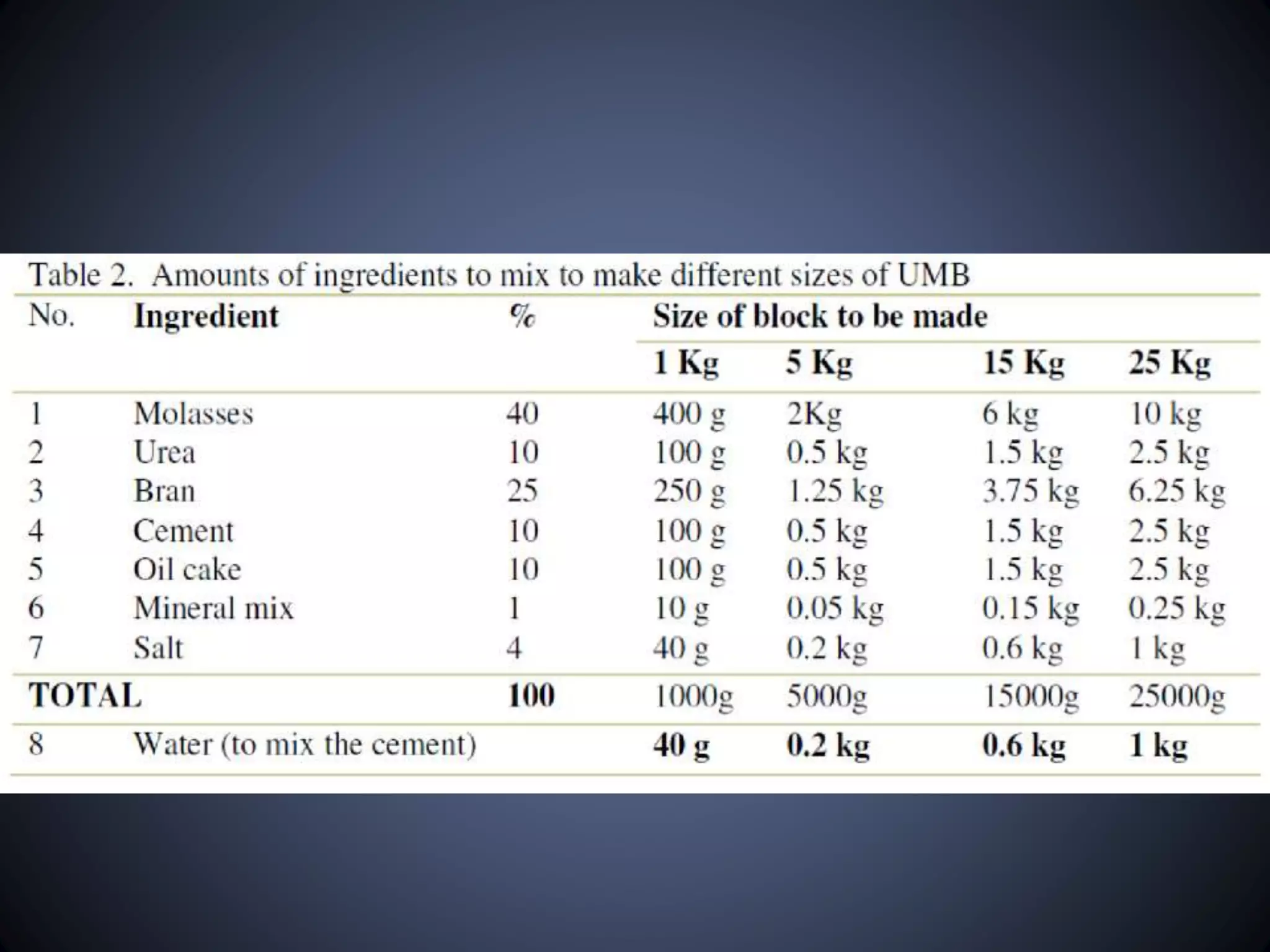
The document discusses Urea Molasses Blocks (UMB), which are supplements that can increase the digestibility and nutrient intake of fibrous feeds for animals. UMB are made from a mixture of molasses, urea, cereal bran, salt, and cement. They provide protein, energy, vitamins, and minerals to animals. Proper mixing, molding, and drying techniques are required to produce high quality blocks that animals will consume safely and in appropriate amounts to benefit their nutrition and productivity.