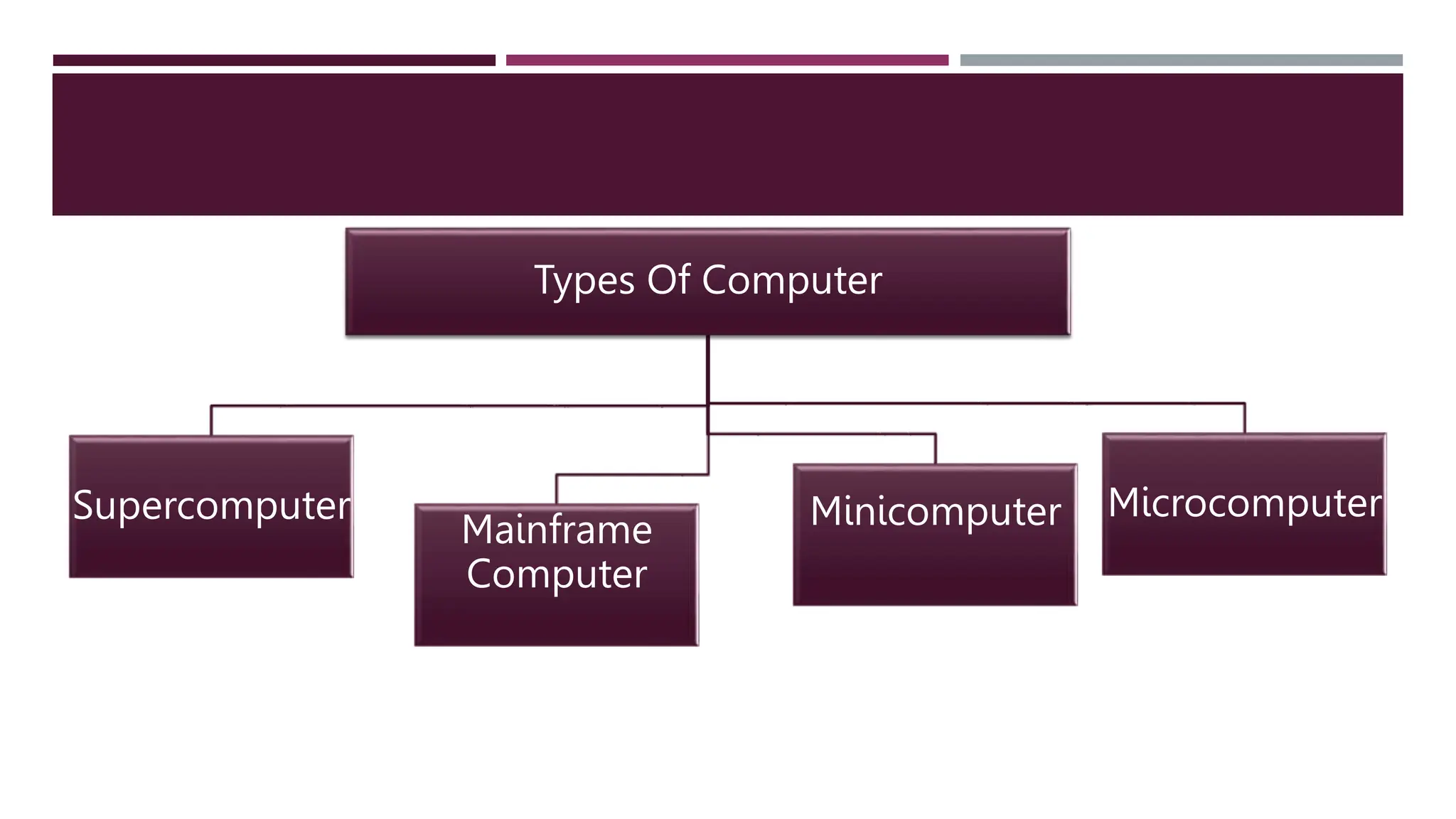
The document discusses four types of computers: microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframe computers, and supercomputers. Microcomputers are the smallest and most common, including desktops, laptops, and smartphones. They are inexpensive and portable but have low processing speed. Minicomputers are mid-sized machines for small businesses. Mainframe computers are the largest, filling entire rooms, and are used for centralized computing by large organizations. Supercomputers are the fastest but also the most expensive, used for specialized tasks like modeling and requiring their own facilities to operate.