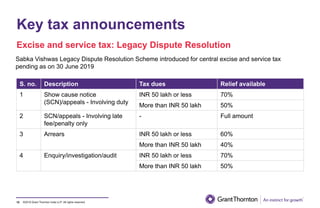
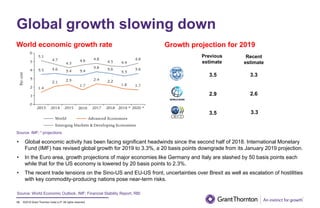
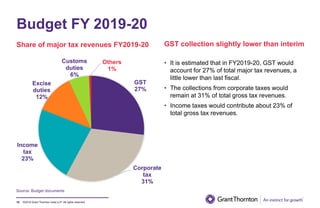
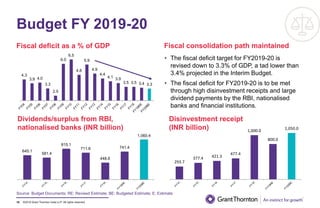
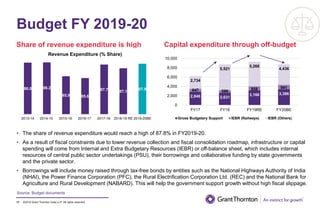
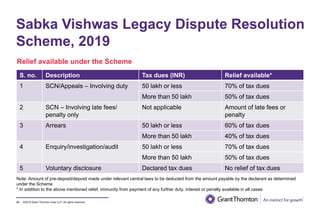
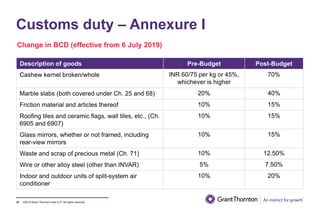
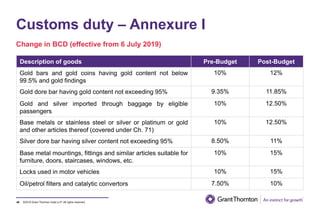
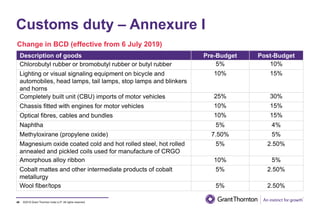
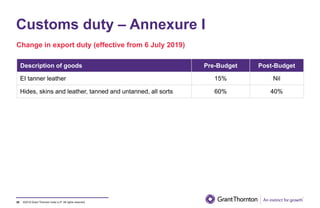
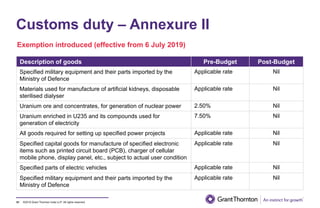
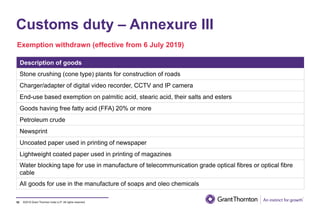
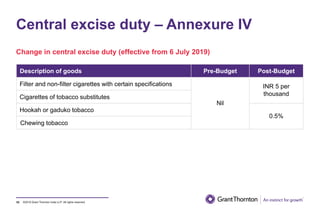
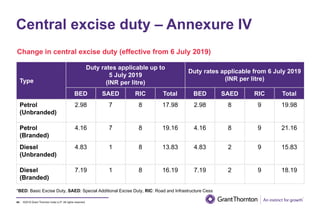
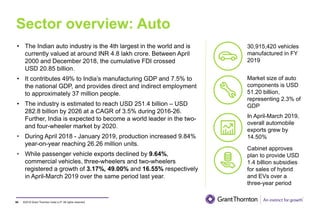
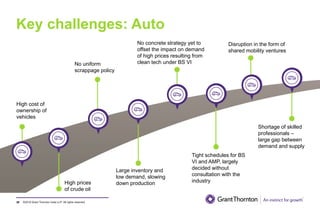
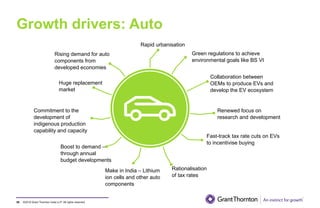
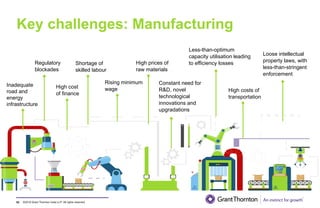
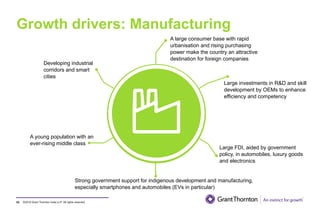
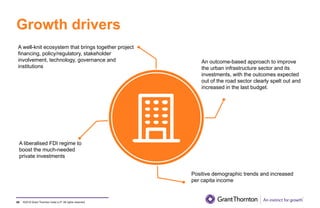
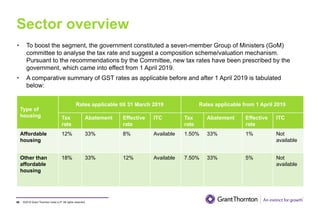
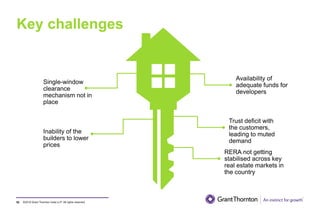
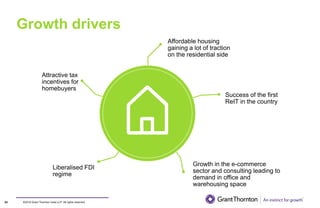
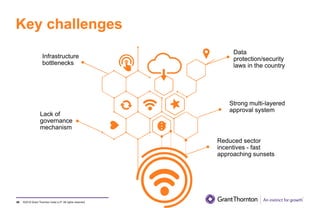
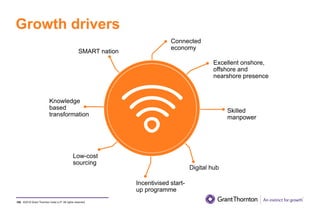
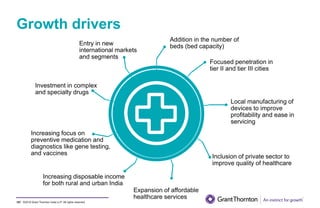
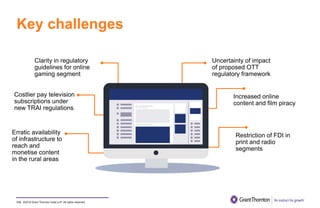
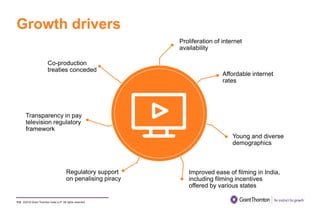
The document provides an executive summary and analysis of the Union Budget of India for fiscal year 2019-20. It highlights key policy announcements, tax proposals, and sectoral impacts. The budget aims to make India a $5 trillion economy by 2024-25 through measures to boost infrastructure, ease of doing business, and rural development. It lowers the fiscal deficit target to 3.3% of GDP and outlines plans to raise revenues through privatization and dividends from public sector companies.