✅ Types of Operating Systems
An Operating System (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
There are several types of operating systems, classified based on how they manage tasks, users, and hardware.
🧩 1. Batch Operating System
No user interaction during processing
Jobs are collected (batched) and processed together
Mostly used in old mainframe systems
🔹 Example: IBM OS/360
🧩 2. Time-Sharing Operating System
Allows multiple users to use the system simultaneously
CPU time is shared among users in small time slots
🔹 Example: UNIX
🧩 3. Distributed Operating System
Manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear as a single system
Resources are shared across multiple systems
🔹 Example: LOCUS, Amoeba
🧩 4. Network Operating System (NOS)
Manages network resources like files, printers, and applications across connected computers
Users log in remotely and share files over a network
🔹 Example: Microsoft Windows Server, Novell NetWare
🧩 5. Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
Provides immediate processing of data
Used in embedded systems and critical applications (e.g., medical systems, robotics)
🔹 Example: VxWorks, RTLinux
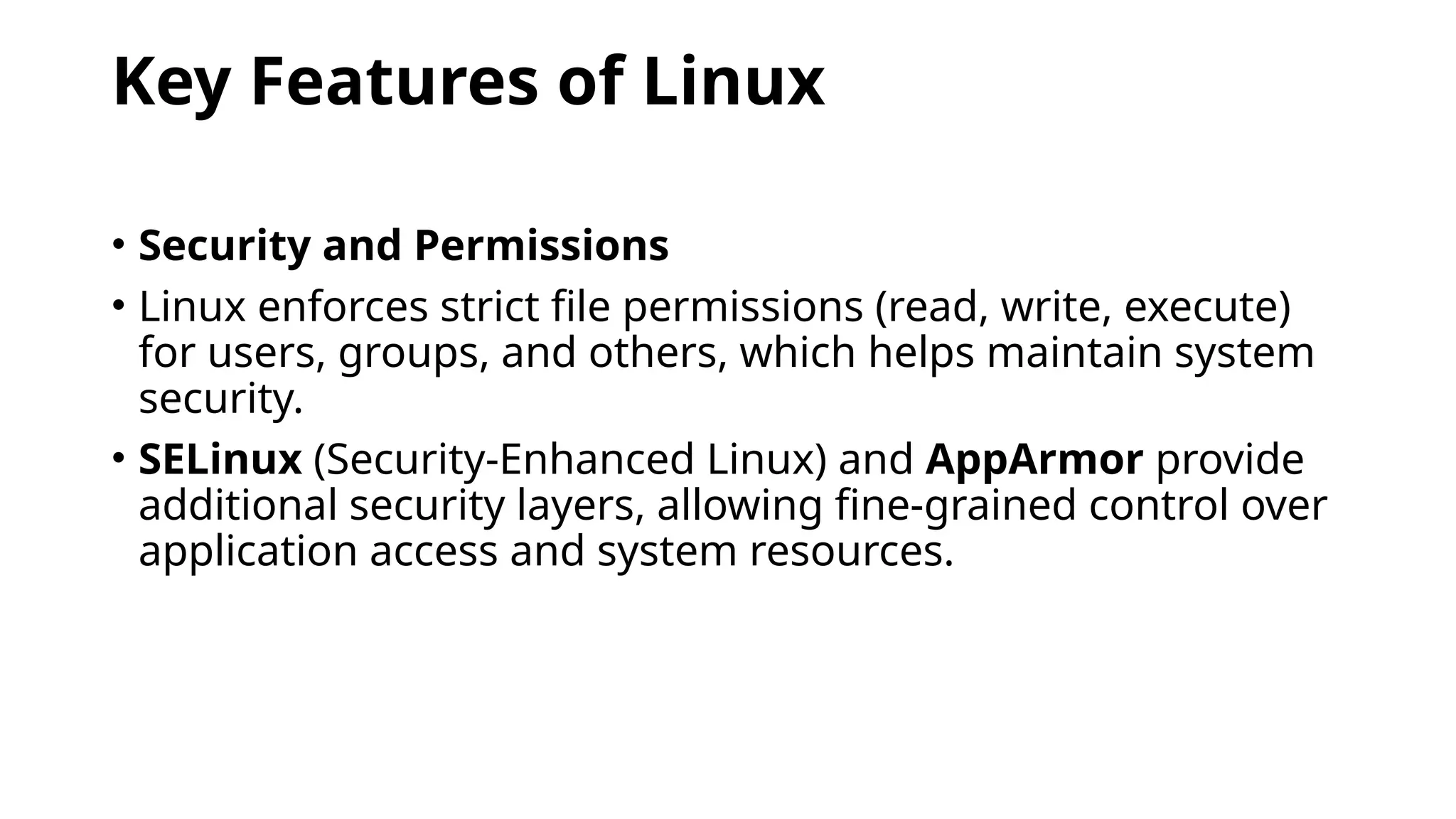
🧩 6. Multi-User Operating System
Allows multiple users to access the computer at the same time
🔹 Example: UNIX, Linux
🧩 7. Single-User Operating System
Designed for one user at a time
🔹 Example: MS-DOS, Windows 10 (single user at a time)
🧩 8. Mobile Operating System
Designed specifically for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets
🔹 Example: Android, iOS
🧠 In Summary:
Type of OS Main Feature Example
Batch OS Executes jobs in batches IBM OS/360
Time-Sharing OS Shares CPU time among users UNIX
Distributed OS Manages multiple systems as one Amoeba
Network OS Manages networked computers Windows Server
Real-Time OS Immediate response time RTLinux
Multi-User OS Supports many users at once Linux
Single-User OS Supports one user at a time MS-DOS
Mobile OS Runs on smartphones and tablets Android, iOS