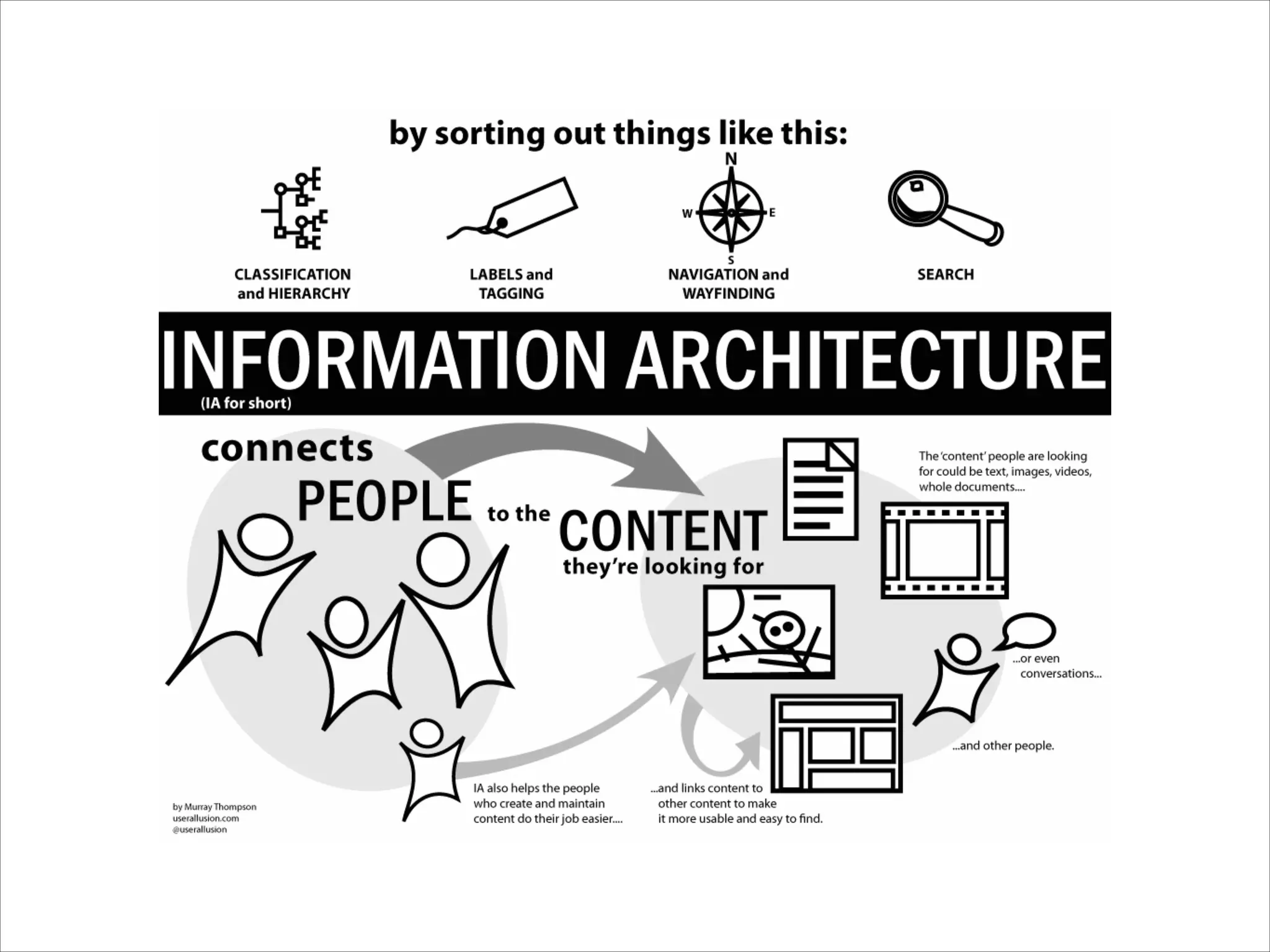
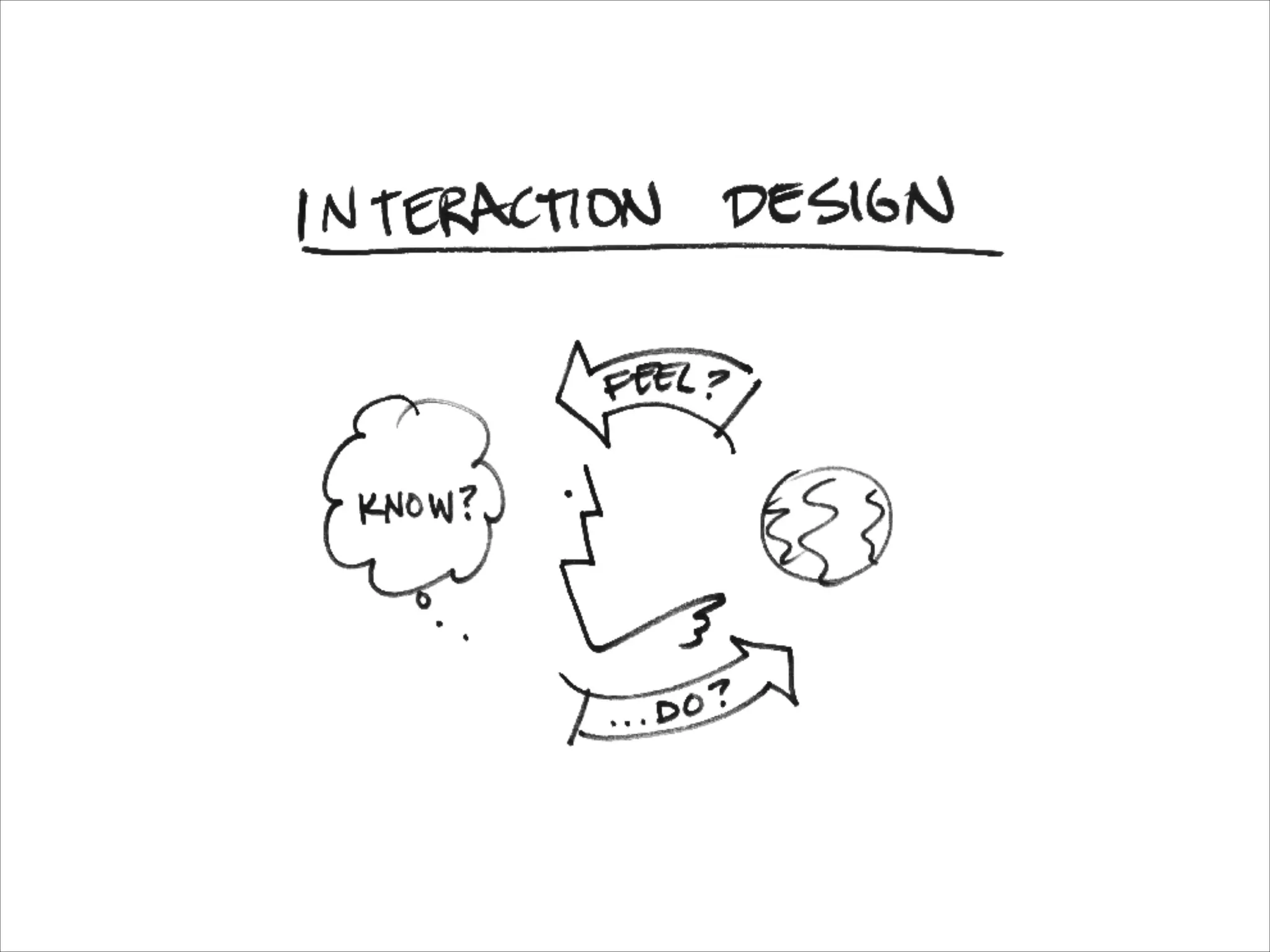
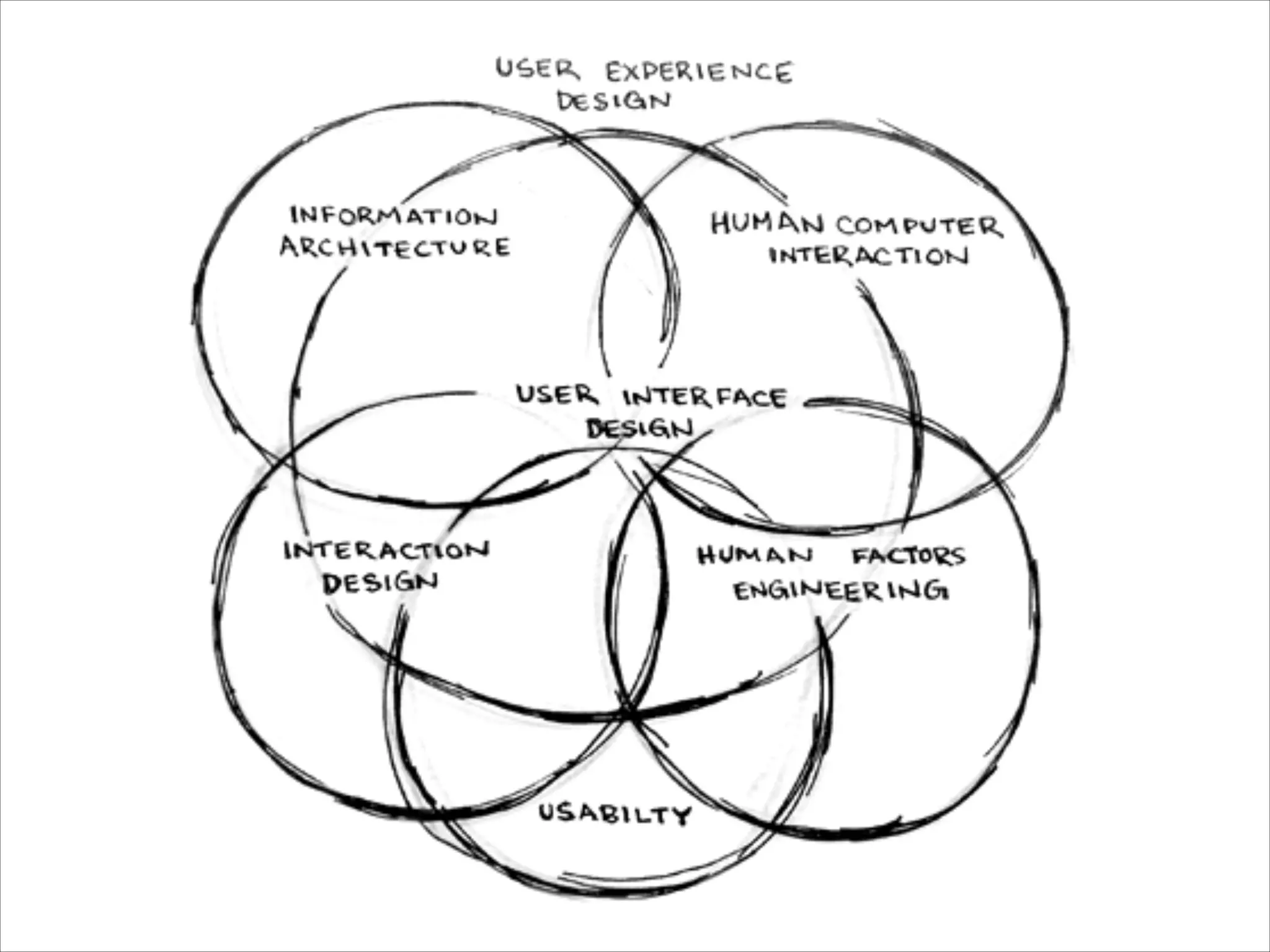
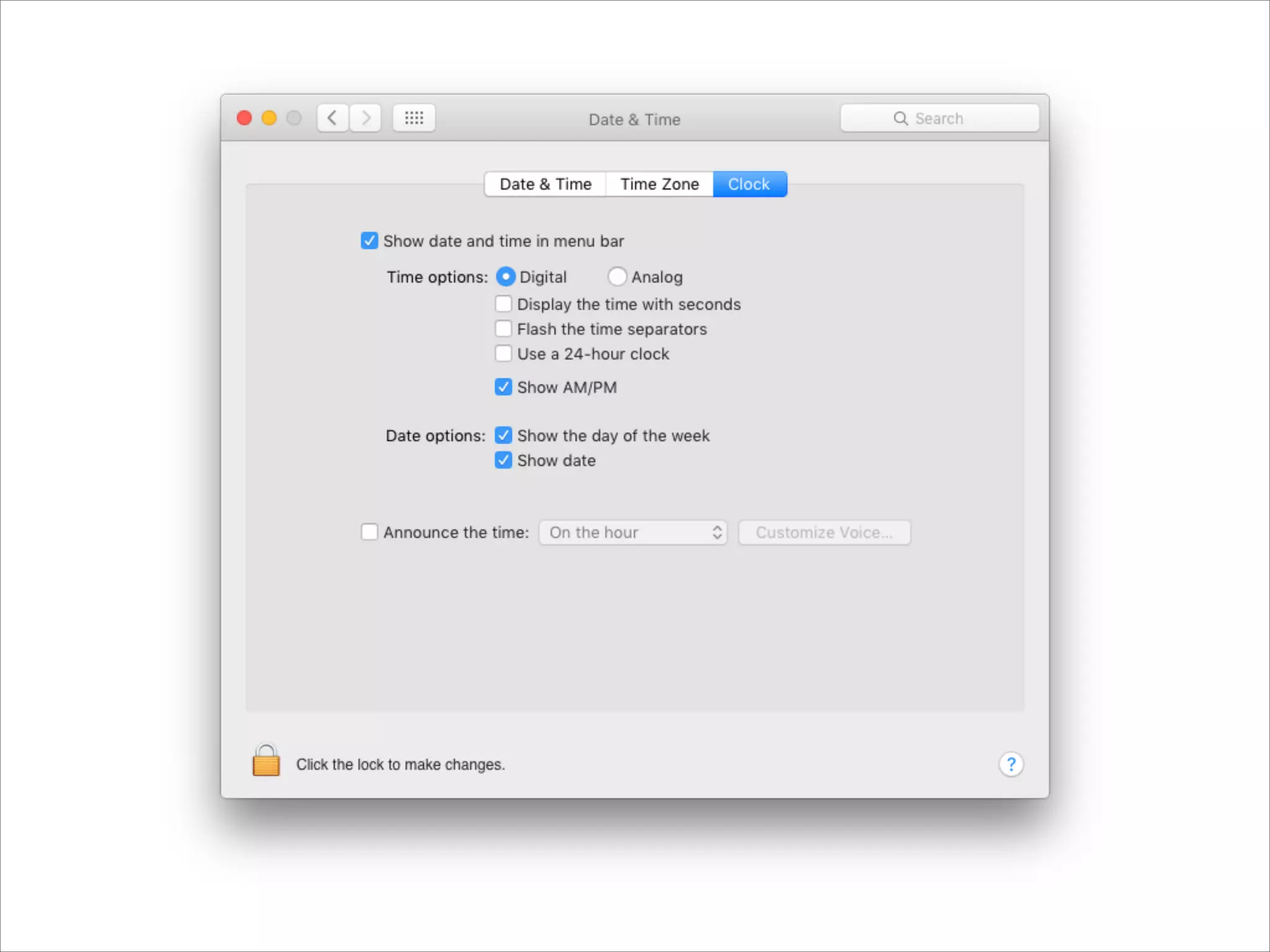
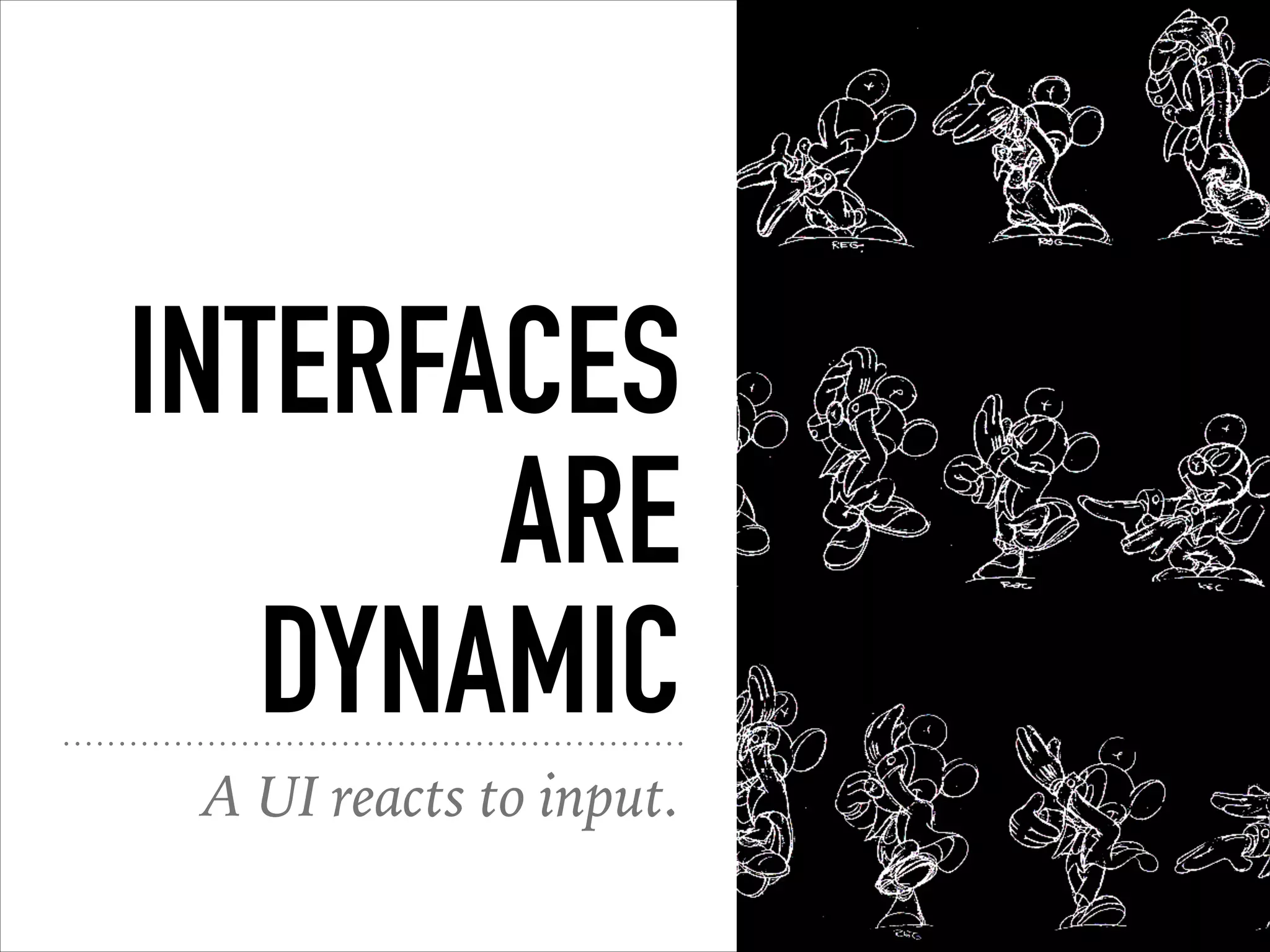
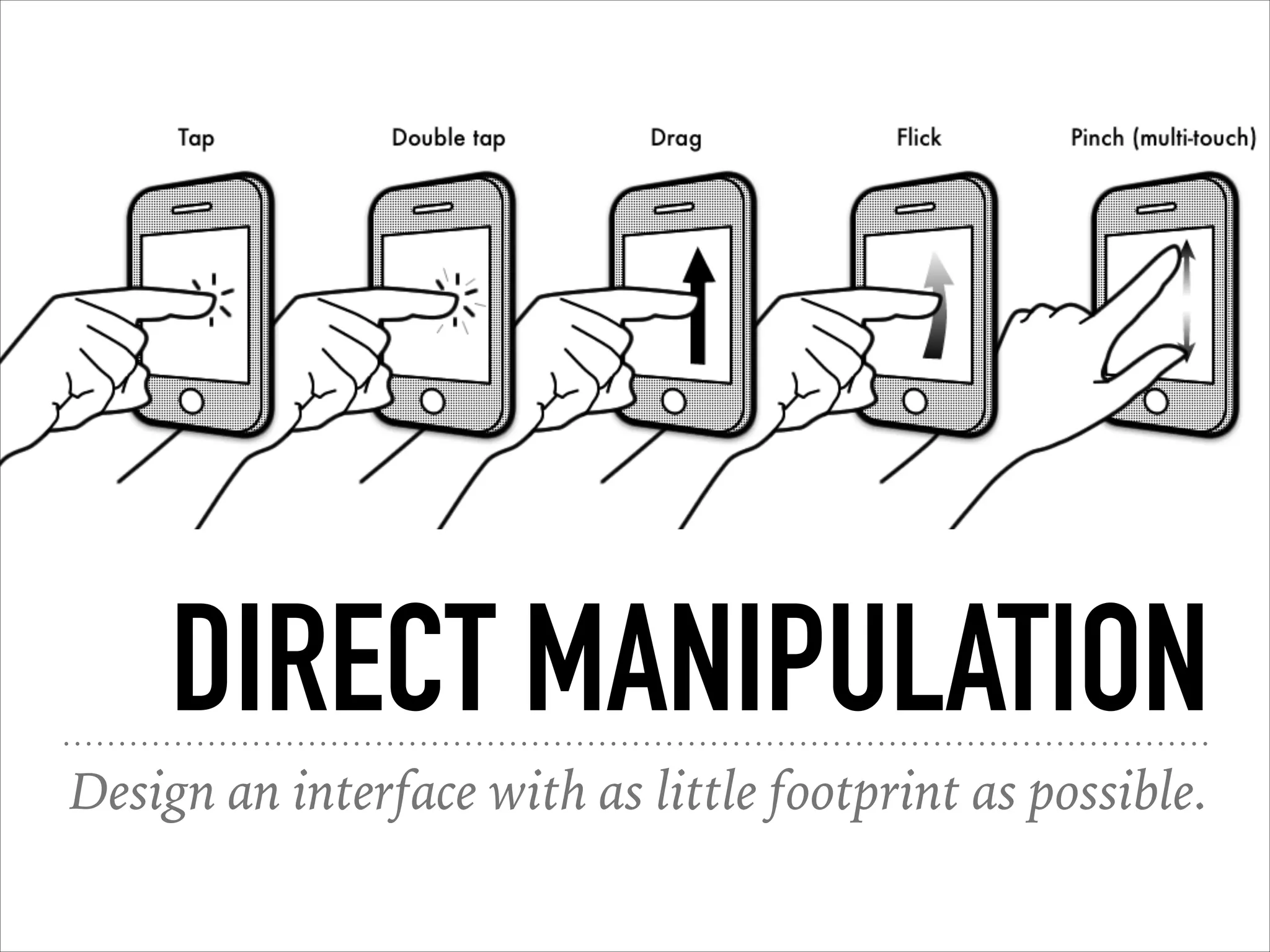
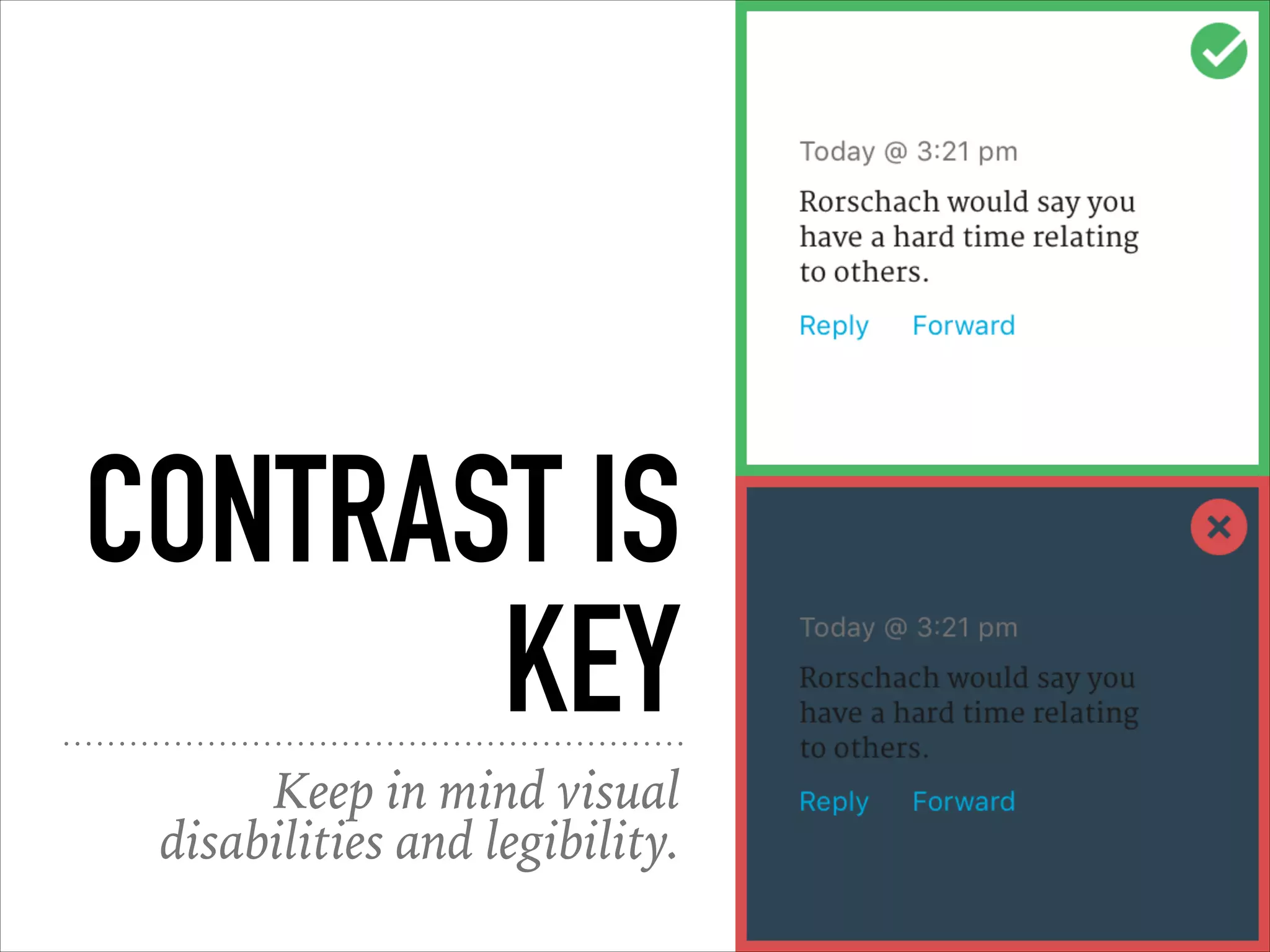
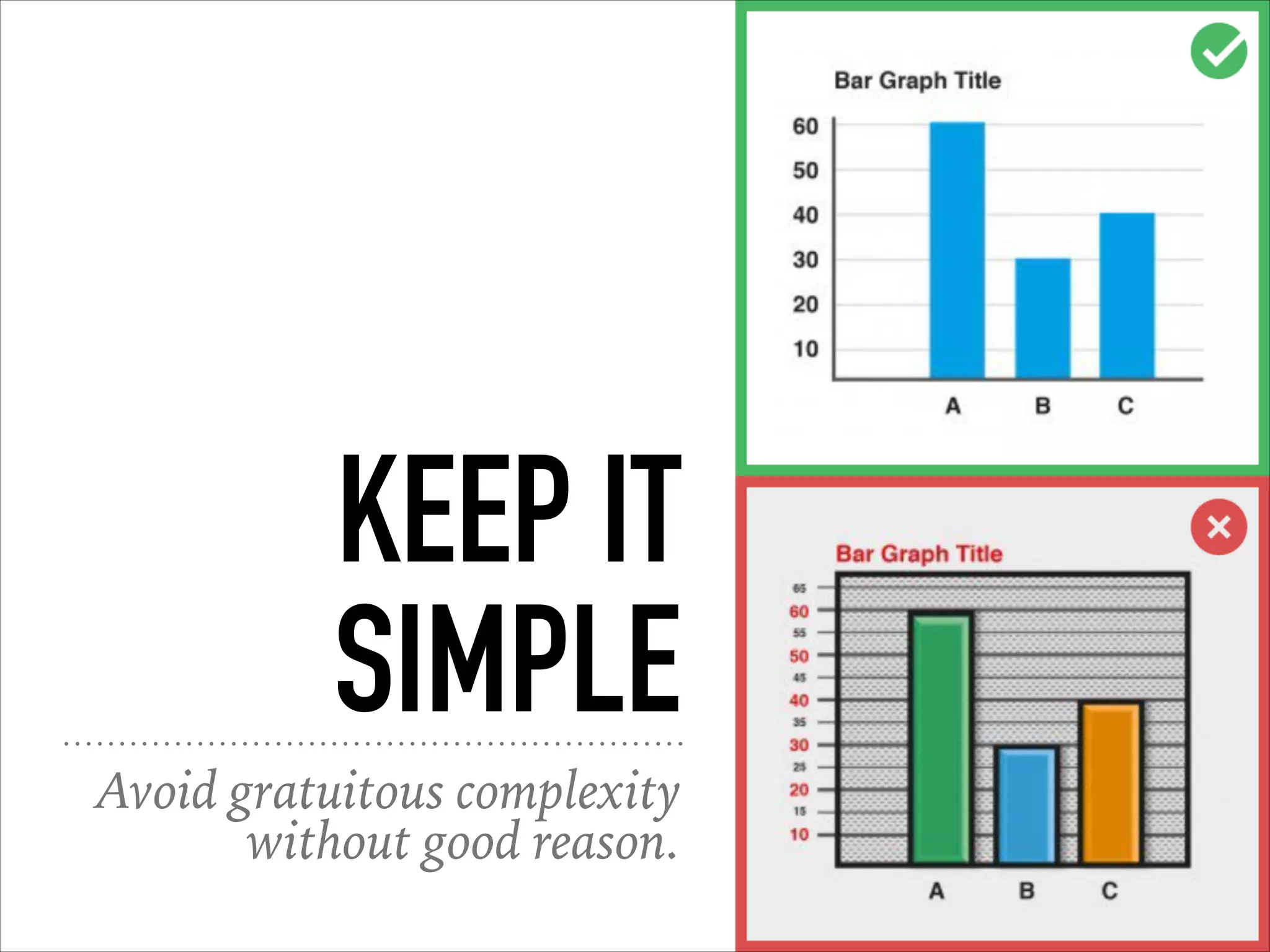
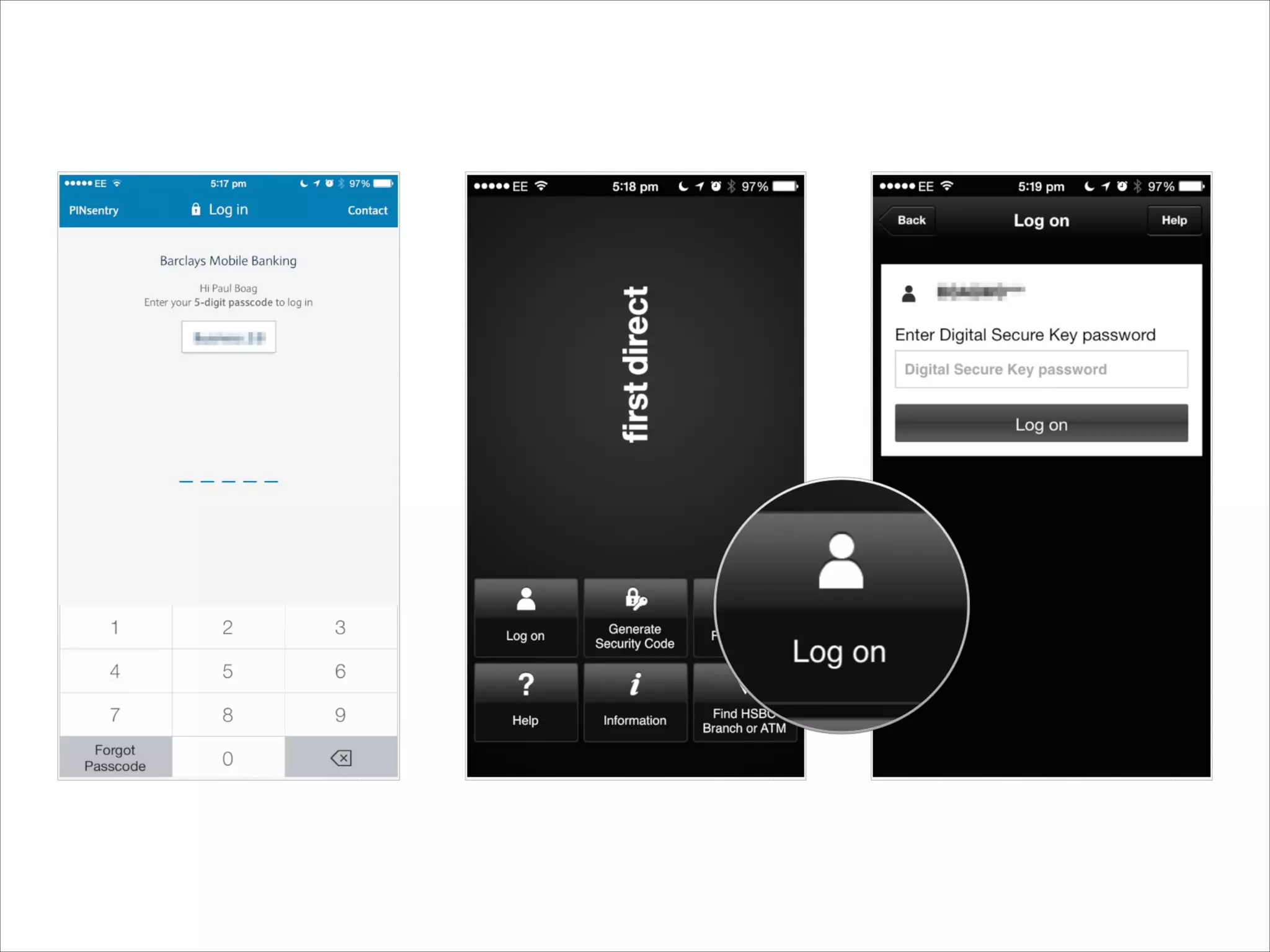
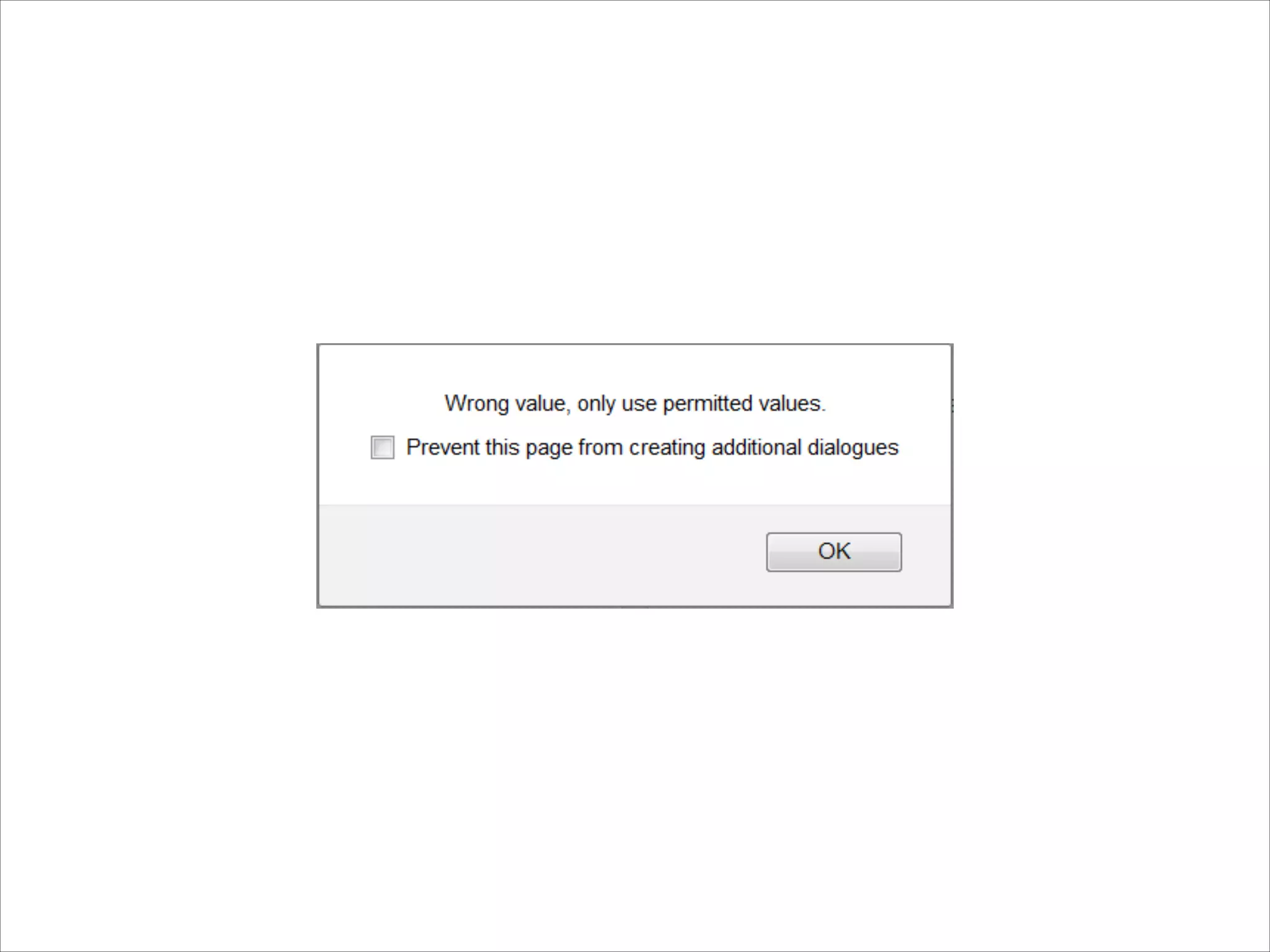
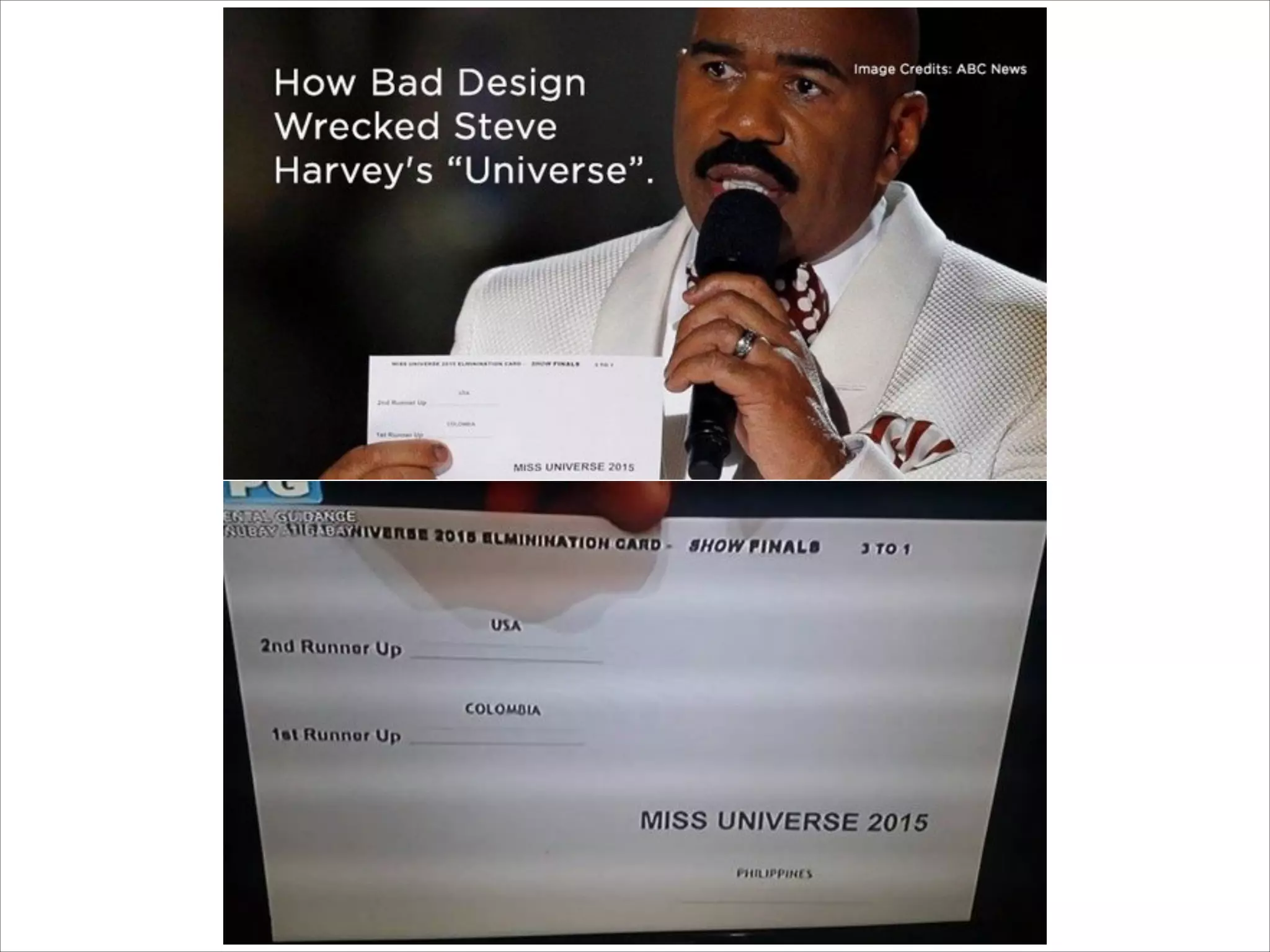
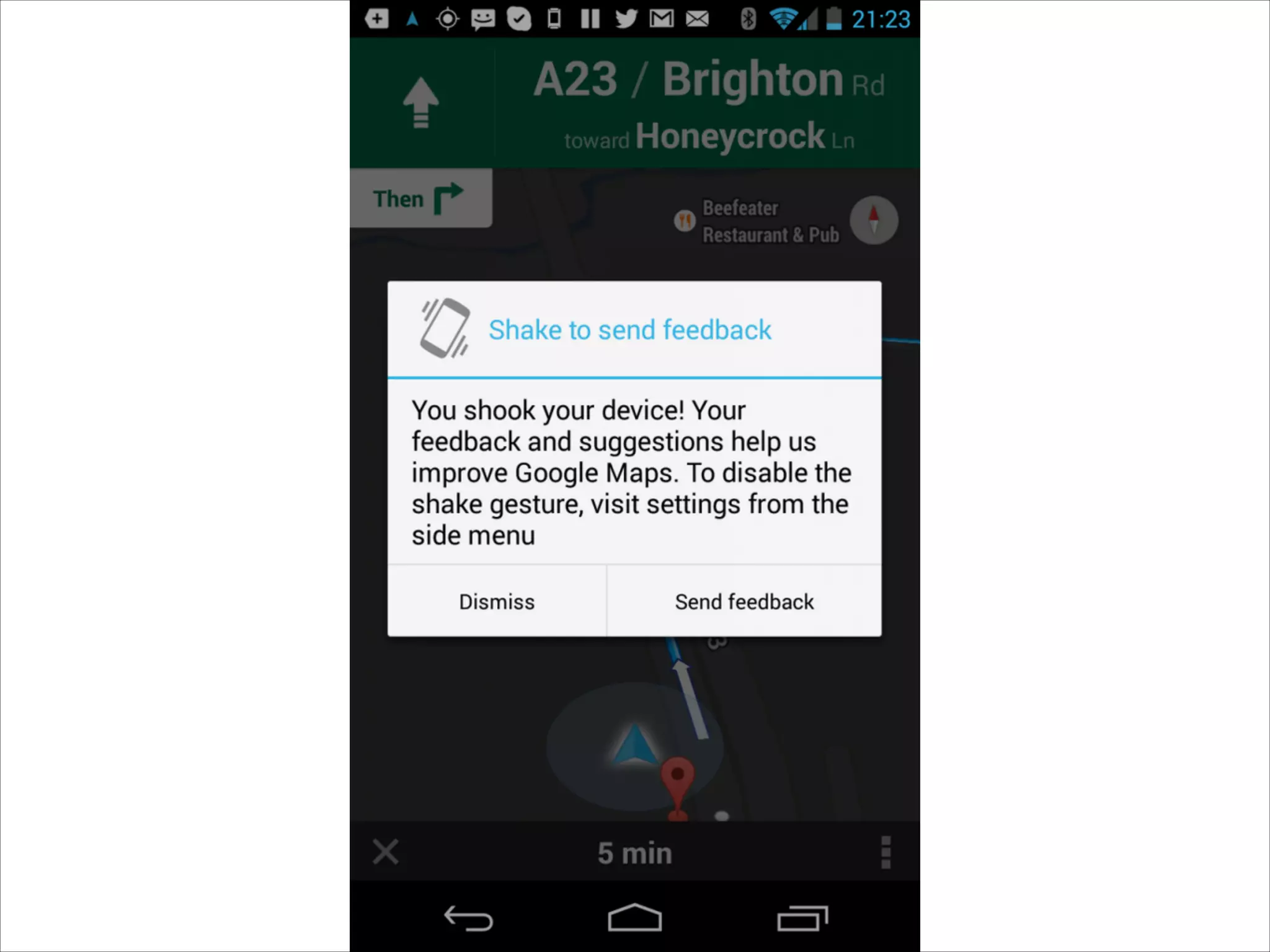
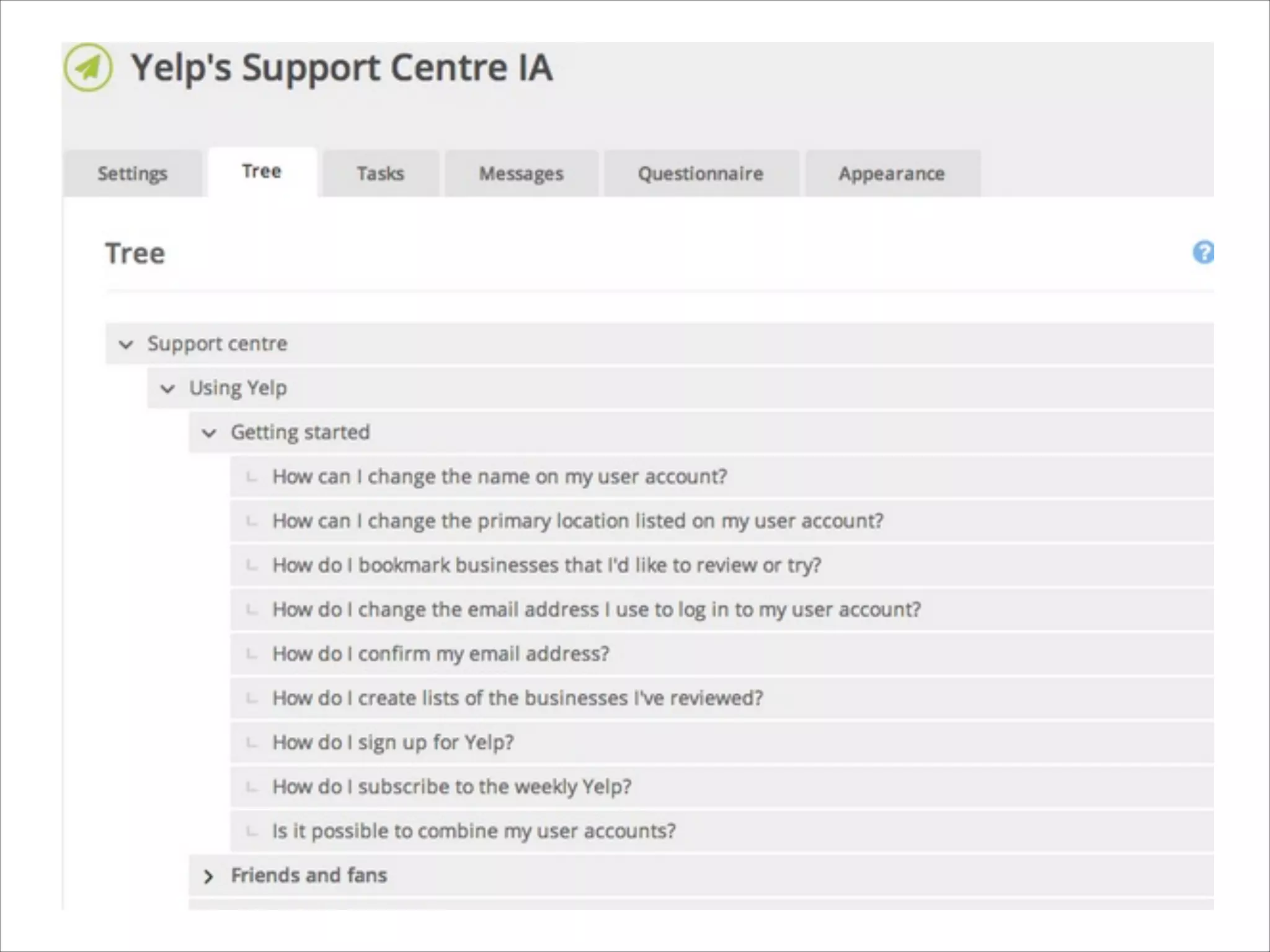
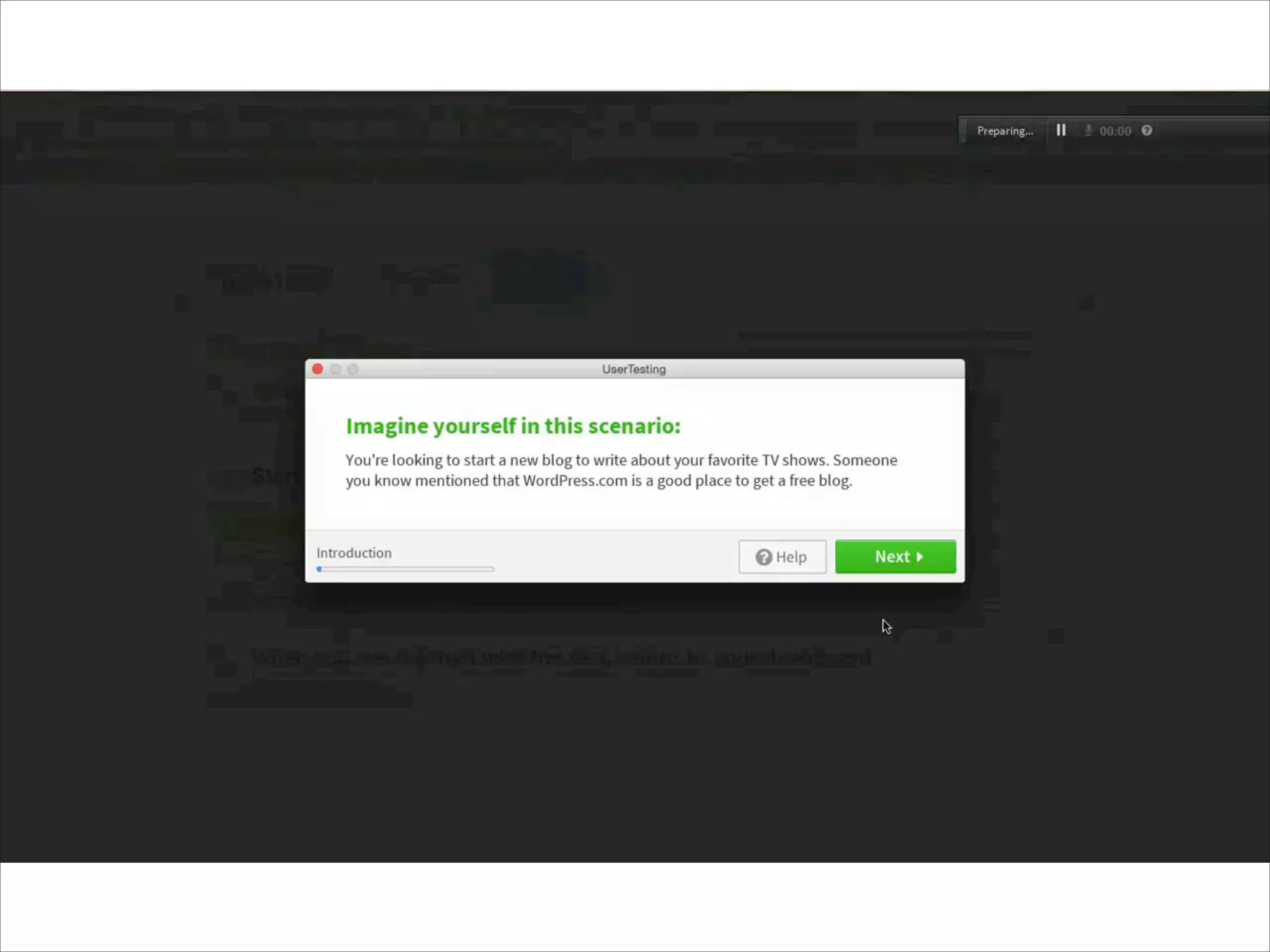
This document provides an overview of UI design basics. It discusses various aspects of UI design like user experience design, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design. It outlines some key principles for designing interfaces, such as making interfaces obvious, consistent, dynamic, conserve attention, allow for control, provide a next step, be helpful and accessible. It also discusses best practices for visual design elements like fonts, color, white space, grammar etc. Finally, it talks about user testing and different types of user testing like moderated vs unmoderated tests, tree testing, benchmark testing and hallway testing.