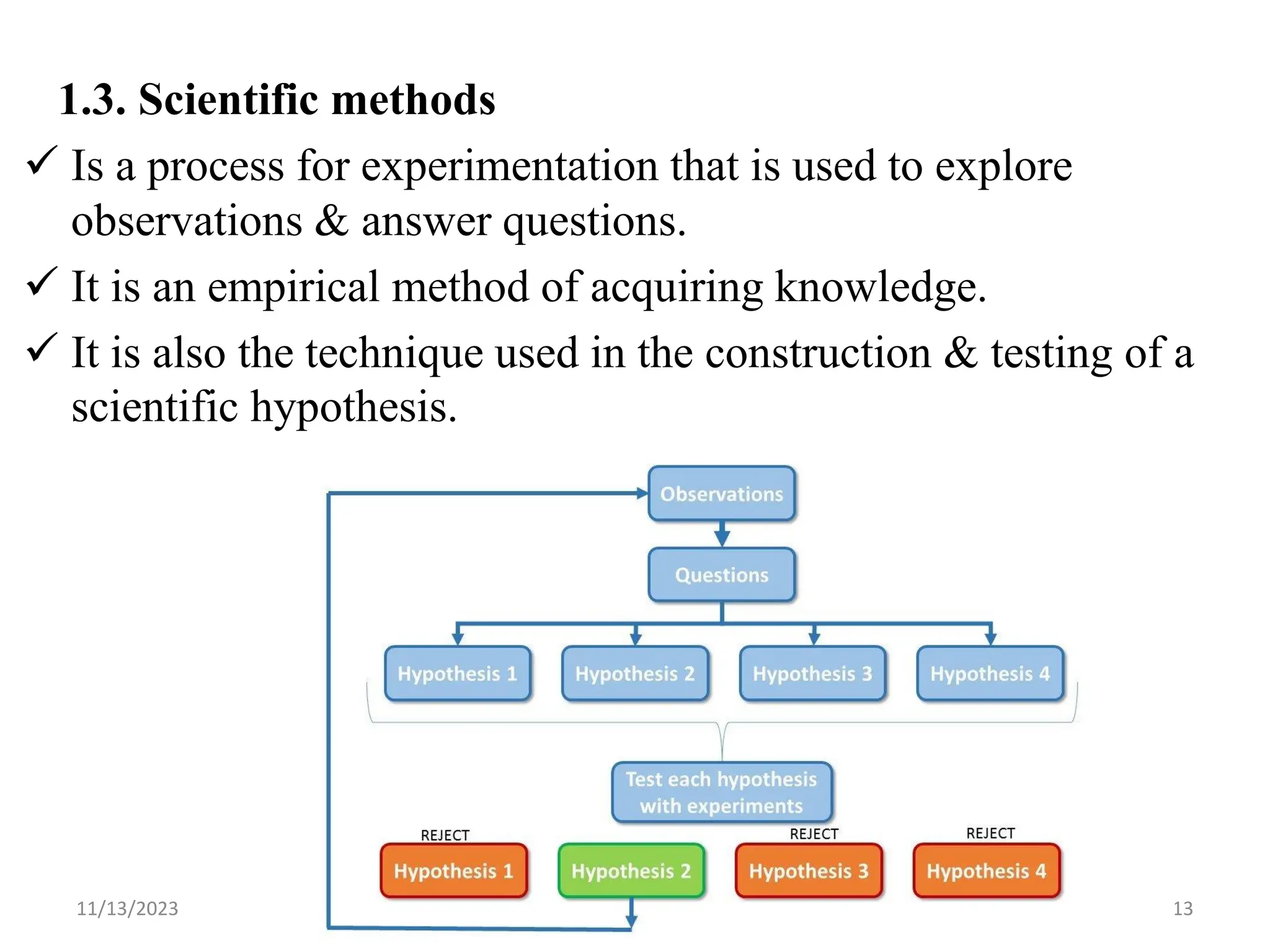
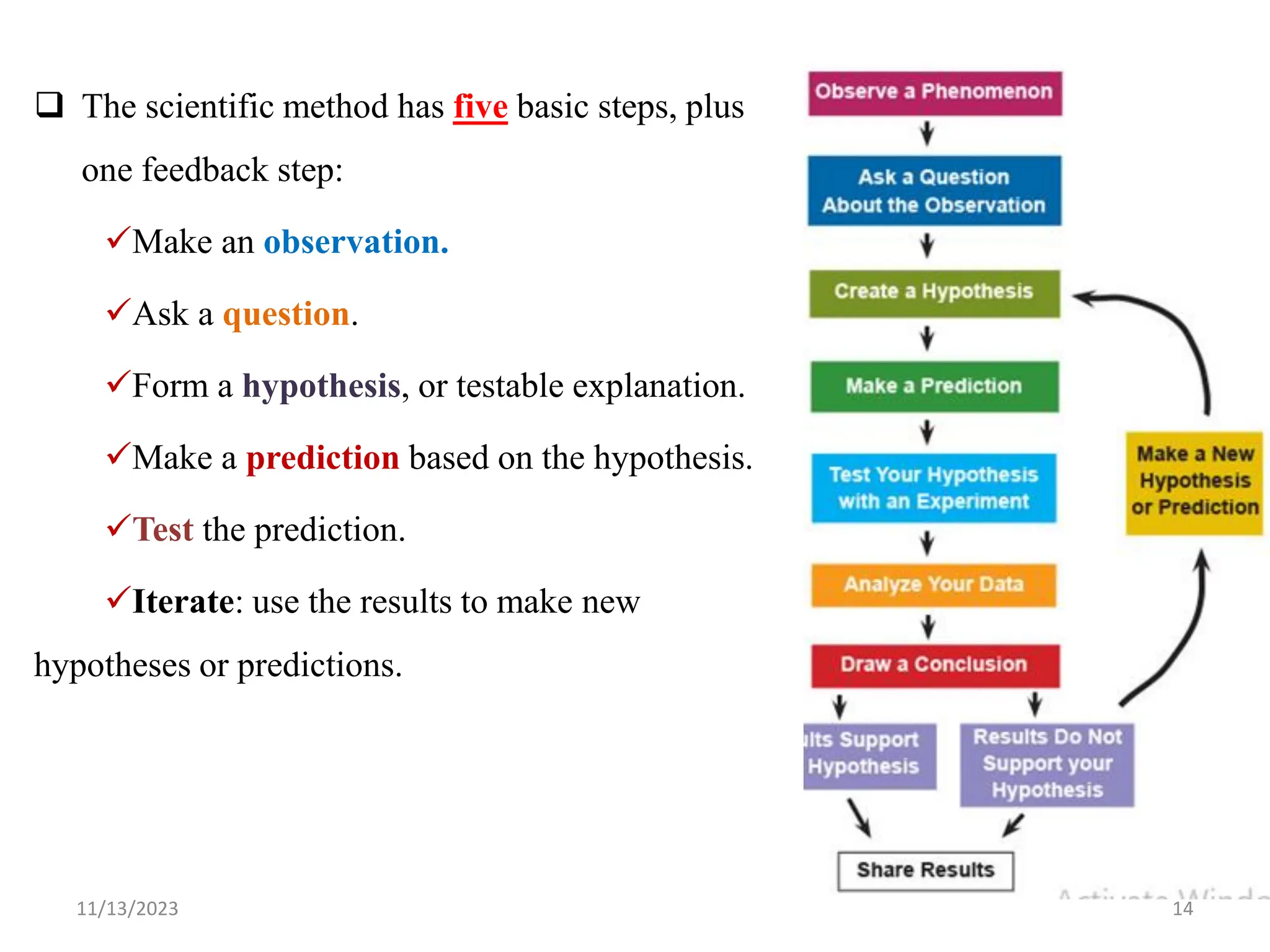
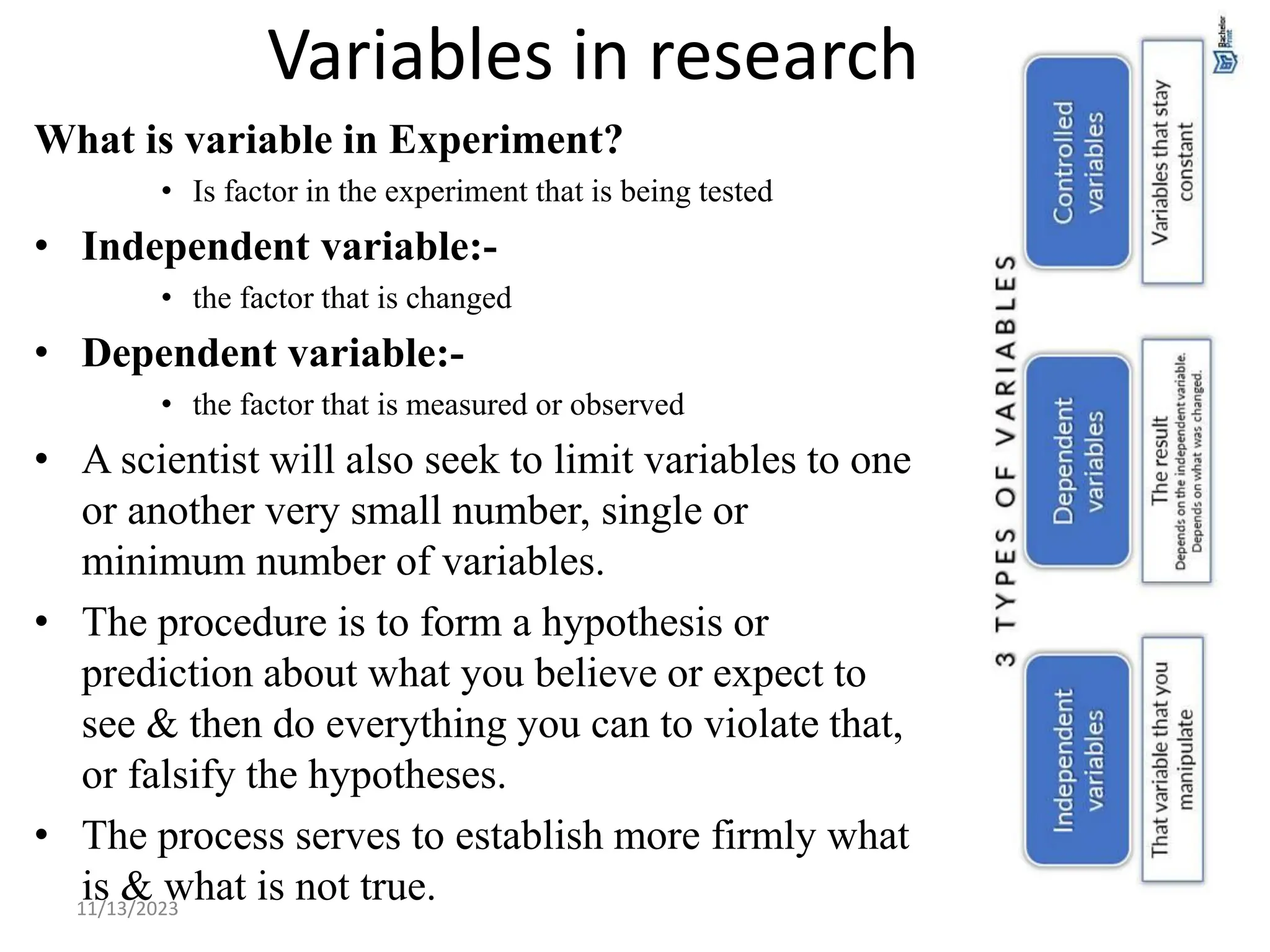
The document outlines the basics of biology, defining it as the study of life and living organisms. It discusses various theories regarding the origin of life, such as special creation and spontaneous generation, and presents the scientific method as a structured approach to inquiry. Key components of life are mentioned, including characteristics and processes common to living things.