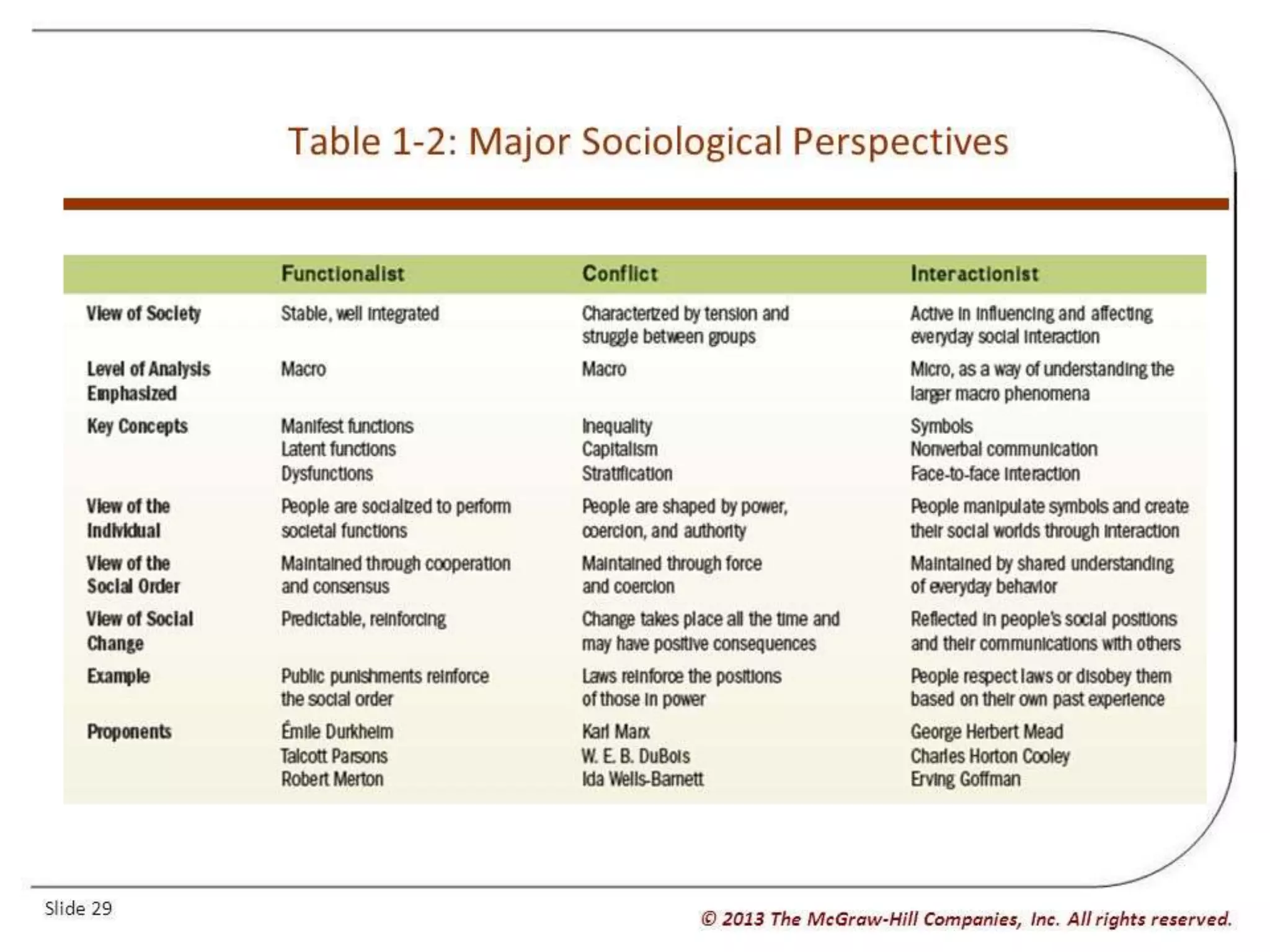
This document provides an overview of sociology, discussing its key concepts and early influential thinkers. It defines sociology as the scientific study of social behavior and human groups, focusing on social relationships and how societies develop and change. It describes the sociological imagination and distinguishes sociology as a social science. The document then profiles influential early sociologists like Comte, Martineau, Spencer, Durkheim, Weber, Marx, DuBois, and Cooley and their major contributions to establishing sociology as a discipline.









![Harriet Martineau
Scholars learned of Comte’s works largely
through translations by the English sociologist
Harriet Martineau (1802–1876).
She offered insightful observations of the customs
and social practices of both her native Britain and
the United States.
Martineau’s book Society in America ([1837]
1962) examined religion, politics, child rearing,
and immigration in the young nation. It gave
special attention to social class distinctions and to
such factors as gender and race.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingsociologychapter01-170604105152/75/Understanding-sociology-chapter01-10-2048.jpg)

![ She spoke out in favor of the rights of women,
the emancipation of slaves, and religious
tolerance. Later in life, deafness did not keep
her from being an activist.
In Martineau’s ([1837] 1962) view, intellectuals
and scholars should not simply offer
observations of social conditions; they should
act on their convictions in a manner that will
benefit society.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingsociologychapter01-170604105152/75/Understanding-sociology-chapter01-12-2048.jpg)









![W. E. B. DuBois
Marx’s work encouraged sociologists to view society through
the eyes of those segments of the population that rarely
influence decision making.
In the United States, some early Black sociologists, including
W. E. B. DuBois (1868–1963), conducted research that they
hoped would assist in the struggle for a racially egalitarian
society.
DuBois believed that knowledge was essential in combating
prejudice and achieving tolerance and justice.
Sociologists, he contended, needed to draw on scientific
principles to study social problems such as those
experienced by Blacks in the United States. To separate
opinion from fact, he advocated basic research on the lives of
Blacks. Through his in-depth studies of urban life, both White
and Black, in cities such as Philadelphia and Atlanta, DuBois
([1899] 1995) made a major contribution to sociology.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingsociologychapter01-170604105152/75/Understanding-sociology-chapter01-23-2048.jpg)