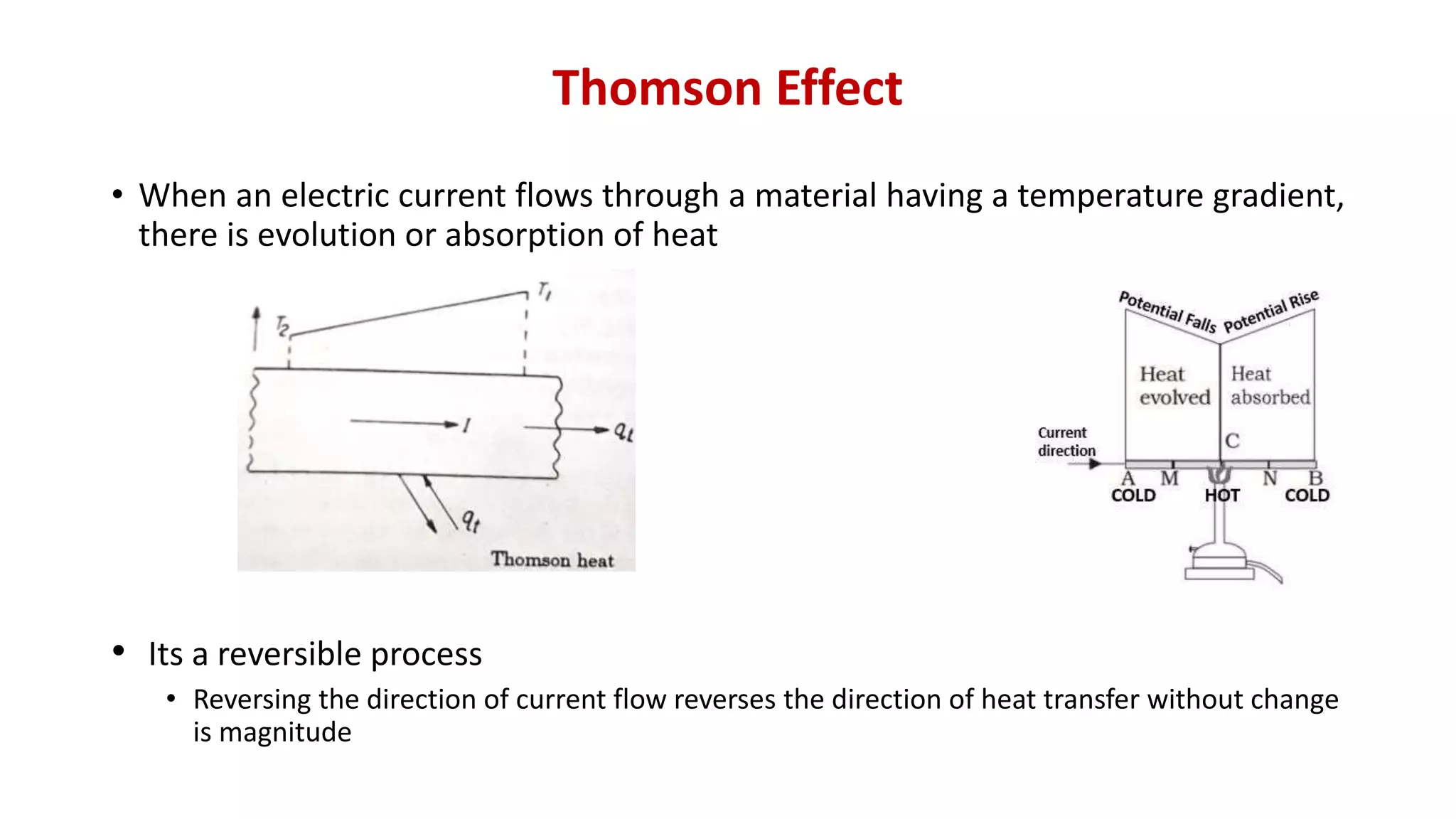
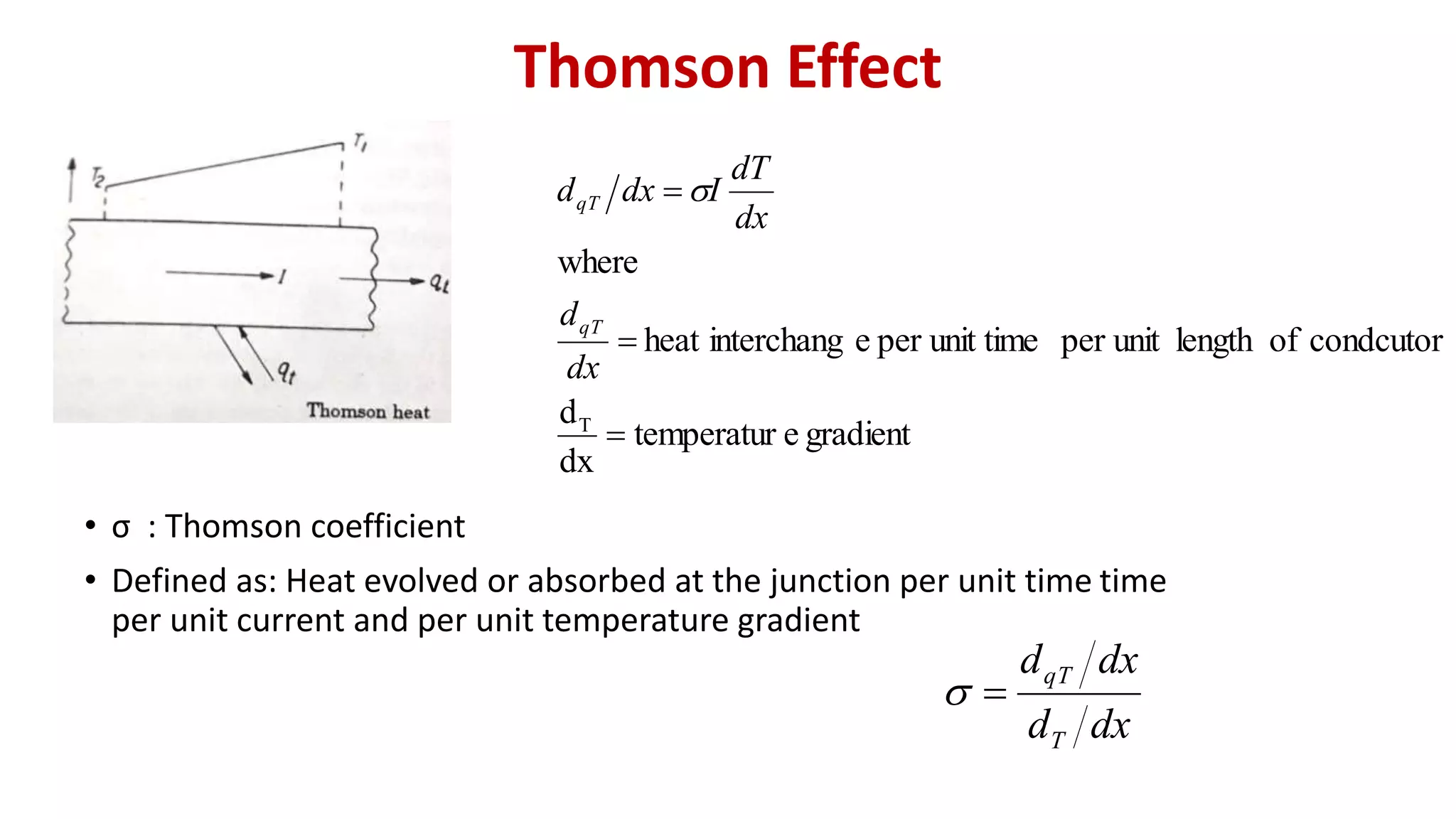
The document discusses direct energy conversion principles, focusing on thermoelectric generators and related effects such as the Seebeck, Peltier, and Thomson effects. It explains how temperature differences can create electric potential and vice versa, as well as the construction and functioning of thermoelectric devices. Basic thermocouple configurations and laws are also briefly described, emphasizing their role in thermoelectric applications.