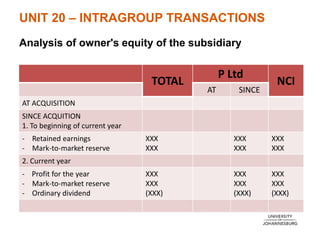
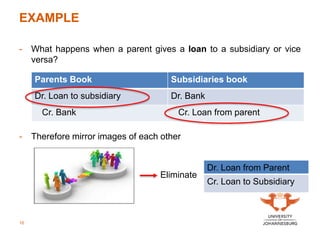
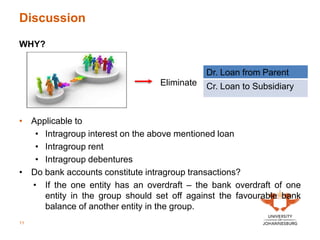
The document outlines consultation times and key learning outcomes for Unit 20 on intragroup transactions, focusing on consolidation journal entries, financial statements, and tax allocations related to such transactions. It emphasizes the importance of understanding unrealized profits within group financial reports and the elimination of these profits during consolidation. Various examples and discussions are provided to illustrate intragroup transactions, their effects on financial statements, and methods for addressing these in reporting.