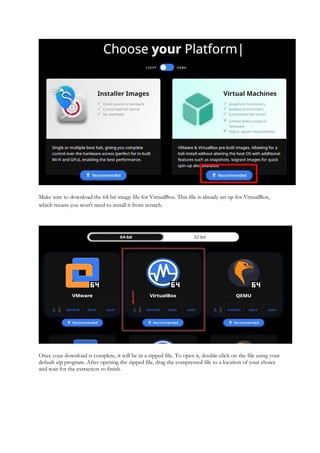
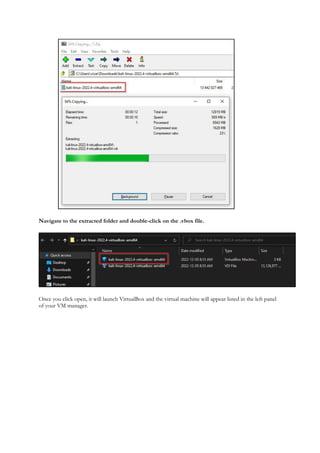
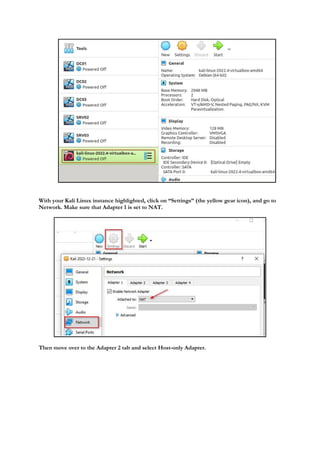
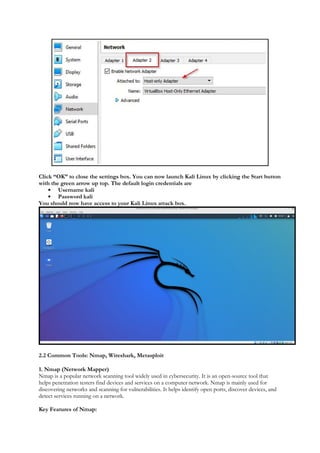
1.1 Virtual Machines and Labs for Ethical Hacking
1.2 Common Tools: Nmap, Wireshark, Metasploit
1.3 Kali Linux Overview
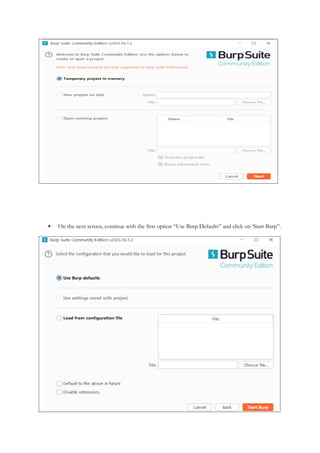
1.4 Introduction to Burp Suite
1.5 Core Tools in Burp Suite (Proxy, Target, Scanner, Repeater, Intruder, Decoder,
Comparer, Sequencer)
1.6 Setting Up and Configurations