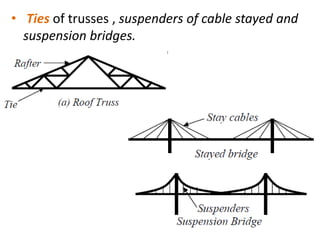
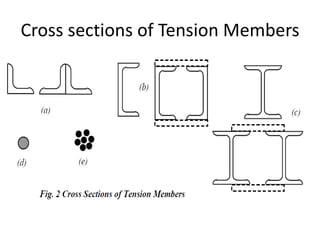
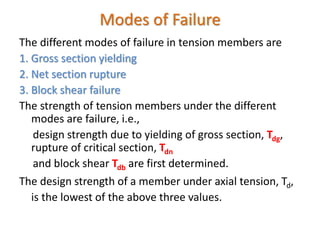
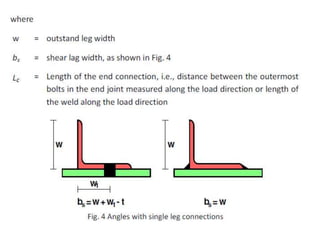
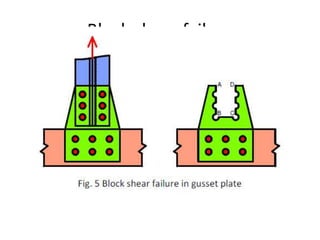
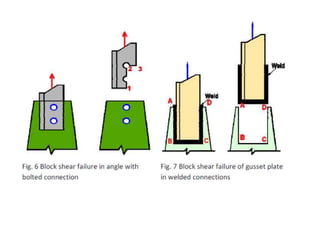
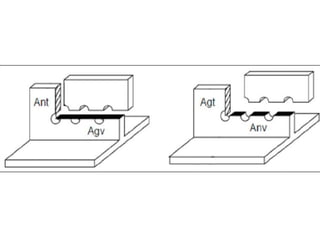
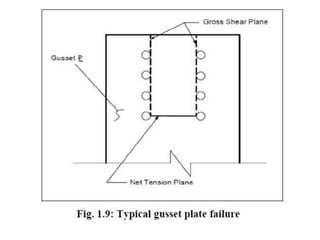
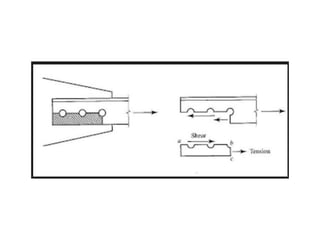
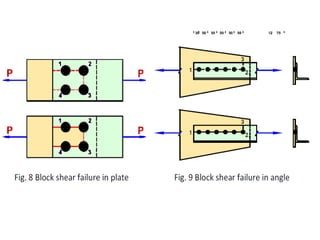
Tension members are structural elements that are designed to carry axial tensile loads. They experience stretching forces that subject their entire cross-section to uniform stress. Common examples include ropes, ties in trusses, and suspenders in bridges. Tension members are most efficient load carriers. They are susceptible to three potential failure modes: gross section yielding, net section rupture, and block shear failure. The design strength of a tension member is the lowest value of its strength under these three failure modes.