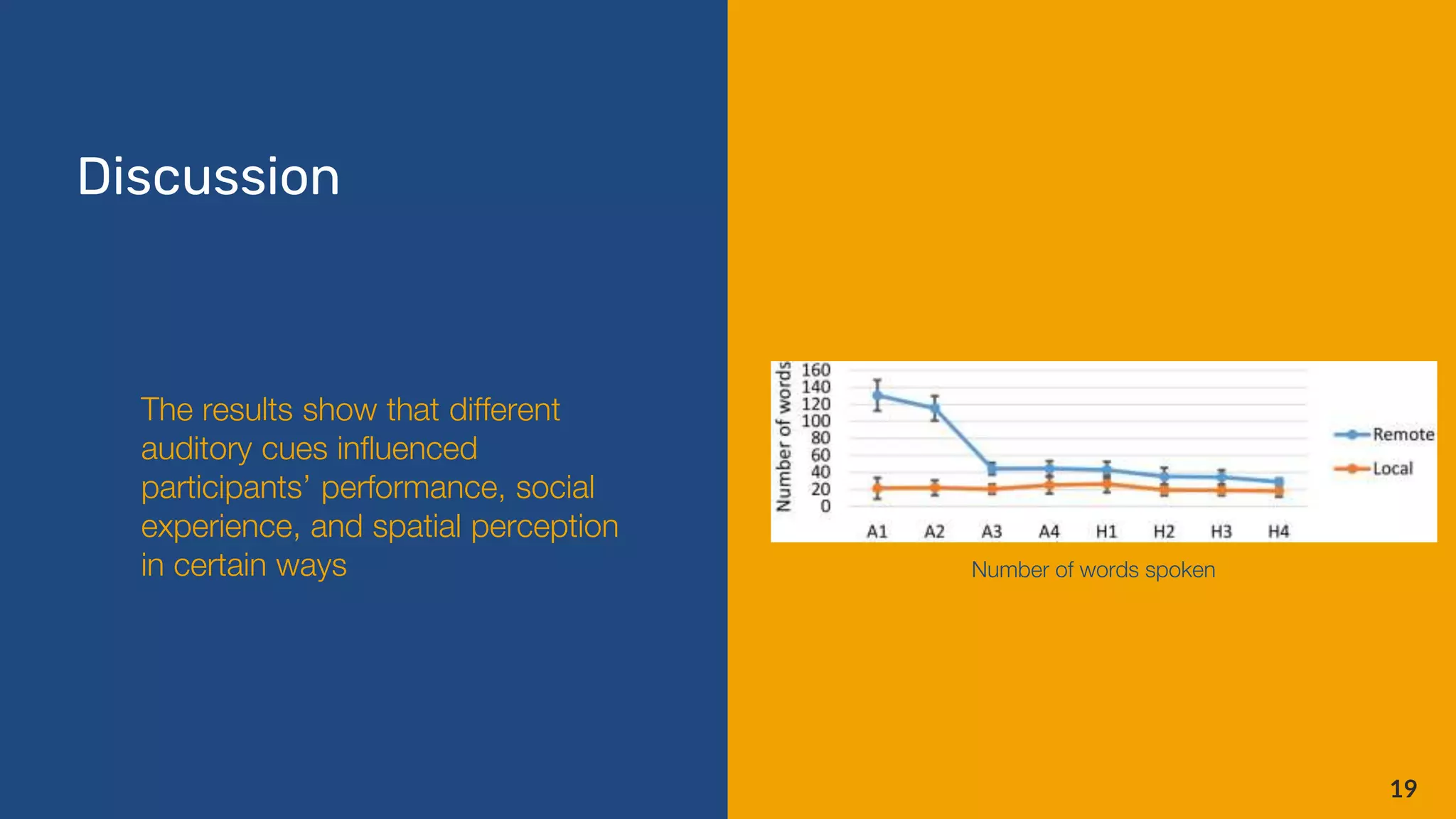
This document describes research into using spatial audio and visual cues to enhance remote collaboration. It discusses prior work exploring spatialized audio and video calls. Two user studies were conducted to test how spatialized voice, auditory beacons, hand gestures, and seeing the remote helper's field of view impacted collaboration on an object search task. The results showed that spatial audio cues helped guide the task and increased social presence, while adding visual cues further improved performance and workload. The research demonstrates the potential for spatial audio and visuals to augment remote collaboration.