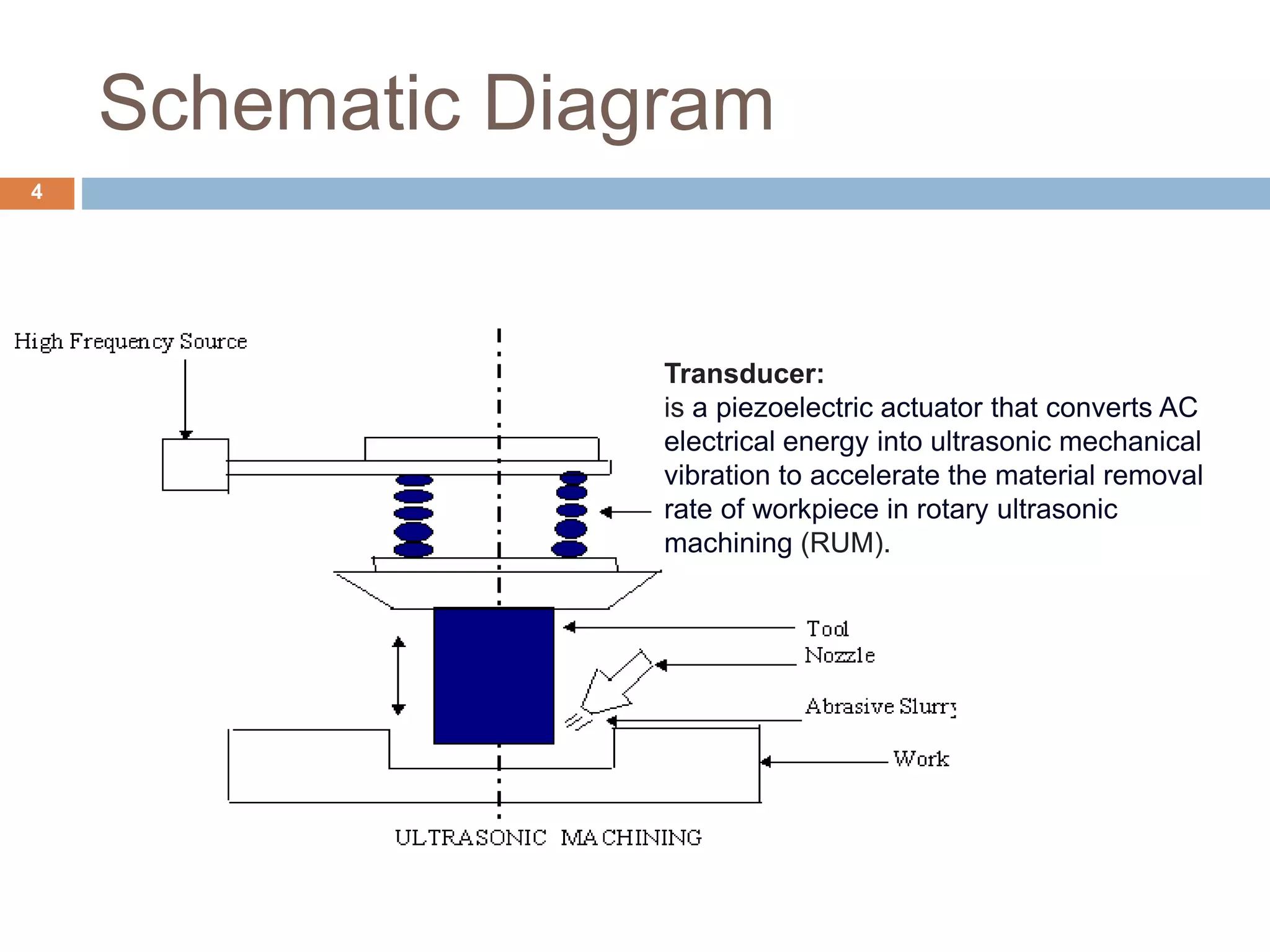
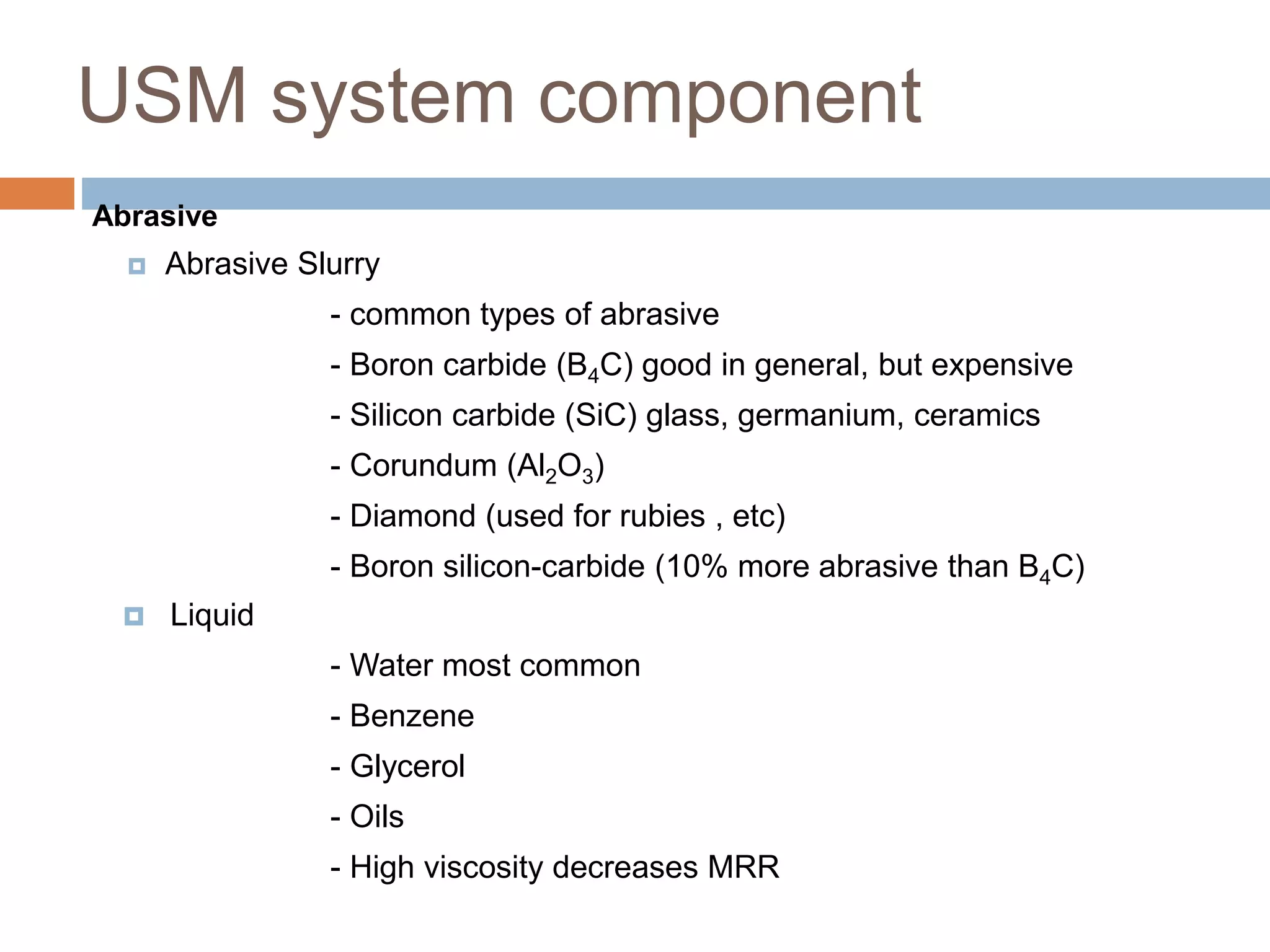
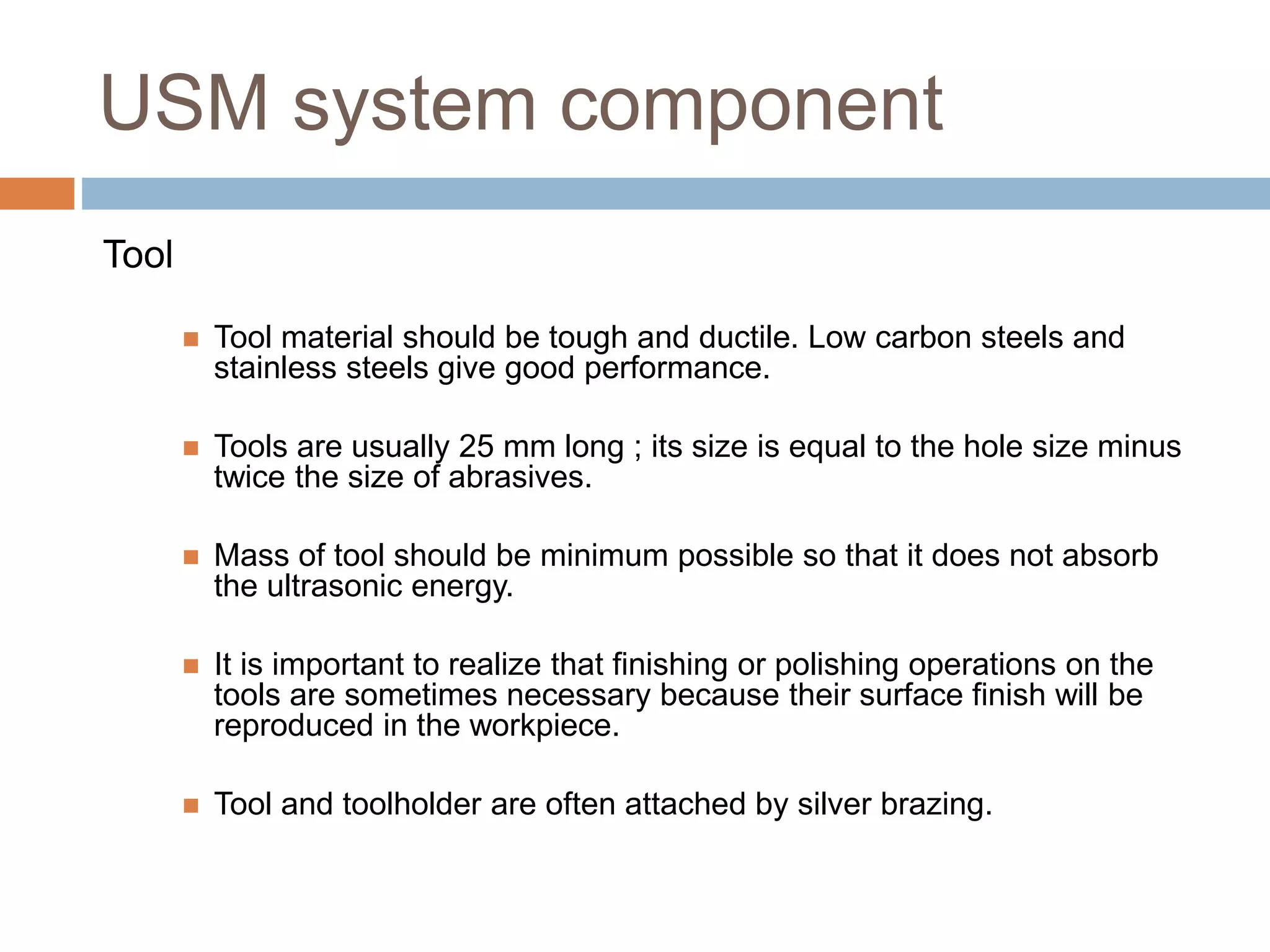
Ultrasonic machining is a non-traditional machining process that uses tools vibrating at ultrasonic frequencies (above 20 kHz) and an abrasive slurry to erode material from hard or brittle workpieces. A transducer converts electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical vibrations, causing the tool and abrasive particles to impact the workpiece and generate microcracks and brittle fracture, removing small particles. Key components of an USM system include a power supply, transducer, tool, abrasive slurry, and process parameters like vibration amplitude and frequency, feed force, abrasive size and concentration. USM is used to drill holes, grind, profile and machine hard materials like carbides and